Example-01: Derivative
[1]:
# Given an input function, its higher order (partial) derivatives with respect to one or sevaral tensor arguments can be computed using forward or reverse mode automatic differentiation
# Derivative orders can be different for each tensor argument
# Input function is expected to return a tensor or a (nested) list of tensors
# Derivatives are computed by nesting torch jacobian functions
# For higher order derivatives, nesting results in exponentially growing redundant computations
# Note, forward mode is more memory efficient in this case
# If the input function returns a tensor, the output is referred as derivative table representation
# This representation can be evaluated near given evaluation point (at a given deviation) if the input function returns a scalar or a vector
# Table representation is a (nested) list of tensors, it can be used as a redundant function representation near given evaluation point (taylor series)
# Table structure for f(x), f(x, y) and f(x, y, z) is shown bellow (similar structure holds for a function with more aruments)
# f(x)
# t(f, x)
# [f, Dx f, Dxx f, ...]
# f(x, y)
# t(f, x, y)
# [
# [ f, Dy f, Dyy f, ...],
# [ Dx f, Dx Dy f, Dx Dyy f, ...],
# [Dxx f, Dxx Dy f, Dxx Dyy f, ...],
# ...
# ]
# f(x, y, z)
# t(f, x, y, z)
# [
# [
# [ f, Dz f, Dzz f, ...],
# [ Dy f, Dy Dz f, Dy Dzz f, ...],
# [ Dyy f, Dyy Dz f, Dyy Dzz f, ...],
# ...
# ],
# [
# [ Dx f, Dx Dz f, Dx Dzz f, ...],
# [ Dx Dy f, Dx Dy Dz f, Dx Dy Dzz f, ...],
# [ Dx Dyy f, Dx Dyy Dz f, Dx Dyy Dzz f, ...],
# ...
# ],
# [
# [ Dxx f, Dxx Dz f, Dxx Dzz f, ...],
# [ Dxx Dy f, Dxx Dy Dz f, Dxx Dy Dzz f, ...],
# [Dxx Dyy f, Dxx Dyy Dz f, Dxx Dyy Dzz f, ...],
# ...
# ],
# ...
# ]
[2]:
# Import
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.series import series
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Basic derivative interface
# derivative(
# order:int, # derivative order
# function:Callable, # input function
# *args, # function(*args) = function(x:Tensor, ...)
# intermediate:bool = True, # flag to return all intermediate derivatives
# jacobian:Callable = torch.func.jacfwd # torch.func.jacfwd or torch.func.jacfrev
# )
# derivative(
# order:tuple[int, ...], # derivative orders
# function:Callable, # input function
# *args, # function(*args) = function(x:Tensor, y:Tensor, z:Tensor, ...)
# intermediate:bool = True, # flag to return all intermediate derivatives
# jacobian:Callable = torch.func.jacfwd # torch.func.jacfwd or torch.func.jacfrev
# )
[5]:
# Derivative
# Input: scalar
# Output: scalar
# Set test function
# Note, the first function argument is a scalar tensor
# Input function can have other additional arguments
# Other arguments are not used in computation of derivatives
def fn(x, a, b, c, d, e, f):
return a + b*x + c*x**2 + d*x**3 + e*x**4 + f*x**5
# Set derivative order
n = 5
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor(0.0, dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Set fixed parameters
a, b, c, d, e, f = torch.tensor([1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute n'th derivative
value = derivative(n, fn, x, a, b, c, d, e, f, intermediate=False, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd)
print(value.cpu().numpy().tolist())
# Compute all derivatives upto given order
# Note, function value itself is referred as zero order derivative
# Since function returns a tensor, output is a list of tensors
values = derivative(n, fn, x, a, b, c, d, e, f, intermediate=True, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd)
print(*[value.cpu().numpy().tolist() for value in values], sep=', ')
# Note, intermediate flag (default=True) can be used to return all derivatives
# For jacobian parameter, torch.func.jacfwd or torch.func.jacrev functions can be passed
# Evaluate derivative table representation for a given deviation from the evaluation point
dx = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(evaluate(derivative(n, fn, x, a, b, c, d, e, f) , [dx]).cpu().numpy().tolist())
print(fn(x + dx, a, b, c, d, e, f).cpu().numpy().tolist())
120.0
1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 6.0, 24.0, 120.0
6.0
6.0
[6]:
# Derivative
# Input: vector
# Output: scalar
# Set test function
# Note, the first function argument is a vector tensor
# Input function can have other additional arguments
# Other arguments are not used in computation of derivatives
def fn(x, a, b, c):
x1, x2 = x
return a + b*(x1 - 1)**2 + c*(x2 + 1)**2
# Set derivative order
n = 2
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Set fixed parameters
a, b, c = torch.tensor([1.0, 1.0, 1.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute only n'th derivative
# Note, for given input & output the result is a hessian
value = derivative(n, fn, x, a, b, c, intermediate=False, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd)
print(value.cpu().numpy().tolist())
# Compute all derivatives upto given order
# Note, fuction value itself is referred as zero order derivative
# Output is a list of tensors (value, jacobian, hessian, ...)
values = derivative(n, fn, x, a, b, c, intermediate=True, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd)
print(*[value.cpu().numpy().tolist() for value in values], sep=', ')
# Compute jacobian and hessian with torch
print(fn(x, a, b, c).cpu().numpy().tolist(),
torch.func.jacfwd(lambda x: fn(x, a, b, c))(x).cpu().numpy().tolist(),
torch.func.hessian(lambda x: fn(x, a, b, c))(x).cpu().numpy().tolist(),
sep=', ')
# Evaluate derivative table representation for a given deviation from the evaluation point
dx = torch.tensor([+1.0, -1.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(evaluate(values, [dx]).cpu().numpy())
print(fn(x + dx, a, b, c).cpu().numpy())
# Evaluate can be mapped over a set of deviation values
print(torch.func.vmap(lambda x: evaluate(values, [x]))(torch.stack(5*[dx])).cpu().numpy().tolist())
# Derivative can be mapped over a set of evaluation points
# Note, the inputt function is expeted to return a tensor
print(torch.func.vmap(lambda x: derivative(1, fn, x, a, b, c, intermediate=False))(torch.stack(5*[x])).cpu().numpy().tolist())
[[2.0, 0.0], [0.0, 2.0]]
3.0, [-2.0, 2.0], [[2.0, 0.0], [0.0, 2.0]]
3.0, [-2.0, 2.0], [[2.0, 0.0], [0.0, 2.0]]
1.0
1.0
[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]
[[-2.0, 2.0], [-2.0, 2.0], [-2.0, 2.0], [-2.0, 2.0], [-2.0, 2.0]]
[7]:
# Derivative
# Input: vector
# Output: vector
# Set test function
# Note, the first function argument is a vector tensor
# Input function can have other additional arguments
# Other arguments (if any) are not used in computation of derivatives
def fn(x):
x1, x2 = x
X1 = 1.0*x1 + 2.0*x2
X2 = 3.0*x1 + 4.0*x2
X3 = 5.0*x1 + 6.0*x2
return torch.stack([X1, X2, X3])
# Set derivative order
n = 1
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute derivatives
values = derivative(n, fn, x)
print(*[value.cpu().numpy().tolist() for value in values], sep=', ')
print()
# Evaluate derivative table representation for a given deviation from the evaluation point
dx = torch.tensor([+1, -1], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(evaluate(values, [dx]).cpu().numpy().tolist())
print(fn(x + dx).cpu().numpy().tolist())
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0], [5.0, 6.0]]
[-1.0, -1.0, -1.0]
[-1.0, -1.0, -1.0]
[8]:
# Derivative
# Input: tensor
# Output: tensor
# Set test function
def fn(x):
return 1 + x + x**2 + x**3
# Set derivative order
n = 3
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.zeros((1, 2, 3), dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute derivatives
# Note, output is a list of tensors
values = derivative(n, fn, x)
print(*[list(value.shape) for value in values], sep='\n')
# Evaluate derivative table representation for a given deviation from the evaluation point
# Note, evaluate function works with scalar or vector tensor input
# One should compute derivatives of a wrapped function and reshape the result of evaluate
# Set wrapped function
def gn(x, shape):
return fn(x.reshape(shape)).flatten()
print(fn(x).cpu().numpy().tolist())
print(gn(x.flatten(), x.shape).reshape(x.shape).cpu().numpy().tolist())
# Compute derivatives
values = derivative(n, gn, x.flatten(), x.shape)
# Set deviation value
dx = torch.ones_like(x)
# Evaluate
print(evaluate(values, [dx.flatten()]).reshape(x.shape).cpu().numpy().tolist())
print(gn((x + dx).flatten(), x.shape).reshape(x.shape).cpu().numpy().tolist())
print(fn(x + dx).cpu().numpy().tolist())
[1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
[[[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]]]
[[[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]]]
[[[4.0, 4.0, 4.0], [4.0, 4.0, 4.0]]]
[[[4.0, 4.0, 4.0], [4.0, 4.0, 4.0]]]
[[[4.0, 4.0, 4.0], [4.0, 4.0, 4.0]]]
[9]:
# Derivative
# Input: vector
# Output: nested list of tensors
# Set test function
def fn(x):
x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6 = x
X1 = 1.0*x1 + 2.0*x2 + 3.0*x3
X2 = 4.0*x4 + 5.0*x5 + 6.0*x6
return [torch.stack([X1]), [torch.stack([X2])]]
# Set derivative order
n = 1
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute derivatives
values = derivative(n, fn, x, intermediate=False)
[10]:
# Derivative
# Input: vector, vector, vector
# Output: vector
# Set test function
def fn(x, y, z):
x1, x2 = x
y1, y2 = y
z1, z2 = z
return torch.stack([(x1 + x2)*(y1 + y2)*(z1 + z2)])
# Set derivative orders for x, y and z
nx, ny, nz = 1, 1, 1
# Set evaluation point
# Note, evaluation point is a list of tensors
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
y = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
z = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute n'th derivativ
value = derivative((nx, ny, nz), fn, x, y, z, intermediate=False)
print(value.cpu().numpy().tolist())
# Compute all derivatives upto given order
values = derivative((nx, ny, nz), fn, x, y, z, intermediate=True)
# Evaluate derivative table representation for a given deviation from the evaluation point
dx = torch.tensor([1.0, 1.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dy = torch.tensor([1.0, 1.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dz = torch.tensor([1.0, 1.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(evaluate(values, [dx, dy, dz]).cpu().numpy().tolist())
print(fn(x + dx, y + dy, z + dz).cpu().numpy().tolist())
# Note, if the input function has vector arguments and returns a tensor, it can be repsented with series
for key, value in series(tuple(map(len, (x, y, z))), (nx, ny, nz), values).items():
print(f'{key}: {value.cpu().numpy().tolist()}')
[[[[1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0]], [[1.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0]]]]
[8.0]
[8.0]
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0): [0.0]
(0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0): [0.0]
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1): [0.0]
(0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0): [0.0]
(0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0): [0.0]
(0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0): [0.0]
(0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1): [0.0]
(0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0): [0.0]
(0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1): [0.0]
(1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0): [0.0]
(0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0): [0.0]
(1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0): [0.0]
(1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1): [0.0]
(0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0): [0.0]
(0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1): [0.0]
(1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0): [0.0]
(1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0): [0.0]
(0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0): [0.0]
(0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0): [0.0]
(1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0): [1.0]
(1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1): [1.0]
(1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0): [1.0]
(1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1): [1.0]
(0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0): [1.0]
(0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1): [1.0]
(0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0): [1.0]
(0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1): [1.0]
[11]:
# Redundancy free computation
# Set test function
def fn(x):
x1, x2 = x
return torch.stack([1.0*x1 + 2.0*x2 + 3.0*x1**2 + 4.0*x1*x2 + 5.0*x2**2])
# Set derivative order
n = 2
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute n'th derivative
value = derivative(n, fn, x, intermediate=False)
print(value.cpu().numpy().tolist())
# Since derivatives are computed by nesting of jacobian function, redundant computations appear starting from the second order
# Redundant computations can be avoided if all input arguments are scalar tensors
def gn(x1, x2):
return fn(torch.stack([x1, x2]))
print(derivative((2, 0), gn, *x, intermediate=False).cpu().numpy().tolist())
print(derivative((1, 1), gn, *x, intermediate=False).cpu().numpy().tolist())
print(derivative((0, 2), gn, *x, intermediate=False).cpu().numpy().tolist())
[[[6.0, 4.0], [4.0, 10.0]]]
[6.0]
[4.0]
[10.0]
Example-02: Derivative table representation
[1]:
# Input function f: R^n x R^m x ... -> R^n is referred as a mapping
# The first function argument is state, other arguments (used in computation of derivatives) and knobs
# State and all knobs are vector-like tensors
# Note, functions of this form can be used to model tranformations throught accelerator magnets
# In this case, derivatives can be used to generate a (parametric) model of the input function
# Function model can be represented as a derivative table or coefficients of monomials (series representation)
# In this example, table representation is used to model transformation throught a sextupole accelerator magnet
# Table is computed with respect to state variables (phase space variables) and knobs (magnet strength and length)
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import signature
from ndmap.signature import get
from ndmap.index import index
from ndmap.index import reduce
from ndmap.index import build
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Mapping (sextupole accelerator magnet transformatijet)
# Given initial state, magnet strength and length, state is propagated using explicit symplectic integration
# Number of integration steps is set by count parameter, integration step length is length/count
def mapping(x, k, l, count=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (k, ), (l, ) = x, k, l/(2.0*count)
for _ in range(count):
qx, qy = qx + l*px, qy + l*py
px, py = px - 2.0*l*k*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*k*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px, qy + l*py
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
[5]:
# Table representation (state)
# Set evaluation point & parameters
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor([10.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
l = torch.tensor([0.1], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute derivatives (table representation)
# Since derivatives are computed only with respect to the state, output table is a list of tensors
t = derivative(6, mapping, x, k, l)
print(*[element.shape for element in t], sep='\n')
torch.Size([4])
torch.Size([4, 4])
torch.Size([4, 4, 4])
torch.Size([4, 4, 4, 4])
torch.Size([4, 4, 4, 4, 4])
torch.Size([4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4])
torch.Size([4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4])
[6]:
# Compare table and exact mapping near the evaluation point (change order to observe convergence)
# Note, table transformation is not symplectic
dx = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.001, 0.0001, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(evaluate(t, [dx]).cpu().tolist())
print(mapping(x + dx, k, l).cpu().tolist())
[0.00010000041624970626, 0.0010000066749862018, 0.00010000016750044096, 5.000018166514047e-09]
[0.0001000004162497062, 0.0010000066749862018, 0.00010000016750044096, 5.000018166514046e-09]
[7]:
# Each bottom element (tensor) in the (flattend) derivative table is assosiated with a signature
# Signature is a tuple of derivative orders
print(signature(t))
[(0,), (1,), (2,), (3,), (4,), (5,), (6,)]
[8]:
# For a given signature, corresponding element can be extracted or changed with get/set functions
print(get(t, (1, )).cpu().numpy())
[[1. 0.1 0. 0. ]
[0. 1. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0. 1. 0.1]
[0. 0. 0. 1. ]]
[9]:
# Each bottom element is related to monomials
# For given order, monomial indices with repetitions can be computed
# These repetitions account for evaluation of the same partial derivatives with diffenent orders, e.g. df/dxdy vs df/dydx
print(index(4, 2))
[[2 0 0 0]
[1 1 0 0]
[1 0 1 0]
[1 0 0 1]
[1 1 0 0]
[0 2 0 0]
[0 1 1 0]
[0 1 0 1]
[1 0 1 0]
[0 1 1 0]
[0 0 2 0]
[0 0 1 1]
[1 0 0 1]
[0 1 0 1]
[0 0 1 1]
[0 0 0 2]]
[10]:
# Explicit evaluation
print(evaluate(t, [dx]).cpu().numpy())
print((t[0] + t[1] @ dx + 1/2 * t[2] @ dx @ dx + 1/2 * 1/3 * t[3] @ dx @ dx @ dx + 1/2 * 1/3 * 1/4 * t[4] @ dx @ dx @ dx @ dx + 1/2 * 1/3 * 1/4 * 1/5 * t[5] @ dx @ dx @ dx @ dx @ dx + 1/2 * 1/3 * 1/4 * 1/5 * 1/6 * t[6] @ dx @ dx @ dx @ dx @ dx @ dx).cpu().numpy())
print((t[0] + (t[1] + 1/2 * (t[2] + 1/3 * (t[3] + 1/4 * (t[4] + 1/5 * (t[5] + 1/6 * t[6] @ dx) @ dx) @ dx) @ dx) @ dx) @ dx).cpu().numpy())
[1.00000416e-04 1.00000667e-03 1.00000168e-04 5.00001817e-09]
[1.00000416e-04 1.00000667e-03 1.00000168e-04 5.00001817e-09]
[1.00000416e-04 1.00000667e-03 1.00000168e-04 5.00001817e-09]
[11]:
# Series representation can be generated from a given table
# This representation stores monomial powers and corresponding coefficients
s = series((4, ), (6, ), t)
print(torch.stack([s[(1, 0, 0, 0)], s[(0, 1, 0, 0)], s[(0, 0, 1, 0)], s[(0, 0, 0, 1)]]).cpu().numpy())
[[1. 0. 0. 0. ]
[0.1 1. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0. 1. 0. ]
[0. 0. 0.1 1. ]]
[12]:
# Evaluate series
print(evaluate(t, [dx]).cpu().numpy())
print(evaluate(s, [dx]).cpu().numpy())
[1.00000416e-04 1.00000667e-03 1.00000168e-04 5.00001817e-09]
[1.00000416e-04 1.00000667e-03 1.00000168e-04 5.00001817e-09]
[13]:
# Table representation (state & knobs)
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor([10.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
l = torch.tensor([0.1], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute derivatives (table representation)
# Since derivatives are computed with respect to state and knobs, output table is a nested list of tensors
t = derivative((6, 1, 1), mapping, x, k, l)
[14]:
# In this case, bottom table element signature is a tuple with several integers
print(get(t, (1, 0, 0)).cpu().numpy())
[[1. 0.1 0. 0. ]
[0. 1. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0. 1. 0.1]
[0. 0. 0. 1. ]]
[15]:
# Compare table and exact mapping near evaluation point (change order to observe convergence)
# Note, table transofrmation is not symplectic
dx = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.001, 0.0001, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dk = torch.tensor([0.1], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dl = torch.tensor([0.001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(evaluate(t, [dx, 0.0*dk, 0.0*dl]).cpu().tolist())
print(evaluate(t, [dx, 1.0*dk, 1.0*dl]).cpu().tolist())
print(mapping(x + dx, k + dk, l + dl).cpu().tolist())
[0.00010000041624970626, 0.0010000066749862018, 0.00010000016750044096, 5.000018166514047e-09]
[0.0001010004271286862, 0.001000006741987918, 0.00010000017425071835, 5.1510191197368185e-09]
[0.00010100042712809422, 0.0010000067409770773, 0.00010000017430164039, 5.151524128394736e-09]
[16]:
# Each bottom element (tensor) in the (flattend) derivative table is assosiated with a signature
# Signature is a tuple of derivative orders
print(*[index for index in signature(t)], sep='\n')
(0, 0, 0)
(0, 0, 1)
(0, 1, 0)
(0, 1, 1)
(1, 0, 0)
(1, 0, 1)
(1, 1, 0)
(1, 1, 1)
(2, 0, 0)
(2, 0, 1)
(2, 1, 0)
(2, 1, 1)
(3, 0, 0)
(3, 0, 1)
(3, 1, 0)
(3, 1, 1)
(4, 0, 0)
(4, 0, 1)
(4, 1, 0)
(4, 1, 1)
(5, 0, 0)
(5, 0, 1)
(5, 1, 0)
(5, 1, 1)
(6, 0, 0)
(6, 0, 1)
(6, 1, 0)
(6, 1, 1)
[17]:
# Compute series
s = series((4, 1, 1), (6, 1, 1), t)
# Keys are generalized monomials
print(s[(1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1)].cpu().numpy())
print()
# Evaluate series
print(evaluate(t, [dx, dk, dl]).cpu().numpy())
print(evaluate(s, [dx, dk, dl]).cpu().numpy())
print()
[1.447578e-06 9.756747e-05 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00]
[1.01000427e-04 1.00000674e-03 1.00000174e-04 5.15101912e-09]
[1.01000427e-04 1.00000674e-03 1.00000174e-04 5.15101912e-09]
[18]:
# Reduced table representation
sequence, shape, unique = reduce((4, 1, 1), t)
out = derivative((6, 1, 1), lambda x, k, l: x, x, k, l)
build(out, sequence, shape, unique)
compare(t, out)
[18]:
True
Example-03: Derivative table propagation
[1]:
# Given a mapping f(state, *knobs, ...) and a derivative table t, derivatives of f(t, *knobs, ...) are computed
# This can be used to propagate derivative table throught a given mapping (computation of parametric fixed points and other applications)
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Define mappings
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=100):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def ring(x, w):
x = quad(x, w, +0.25, 0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 5.0)
x = quad(x, w, -0.20, 0.5)
x = quad(x, w, -0.20, 0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 5.0)
x = quad(x, w, +0.25, 0.5)
return x
[5]:
# Direct
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor([0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute derivatives
t = derivative((1, 4), ring, x, w)
# Evaluate for a given deviation
dx = torch.tensor([0.001, 0.0, 0.001, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dw = torch.tensor([0.001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(ring(x + dx, w + dw).cpu().numpy())
print(evaluate(t, [dx, dw]).cpu().numpy())
[-8.88568650e-05 -5.43957672e-05 4.97569694e-04 -1.40349102e-04]
[-8.88568650e-05 -5.43957672e-05 4.97569694e-04 -1.40349102e-04]
[6]:
# Propagation
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor([0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Set identity table
t = identity((1, 4), [x, w])
# Propagate table
t = propagate((4, 1), (1, 4), t, [w], quad, +0.25, 0.5)
t = propagate((4, 1), (1, 4), t, [w], drif, 5.0)
t = propagate((4, 1), (1, 4), t, [w], quad, -0.20, 0.5)
t = propagate((4, 1), (1, 4), t, [w], quad, -0.20, 0.5)
t = propagate((4, 1), (1, 4), t, [w], drif, 5.0)
t = propagate((4, 1), (1, 4), t, [w], quad, +0.25, 0.5)
# Evaluate for a given deviation
dx = torch.tensor([0.001, 0.0, 0.001, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dw = torch.tensor([0.001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(ring(x + dx, w + dw).cpu().numpy())
print(evaluate(t, [dx, dw]).cpu().numpy())
[-8.88568650e-05 -5.43957672e-05 4.97569694e-04 -1.40349102e-04]
[-8.88568650e-05 -5.43957672e-05 4.97569694e-04 -1.40349102e-04]
[7]:
# Series representation
s = clean(series((4, 1), (1, 4), t))
for key, value in s.items():
print(f'{key}: {value.cpu().numpy()}')
(1, 0, 0, 0, 0): [-0.09072843 -0.05430498 0. 0. ]
(0, 1, 0, 0, 0): [18.26293553 -0.09072843 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 1, 0, 0): [ 0. 0. 0.49625858 -0.14063034]
(0, 0, 0, 1, 0): [0. 0. 5.35963583 0.49625858]
(1, 0, 0, 0, 1): [ 1.87420951 -0.09097396 0. 0. ]
(0, 1, 0, 0, 1): [-24.33227046 1.87420951 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 1, 0, 1): [0. 0. 1.31324305 0.28161167]
(0, 0, 0, 1, 1): [0. 0. 1.46426265 1.31324305]
(1, 0, 0, 0, 2): [-2.65007558 0.18727838 0. 0. ]
(0, 1, 0, 0, 2): [30.20570906 -2.65007558 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 1, 0, 2): [ 0. 0. -2.12812904 -0.37146989]
(0, 0, 0, 1, 2): [ 0. 0. -8.46895909 -2.12812904]
(1, 0, 0, 0, 3): [ 3.41796043 -0.28459189 0. 0. ]
(0, 1, 0, 0, 3): [-35.88102956 3.41796043 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 1, 0, 3): [0. 0. 2.94802229 0.46018886]
(0, 0, 0, 1, 3): [ 0. 0. 15.6516443 2.94802229]
(1, 0, 0, 0, 4): [-4.17749922 0.38289808 0. 0. ]
(0, 1, 0, 0, 4): [41.3560843 -4.17749922 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 1, 0, 4): [ 0. 0. -3.77254434 -0.54775243]
(0, 0, 0, 1, 4): [ 0. 0. -23.00943634 -3.77254434]
[8]:
# Check invariant
# Note, ring has two quadratic invariants (actions), zeros are padded to match state length
# Define invariant
matrix = torch.tensor([[4.282355639365032, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.23351633638449415, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 2.484643367729646, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.40247224732044934]], dtype=dtype, device=device)
def invariant(x):
qx, px, qy, py = matrix.inverse() @ x
return torch.stack([0.5*(qx**2 + px**2), 0.5*(qy**2 + py**2), *torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)])
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.001, 0.0, 0.001, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor([0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Evaluate invarint for a given state and transformed state
print(invariant(x).cpu().numpy())
print(invariant(ring(x, w)).cpu().numpy())
[2.72649397e-08 8.09919549e-08 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[2.72649397e-08 8.09919549e-08 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[9]:
# Invariant propagation
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor([0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute table and series representations of invariant
t = derivative((2, ), invariant, x)
s = series((4, ), (2, ), t)
print(*[f'{key}: {value.cpu().numpy()}' for key, value in clean(s, epsilon=1.0E-14).items()], sep='\n')
print()
# Compute table and series representations of transformed invariant
t = derivative((2, ), lambda x: invariant(ring(x, w)), x)
s = series((4, ), (2, ), t)
print(*[f'{key}: {value.cpu().numpy()}' for key, value in clean(s, epsilon=1.0E-14).items()], sep='\n')
print()
# Propagate invariant
t = derivative((2, ), ring, x, w)
t = propagate((4, ), (2, ), t, [], invariant)
s = series((4, ), (2, ), t)
print(*[f'{key}: {value.cpu().numpy()}' for key, value in clean(s, epsilon=1.0E-14).items()], sep='\n')
print()
(2, 0, 0, 0): [0.02726494 0. 0. 0. ]
(0, 2, 0, 0): [9.16928491 0. 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 2, 0): [0. 0.08099195 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 0, 2): [0. 3.08672633 0. 0. ]
(2, 0, 0, 0): [0.02726494 0. 0. 0. ]
(0, 2, 0, 0): [9.16928491 0. 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 2, 0): [0. 0.08099195 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 0, 2): [0. 3.08672633 0. 0. ]
(2, 0, 0, 0): [0.02726494 0. 0. 0. ]
(0, 2, 0, 0): [9.16928491 0. 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 2, 0): [0. 0.08099195 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 0, 2): [0. 3.08672633 0. 0. ]
Example-04: Jet class
[1]:
# Jet is a convenience class to work with jets (evaluation point & derivative table)
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.jet import Jet
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Define mappings
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=100):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor([0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute table representation
t = derivative((1, 4), lambda x, w: quad(drif(x, w, 1.0), w, 1.0, 1.0, 1), x, w)
[5]:
# Set jet
j = Jet((4, 1), (1, 4), point=[x, w], dtype=dtype, device=device)
j = j.propagate(drif, 1.0)
j = j.propagate(quad, 1.0, 1.0, 1)
[6]:
# Evaluate at given deviation
dx = torch.tensor([0.001, 0.0, 0.001, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dw = torch.tensor([0.001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(evaluate(t, [dx, dw]).cpu().numpy())
print(j([dx, dw]).cpu().numpy())
[ 0.0005005 -0.001 0.0014995 0.001 ]
[ 0.0005005 -0.001 0.0014995 0.001 ]
[7]:
# Composition
j1 = Jet.from_mapping((4, 1), (1, 4), [x, w], drif, 1.0, dtype=dtype, device=device)
j2 = Jet.from_mapping((4, 1), (1, 4), [x, w], quad, 1.0, 1.0, 1, dtype=dtype, device=device)
print((j1 @ j2)([dx, dw]).cpu().numpy())
[ 0.0005005 -0.001 0.0014995 0.001 ]
Example-05: Nonlinear mapping approximation
[1]:
# Composition of several nonlinear mappings can be approximated by its table representation
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set test mapping
# Rotation with two sextupoles separated by negative identity linear transformation
# Note, result is expected to have zero degree two coefficients due to negative identity linear transformation between sextupoles
def spin(x, mux, muy):
(qx, px, qy, py), mux, muy = x, mux, muy
return torch.stack([qx*mux.cos() + px*mux.sin(), px*mux.cos() - qx*mux.sin(), qy*muy.cos() + py*muy.sin(), py*muy.cos() - qy*muy.sin()])
def drif(x, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), l = x, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px, px, qy + l*py, py])
def sext(x, ks, l, n=1):
(qx, px, qy, py), ks, l = x, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px, qy + l*py
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px, qy + l*py
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def ring(x):
mux, muy = 2.0*numpy.pi*torch.tensor([1/3 + 0.01, 1/4 + 0.01], dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = spin(x, mux, muy)
x = drif(x, -0.05)
x = sext(x, 10.0, 0.1, 100)
x = drif(x, -0.05)
mux, muy = 2.0*numpy.pi*torch.tensor([0.50, 0.50], dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = spin(x, mux, muy)
x = drif(x, -0.05)
x = sext(x, 10.0, 0.1, 100)
x = drif(x, -0.05)
return x
[5]:
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute derivative table
n = 4
t = derivative(n, ring, x)
# Compute and print series
s = clean(series((4, ), (n, ), t), epsilon=1.0E-12)
print(*[f'{key}: {value.cpu().numpy()}' for key, value in clean(s, epsilon=1.0E-14).items()], sep='\n')
(1, 0, 0, 0): [0.55339155 0.83292124 0. 0. ]
(0, 1, 0, 0): [-0.83292124 0.55339155 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 1, 0): [0. 0. 0.06279052 0.99802673]
(0, 0, 0, 1): [ 0. 0. -0.99802673 0.06279052]
(3, 0, 0, 0): [-7.53257307e-09 2.82424677e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(2, 1, 0, 0): [-1.96250238e-08 -1.27525063e-02 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(2, 0, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 9.21186111e-06 3.34331441e-04]
(2, 0, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 1.59704766e-05 -5.06941449e-03]
(1, 2, 0, 0): [-1.11004920e-08 1.91940679e-02 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 1, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -2.98671134e-05 -9.79459005e-04]
(1, 1, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -1.48185697e-05 1.53623878e-02]
(1, 0, 2, 0): [-1.05857397e-06 1.97282603e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 0, 1, 1): [ 1.48154798e-05 -1.18570682e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 0, 0, 2): [2.88067554e-05 9.18409783e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 3, 0, 0): [-9.21338044e-10 -9.62979589e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 2, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 2.40366928e-05 7.09979811e-04]
(0, 2, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -1.38786549e-05 -1.15294375e-02]
(0, 1, 2, 0): [ 1.80396305e-06 -2.59196622e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 1, 1, 1): [-2.98509155e-05 1.72488752e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 1, 0, 2): [ 1.66318846e-05 -1.38269522e-02 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 3, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -1.47704279e-08 4.12534350e-06]
(0, 0, 2, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -3.31103168e-09 -1.96719688e-04]
(0, 0, 1, 2): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 3.93325786e-09 3.12683573e-03]
(0, 0, 0, 3): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 2.56887204e-10 -1.65665408e-02]
(4, 0, 0, 0): [ 6.48869023e-07 -3.91844462e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(3, 1, 0, 0): [-3.91685700e-06 1.51001133e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(3, 0, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -4.36165465e-07 5.76316391e-06]
(3, 0, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 6.56410859e-06 1.31668166e-05]
(2, 2, 0, 0): [ 8.85501662e-06 -1.48880894e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(2, 1, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 1.92232731e-06 -2.78183189e-05]
(2, 1, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -2.96894787e-05 -3.16635607e-05]
(2, 0, 2, 0): [1.81838643e-08 2.18816315e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(2, 0, 1, 1): [-9.93314202e-07 -3.25277215e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(2, 0, 0, 2): [ 7.67316422e-06 -2.51871510e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 3, 0, 0): [-8.88618620e-06 -4.33921249e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 2, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -2.81910856e-06 4.44963121e-05]
(1, 2, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 4.47107608e-05 6.22767407e-06]
(1, 1, 2, 0): [-5.02653030e-08 -6.69892371e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 1, 1, 1): [2.90625131e-06 1.04277202e-04 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 1, 0, 2): [-2.28808176e-05 2.60346923e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 0, 3, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 2.09236592e-09 3.51323891e-08]
(1, 0, 2, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -6.41657941e-09 -1.78350571e-06]
(1, 0, 1, 2): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -6.10954936e-07 1.86435774e-05]
(1, 0, 0, 3): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 3.05503037e-06 -5.00150901e-05]
(0, 4, 0, 0): [3.33982092e-06 8.88114110e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 3, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 1.37553970e-06 -2.36217768e-05]
(0, 3, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -2.24184174e-05 1.77513110e-05]
(0, 2, 2, 0): [3.54703897e-08 5.11986525e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 2, 1, 1): [-2.15414781e-06 -8.31702815e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 2, 0, 2): [1.72952174e-05 1.78791226e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 1, 3, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -3.32576455e-09 -2.16775859e-08]
(0, 1, 2, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 1.73891518e-08 1.32003603e-06]
(0, 1, 1, 2): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 8.58583303e-07 -7.35197022e-06]
(0, 1, 0, 3): [ 0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -4.60205741e-06 -3.44817289e-05]
(0, 0, 4, 0): [-2.95410616e-10 -3.91436795e-10 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 3, 1): [ 1.72261161e-08 -3.76703368e-08 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 2, 2): [-3.76632244e-07 1.04173914e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 1, 3): [ 3.81179356e-06 -5.44741177e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 0, 4): [-1.51552013e-05 -3.46854944e-07 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
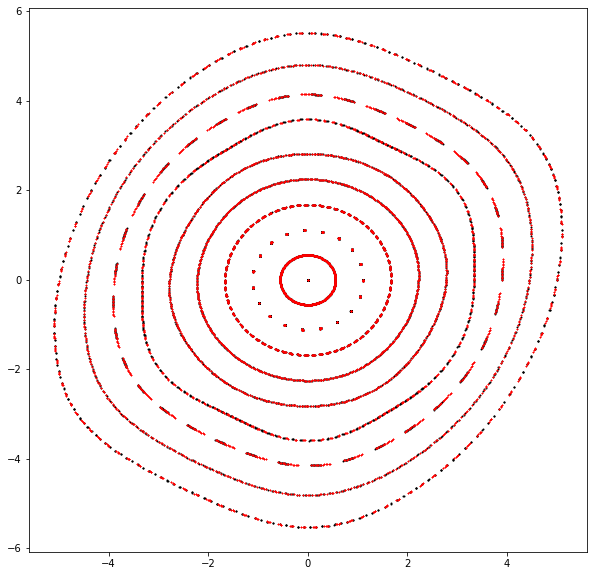
[6]:
# Compare phase space trajectories
# Note, change order to observe convergence
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
# Direct tracking
x = torch.linspace(0.0, 5.0, 10, dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = torch.stack([x, *3*[torch.zeros_like(x)]]).T
count = 512
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(x)
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: ring(x))(x)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qx, px, *_ = table
for q, p in zip(qx.cpu().numpy(), px.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='black', marker='o', s=1)
# Table tracking
# Note, table representation is not symplectic
x = torch.linspace(0.0, 5.0, 10, dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = torch.stack([x, *3*[torch.zeros_like(x)]]).T
count = 512
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(x)
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: evaluate(t, [x]))(x)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qx, px, *_ = table
for q, p in zip(qx.cpu().numpy(), px.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='red', marker='x', s=1)
plt.show()
Example-06: Fixed point
[1]:
# In this example fixed points are computed for a simple symplectic nonlinear transformation
# Fixed point are computed with Newton root search
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import clean_point
from ndmap.pfp import chain_point
from ndmap.pfp import matrix
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set forward & inverse mappings
mu = 2.0*numpy.pi*torch.tensor(1/3 - 0.01, dtype=dtype)
kq, ks, ko = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.25, -0.25], dtype=dtype)
def forward(x):
q, p = x
q, p = q*mu.cos() + p*mu.sin(), p*mu.cos() - q*mu.sin()
q, p = q, p + (kq*q + ks*q**2 + ko*q**3)
return torch.stack([q, p])
def inverse(x):
q, p = x
q, p = q, p - (kq*q + ks*q**2 + ko*q**3)
q, p = q*mu.cos() - p*mu.sin(), p*mu.cos() + q*mu.sin()
return torch.stack([q, p])
[5]:
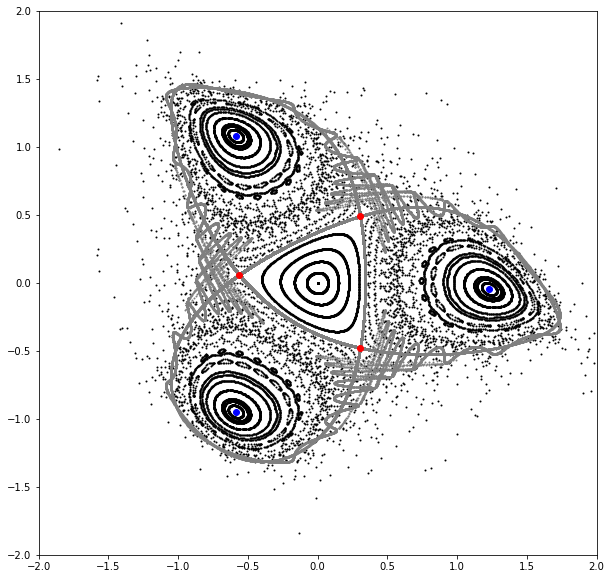
# Compute period three fixed points
# Set fixed point period
period = 3
# Set tolerance epsilon
epsilon = 1.0E-12
# Set random initial points
points = 4.0*torch.rand((128, 2), dtype=dtype, device=device) - 2.0
# Perform 512 root search iterations for each initial point
points = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: fixed_point(512, forward, point, power=period))(points)
# Clean points (remove nans, duplicates, points from the same chain)
points = clean_point(period, forward, points, epsilon=epsilon)
# Generate fixed point chains
chains = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: chain_point(period, forward, point))(points)
# Classify fixed point chains (elliptic vs hyperbolic)
# Generate initials for hyperbolic fixed points using corresponding eigenvectors
kinds = []
for chain in chains:
point, *_ = chain
values, vectors = torch.linalg.eig(matrix(period, forward, point))
kind = all(values.log().real < epsilon)
kinds.append(kind)
if not kind:
lines = [point + vector*torch.linspace(-epsilon, +epsilon, 1024, dtype=dtype).reshape(-1, 1) for vector in vectors.real.T]
lines = torch.stack(lines)
# Plot phase space
x = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.5, 21, dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = torch.stack([x, torch.zeros_like(x)]).T
count = 1024
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(x)
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: forward(x))(x)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.xlim(-2.0, 2.0)
plt.ylim(-2.0, 2.0)
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='black', marker='o', s=1)
# Plot (approximated) stable and unstable manifolds of hyperbolic fixed points
count = 310
for line in lines:
x = torch.clone(line)
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(x)
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: forward(x))(x)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='gray', marker='o', s=1)
x = torch.clone(line)
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(x)
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: inverse(x))(x)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='gray', marker='o', s=1)
# Plot chains
for chain, kind in zip(chains, kinds):
plt.scatter(*chain.T, color = {True:'blue', False:'red'}[kind], marker='o')
[6]:
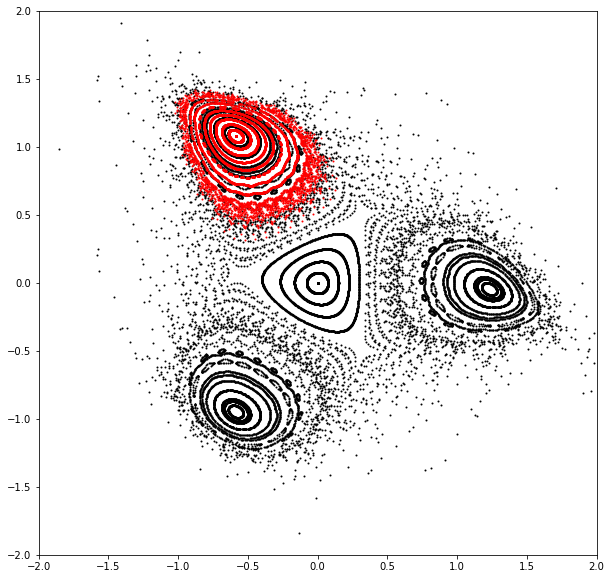
# Set mapping around elliptic fixed point
point, *_ = chains[kinds].squeeze()
def mapping(x):
x = x + point
for _ in range(period):
x = forward(x)
x = x - point
return x
# Test mapping
x = torch.zeros_like(point)
print(x)
print(mapping(x))
# Plot phase space
x = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.5, 21, dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = torch.stack([x, torch.zeros_like(x)]).T
count = 1024
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(x)
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: forward(x))(x)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.xlim(-2.0, 2.0)
plt.ylim(-2.0, 2.0)
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='black', marker='o', s=1)
x = torch.linspace(0.0, 0.5, 11, dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = torch.stack([x, torch.zeros_like(x)]).T
count = 1024
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(x)
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: mapping(x))(x)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table + point.reshape(2, 1, 1)
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='red', marker='o', s=1)
tensor([0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.110223024625e-16, 0.000000000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-07: Parametric fixed point
[1]:
# Given a mapping depending on a set of knobs (parameters), parametric fixed points can be computed (position of a fixed point as function of parameters)
# Parametric fixed points can be used to construct responce matrices, e.g. closed orbit responce
# In this case only first order derivatives of the fixed point(s) with respect to parameters are computed
# Or higher order expansions can be computed
# In this example parametric fixed points of a symplectic mapping are computed
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.util import flatten
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import clean_point
from ndmap.pfp import chain_point
from ndmap.pfp import matrix
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set mapping
def mapping(x, k):
q, p = x
a, b = k
q, p = q*mu.cos() + p*mu.sin(), p*mu.cos() - q*mu.sin()
return torch.stack([q, p + a*q**2 + b*q**3])
[5]:
# Compute dynamical fixed points
# Note, fixed point might fail due to escape to large values
# Set parameters
mu = 2.0*numpy.pi*torch.tensor(1/5 - 0.01, dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor([0.25, -0.25], dtype=dtype, device=device)
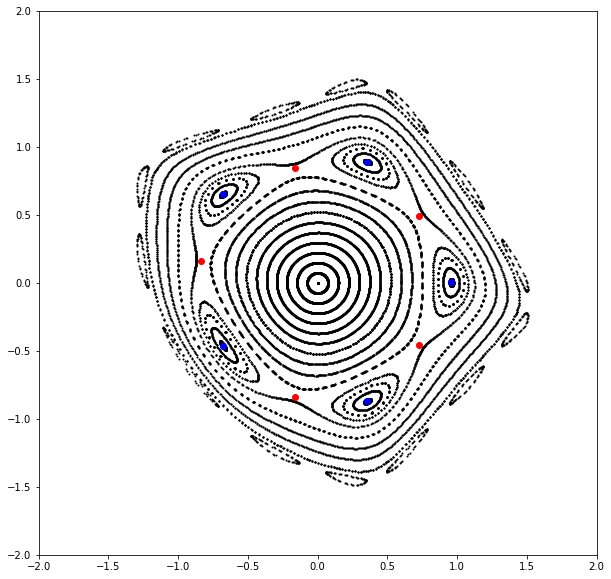
# Compute and plot phase space trajectories
x = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.5, 21, dtype=dtype)
x = torch.stack([x, torch.zeros_like(x)]).T
count = 1024
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(x)
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: mapping(x, k))(x)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.xlim(-2.0, 2.0)
plt.ylim(-2.0, 2.0)
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='black', marker='o', s=1)
# Set tolerance epsilon
epsilon = 1.0E-12
# Compute chains
period = 5
points = torch.rand((32, 2), dtype=dtype, device=device)
points = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: fixed_point(16, mapping, point, k, power=period))(points)
points = clean_point(period, mapping, points, k, epsilon=epsilon)
chains = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: chain_point(period, mapping, point, k))(points)
# Plot chains
for chain in chains:
point, *_ = chain
value, vector = torch.linalg.eig(matrix(period, mapping, point, k))
color = 'blue' if all(value.log().real < epsilon) else 'red'
plt.scatter(*chain.T, color=color, marker='o')
if color == 'blue':
ep, *_ = chain
else:
hp, *_ = chain
plt.show()
[6]:
# Compute hyperbolic fixed point for a set of knobs
dks = torch.stack(2*[torch.linspace(0.0, 0.01, 101, dtype=dtype, device=device)]).T
fps = [hp]
for dk in dks:
*_, initial = fps
fps.append(fixed_point(16, mapping, initial, k + dk, power=period))
fps = torch.stack(fps)
[7]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
# Set computation order
# Note, change order to observe convergence
order = 4
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), hp, [k], mapping, power=period)
# Set period mapping and check fixed point propagation
def function(x, k):
for _ in range(period):
x = mapping(x, k)
return x
out = propagate((2, 2), (0, order), pfp, [k], function)
for x, y in zip(flatten(pfp, target=list), flatten(out, target=list)):
print(torch.allclose(x, y))
True
True
True
True
True
[8]:
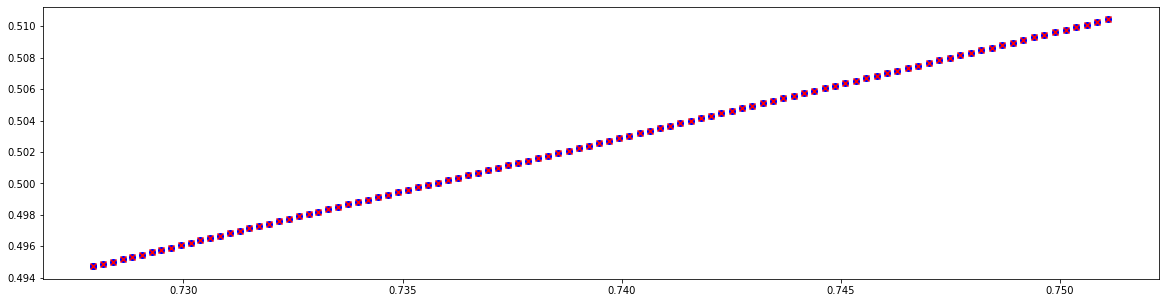
# Plot parametric fixed point position for a given set of knobs
out = torch.func.vmap(lambda dk: evaluate(pfp, [hp, dk]))(dks)
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.scatter(*fps.T.cpu().numpy(), color='blue', marker='o')
plt.scatter(*out.T.cpu().numpy(), color='red', marker='x')
plt.show()
Example-08: Fixed point manipulation (collision)
[1]:
# In this example the distance between a pair of hyperbolic and elliptic fixed points is minimized
# First, using a set of initial guesses within a region, a pair is obtained
# For a given pair, first order parametric dependence of fixed point positions is computed
# Gradient of the distance function between the points is computed (GD minimization)
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import clean_point
from ndmap.pfp import chain_point
from ndmap.pfp import matrix
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set mapping
limit = 8
phase = 2.0*numpy.pi*(1/4 + 0.005)
phase = torch.tensor(phase/(limit + 1), dtype=dtype, device=device)
def mapping(state, knobs):
q, p = state
for index in range(limit):
q, p = q*phase.cos() + p*phase.sin(), p*phase.cos() - q*phase.sin()
q, p = q, p + knobs[index]*q**2
q, p = q*phase.cos() + p*phase.sin(), p*phase.cos() - q*phase.sin()
q, p = q, p + q**2
return torch.stack([q, p])
[5]:
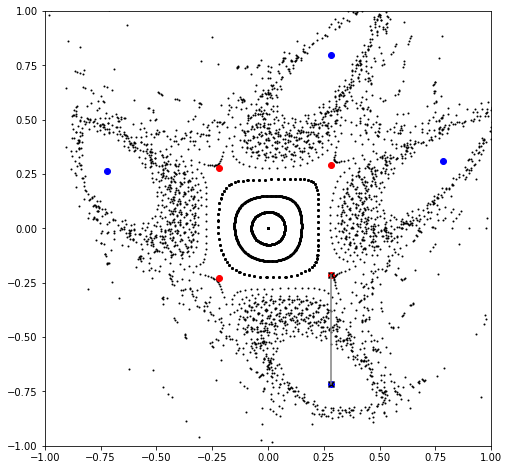
# Locate fixed points and select a pair
# Set initial knobs
knobs = torch.tensor(limit*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute and plot phase space trajectories
state = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.5, 21, dtype=dtype)
state = torch.stack([state, torch.zeros_like(state)]).T
count = 1024
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(state)
state = torch.func.vmap(lambda state: mapping(state, knobs))(state)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.xlim(-1., 1.)
plt.ylim(-1., 1.)
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='black', marker='o', s=1)
# Set tolerance epsilon
epsilon = 1.0E-12
# Compute chains
period = 4
points = 4.0*torch.rand((512, 2), dtype=dtype, device=device) - 2.0
points = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: fixed_point(64, mapping, point, knobs, power=period))(points)
points = clean_point(period, mapping, points, knobs, epsilon=epsilon)
chains = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: chain_point(period, mapping, point, knobs))(points)
# Plot chains
for chain in chains:
point, *_ = chain
value, vector = torch.linalg.eig(matrix(period, mapping, point, knobs))
color = 'blue' if all(value.log().real < epsilon) else 'red'
plt.scatter(*chain.T, color=color, marker='o')
if color == 'blue':
ep, *_ = chain
else:
hp, *_ = chain
ep_chain, *_ = [chain for chain in chains if ep in chain]
hp_chain, *_ = [chain for chain in chains if hp in chain]
ep, *_ = ep_chain
hp, *_ = hp_chain[(ep - hp_chain).norm(dim=-1) == (ep - hp_chain).norm(dim=-1).min()]
plt.scatter(*ep.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.scatter(*hp.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.plot(*torch.stack([ep, hp]).T.cpu().numpy(), color='gray')
plt.show()
[6]:
# Compute first order parametric fixed points
order = 1
php = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), hp, [knobs], mapping, power=period)
pep = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), ep, [knobs], mapping, power=period)
[7]:
# Set objective function
def objective(knobs, php, pep):
dhp = evaluate(php, [torch.zeros_like(knobs), knobs])
dep = evaluate(pep, [torch.zeros_like(knobs), knobs])
return (dep - dhp).norm()
[8]:
# Set learning rate and update knobs
lr = 0.0025
gradient = derivative(1, objective, knobs, php, pep, intermediate=False)
knobs -= lr*gradient
[9]:
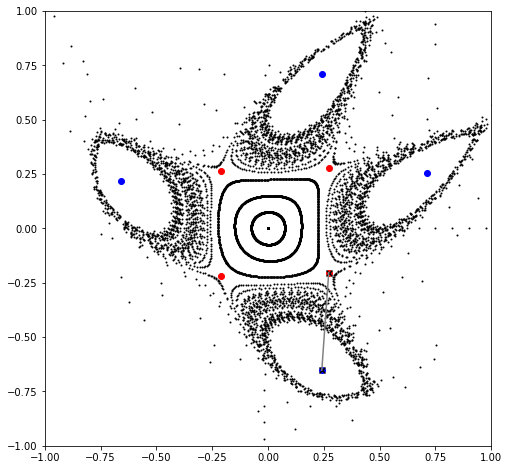
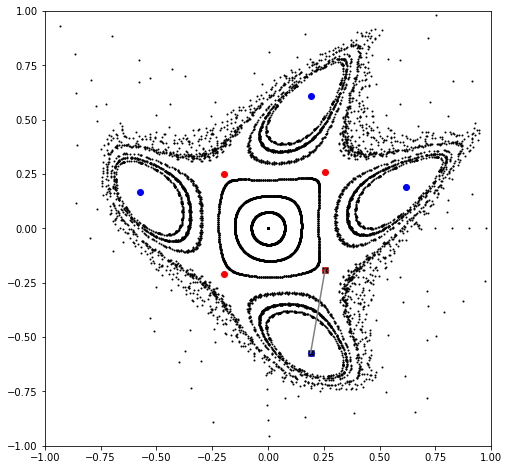
# Iterate
# Set number of iterations
nitr = 5
# Loop
for intr in range(nitr):
# Compute and plot phase space trajectories
state = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.5, 21, dtype=dtype)
state = torch.stack([state, torch.zeros_like(state)]).T
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(state)
state = torch.func.vmap(lambda state: mapping(state, knobs))(state)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.xlim(-1., 1.)
plt.ylim(-1., 1.)
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='black', marker='o', s=1)
# Find fixed points near previous values
points = torch.stack([hp, ep])
points = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: fixed_point(64, mapping, point, knobs, power=period))(points)
points = clean_point(period, mapping, points, knobs, epsilon=epsilon)
chains = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: chain_point(period, mapping, point, knobs))(points)
# Plot chains and selected pair
for chain in chains:
point, *_ = chain
value, vector = torch.linalg.eig(matrix(period, mapping, point, knobs))
color = 'blue' if all(value.log().real < epsilon) else 'red'
plt.scatter(*chain.T, color=color, marker='o')
if color == 'blue':
ep, *_ = chain
else:
hp, *_ = chain
ep_chain, *_ = [chain for chain in chains if ep in chain]
hp_chain, *_ = [chain for chain in chains if hp in chain]
ep, *_ = ep_chain
hp, *_ = hp_chain[(ep - hp_chain).norm(dim=-1) == (ep - hp_chain).norm(dim=-1).min()]
plt.scatter(*ep.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.scatter(*hp.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.plot(*torch.stack([ep, hp]).T.cpu().numpy(), color='gray')
plt.show()
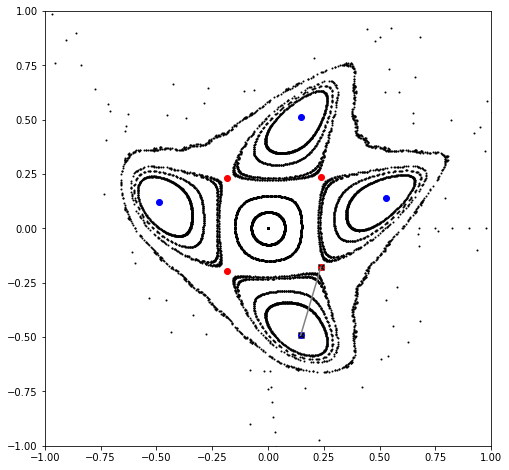
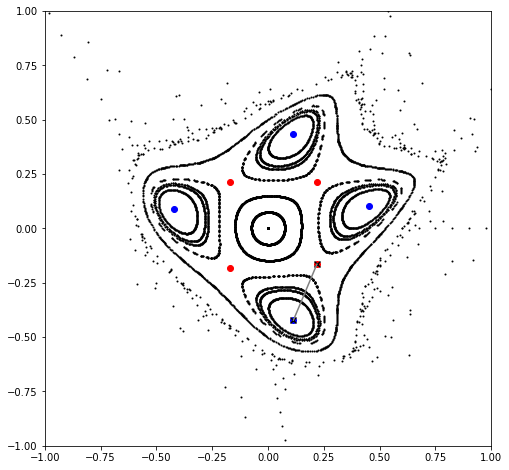
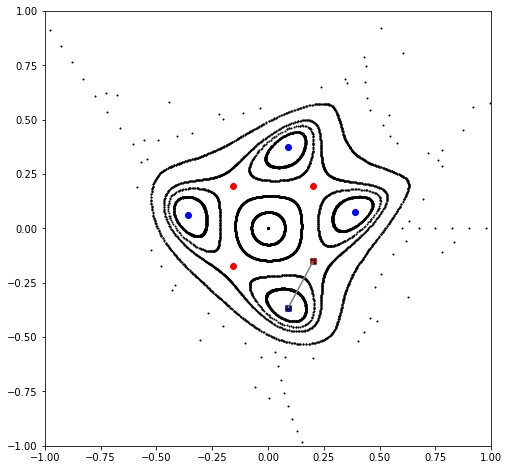
# Recompute parametric fixed points
# Note, not strictly necessary to do at each iteration
php = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), hp, [knobs], mapping, power=period)
pep = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), ep, [knobs], mapping, power=period)
# Update
lr *= 2.0
gradient = derivative(1, objective, knobs, php, pep, intermediate=False)
knobs -= lr*gradient
Example-09: Fixed point manipulation (change point type)
[1]:
# In this example real parts of the eigenvalues of a hyperbolic fixed point are minimized
# First, using a set of initial guesses within a region, a hyperbolic point is located
# Parametric fixed point is computed and propagated
# Propagated table is used as a surrogate model to generate differentible objective
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.util import nest
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import clean_point
from ndmap.pfp import chain_point
from ndmap.pfp import matrix
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set mapping
limit = 8
phase = 2.0*numpy.pi*(1/4 + 0.005)
phase = torch.tensor(phase/(limit + 1), dtype=dtype, device=device)
def mapping(state, knobs):
q, p = state
for index in range(limit):
q, p = q*phase.cos() + p*phase.sin(), p*phase.cos() - q*phase.sin()
q, p = q, p + knobs[index]*q**2
q, p = q*phase.cos() + p*phase.sin(), p*phase.cos() - q*phase.sin()
q, p = q, p + q**2
return torch.stack([q, p])
[5]:
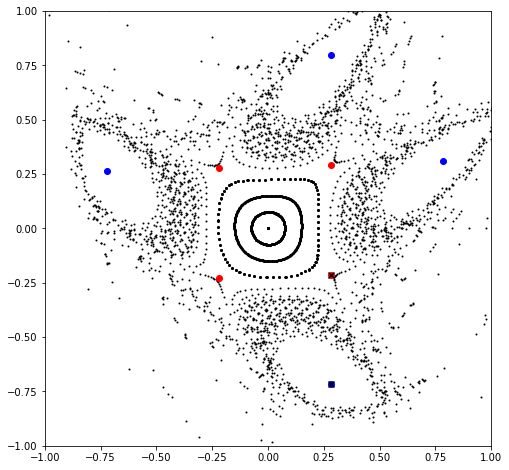
# Locate fixed points and select a pair
# Set initial knobs
knobs = torch.tensor(limit*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute and plot phase space trajectories
state = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.5, 21, dtype=dtype)
state = torch.stack([state, torch.zeros_like(state)]).T
count = 1024
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(state)
state = torch.func.vmap(lambda state: mapping(state, knobs))(state)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.xlim(-1., 1.)
plt.ylim(-1., 1.)
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='black', marker='o', s=1)
# Set tolerance epsilon
epsilon = 1.0E-12
# Compute chains
period = 4
points = 4.0*torch.rand((512, 2), dtype=dtype, device=device) - 2.0
points = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: fixed_point(64, mapping, point, knobs, power=period))(points)
points = clean_point(period, mapping, points, knobs, epsilon=epsilon)
chains = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: chain_point(period, mapping, point, knobs))(points)
# Plot chains
for chain in chains:
point, *_ = chain
value, vector = torch.linalg.eig(matrix(period, mapping, point, knobs))
color = 'blue' if all(value.log().real < epsilon) else 'red'
plt.scatter(*chain.T, color=color, marker='o')
if color == 'blue':
ep, *_ = chain
else:
hp, *_ = chain
ep_chain, *_ = [chain for chain in chains if ep in chain]
hp_chain, *_ = [chain for chain in chains if hp in chain]
ep, *_ = ep_chain
hp, *_ = hp_chain[(ep - hp_chain).norm(dim=-1) == (ep - hp_chain).norm(dim=-1).min()]
plt.scatter(*ep.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.scatter(*hp.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
[6]:
# Matrix around (dynamical) fixed points
# Note, eigenvalues of a hyperbolic fixed point are not on the unit circle
em = matrix(period, mapping, ep, knobs)
print(em)
print(torch.linalg.eigvals(em).log().real)
print()
hm = matrix(period, mapping, hp, knobs)
print(hm)
print(torch.linalg.eigvals(hm).log().real)
print()
tensor([[2.739351528140e-01, -1.149307994931e+00],
[5.971467208895e-01, 1.145141455240e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.784726318725e-15, -1.784726318725e-15], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([[1.251182357765e+00, 1.288812994113e-01],
[1.428760927086e-01, 8.139613303868e-01]], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.545448611841e-01, -2.545448611841e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Compute first order parametric fixed points
order = 1
php = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), hp, [knobs], mapping, power=period)
pep = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), ep, [knobs], mapping, power=period)
[8]:
# Propagate parametric identity table
# Note, propagated table can be used as a surrogate model around (parametric) fixed point
# Here it is used to compute parametric matrix around fixed point and its egenvalues
t = identity((1, 1), [hp, knobs], parametric=php)
t = propagate((2, limit), (1, 1), t, [knobs], nest(period, mapping, knobs))
[9]:
# Set objective function
def objective(knobs):
hm = derivative(1, lambda x, k: evaluate(t, [x, k]), hp, knobs, intermediate=False)
return torch.linalg.eigvals(hm).log().real.abs().sum()
[10]:
# Initial objective value
print(objective(knobs))
tensor(5.090897223682e-01, dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Objective gradient
print(derivative(1, objective, knobs, intermediate=False))
tensor([-1.974190541982e-01, -4.137846718749e-01, -5.970747283789e-01, -7.018818743275e-01,
-7.018818743275e-01, -5.970747283789e-01, -4.137846718749e-01, -1.974190541982e-01],
dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Set learning rate and update knobs
lr = 0.01
gradient = derivative(1, objective, knobs, intermediate=False)
knobs -= lr*gradient
[13]:
# Iterate
# Set number of iterations
nitr = 5
# Loop
for intr in range(nitr):
state = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.5, 21, dtype=dtype)
state = torch.stack([state, torch.zeros_like(state)]).T
count = 1024
table = []
for _ in range(count):
table.append(state)
state = torch.func.vmap(lambda state: mapping(state, knobs))(state)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qs, ps = table
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.xlim(-1., 1.)
plt.ylim(-1., 1.)
for q, p in zip(qs.cpu().numpy(), ps.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='black', marker='o', s=1)
# Set tolerance epsilon
epsilon = 1.0E-12
# Compute chains
period = 4
points = torch.stack([hp, ep])
points = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: fixed_point(64, mapping, point, knobs, power=period))(points)
points = clean_point(period, mapping, points, knobs, epsilon=epsilon)
chains = torch.func.vmap(lambda point: chain_point(period, mapping, point, knobs))(points)
# Plot chains
for chain in chains:
point, *_ = chain
value, vector = torch.linalg.eig(matrix(period, mapping, point, knobs))
color = 'blue' if all(value.log().real < epsilon) else 'red'
plt.scatter(*chain.T, color=color, marker='o')
if color == 'blue':
ep, *_ = chain
else:
hp, *_ = chain
ep_chain, *_ = [chain for chain in chains if ep in chain]
hp_chain, *_ = [chain for chain in chains if hp in chain]
ep, *_ = ep_chain
hp, *_ = hp_chain[(ep - hp_chain).norm(dim=-1) == (ep - hp_chain).norm(dim=-1).min()]
plt.scatter(*ep.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.scatter(*hp.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
print(objective(knobs).item())
# Compute parametric fixed points
php = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), hp, [knobs], mapping, power=period)
pep = parametric_fixed_point((order, ), ep, [knobs], mapping, power=period)
# Propagate parametric fixed points
t = identity((1, 1), [hp, knobs], parametric=php)
t = propagate((2, limit), (1, 1), t, [knobs], nest(period, mapping, knobs))
# Update
lr += 0.005
gradient = derivative(1, objective, knobs, intermediate=False)
knobs = knobs - lr*gradient
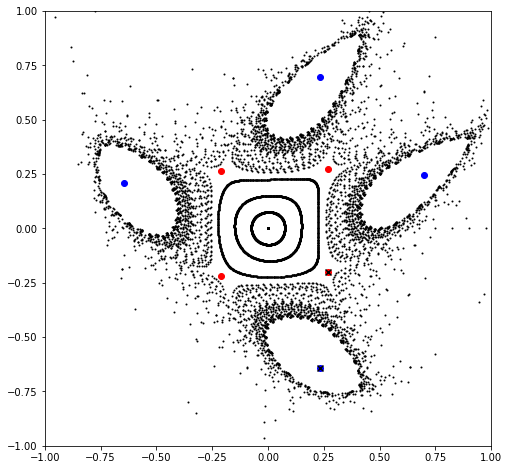
0.4875424149522949
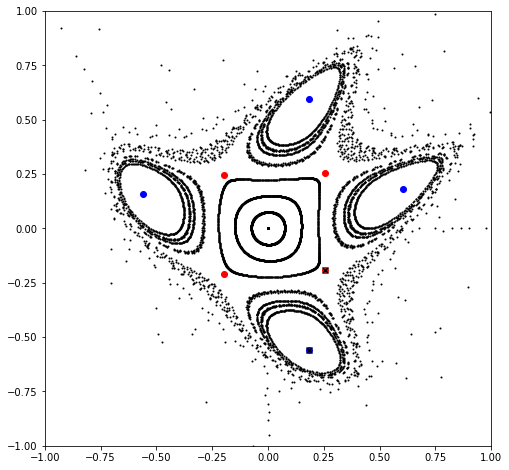
0.44253915640171704
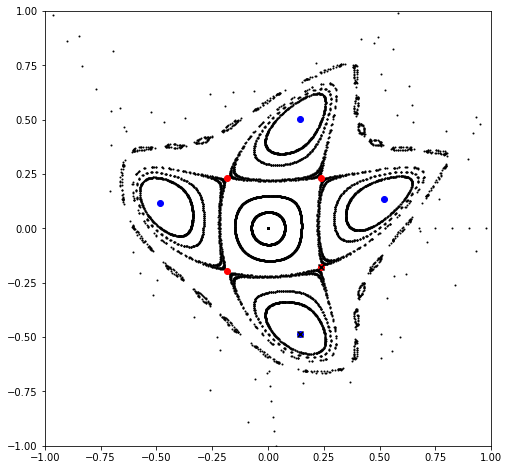
0.3947019262885917
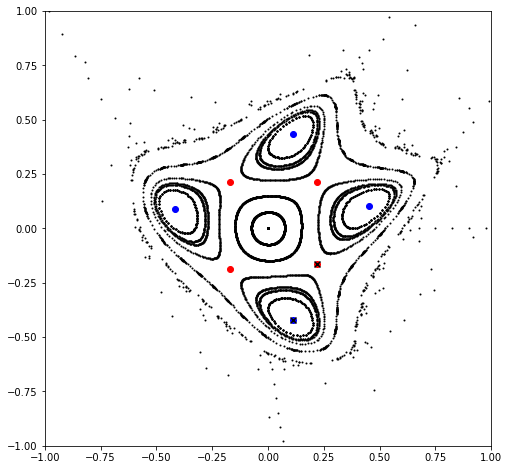
0.34869831355705994
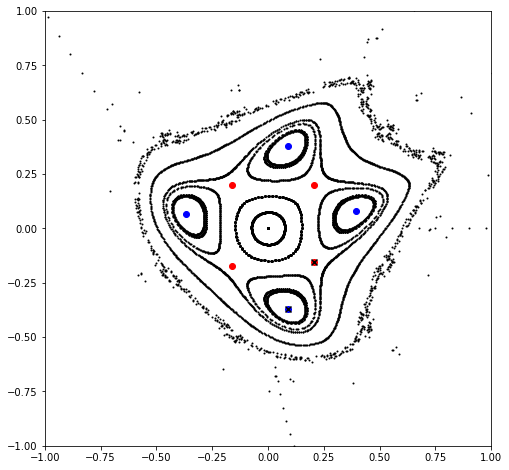
0.3054166976781556
Example-10: Alignment indices chaos indicators
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
torch.set_printoptions(precision=8, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set fixed parameters
a1, b1 = 0, 1
a2, b2 = 0, 1
f1 = torch.tensor(2.0*numpy.pi*0.38, dtype=dtype, device=device)
f2 = torch.tensor(2.0*numpy.pi*0.41, dtype=dtype, device=device)
cf1, sf1 = f1.cos(), f1.sin()
cf2, sf2 = f2.cos(), f2.sin()
[4]:
# Set 4D symplectic mapping
def mapping(x):
q1, p1, q2, p2 = x
return torch.stack([
b1*(p1 + (q1**2 - q2**2))*sf1 + q1*(cf1 + a1*sf1),
-((q1*(1 + a1**2)*sf1)/b1) + (p1 + (q1**2 - q2**2))*(cf1 - a1*sf1),
q2*cf2 + (p2*b2 + q2*(a2 - 2*q1*b2))*sf2,
-((q2*(1 + a2**2)*sf2)/b2) + (p2 - 2*q1*q2)*(cf2 - a2*sf2)
])
[5]:
# Set 4D symplectic mapping with tangent dynamics
def tangent(x, vs):
x, m = derivative(1, mapping, x)
vs = torch.func.vmap(lambda v: m @ v)(vs)
return x, vs/vs.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
[6]:
# Set generalized alignment indices computation
# Note, if number if vectors is equal to two, the index tends towards zero for regular orbits
# And tends towards a constant value for chaotic motion
# If the number of vectors is greater than two, index tends towards zero for all cases
# But for chaotic orbits, zero is reached (exponentialy) faster
def gali(vs, threshold=1.0E-12):
return (threshold + torch.linalg.svdvals(vs).prod()).log10()
[7]:
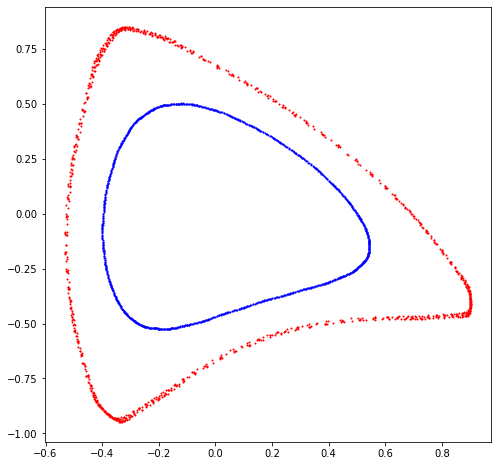
# First, consider two initial conditions (regular and chaotic)
count = 1024
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
x = torch.tensor([0.50000, 0.0, 0.05, 0.0], dtype=dtype)
orbit = []
for _ in range(count):
x = mapping(x)
orbit.append(x)
q, p, *_ = torch.stack(orbit).T
plt.scatter(q, p, s =1, color='blue')
x = torch.tensor([0.68925, 0.0, 0.10, 0.0], dtype=dtype)
orbit = []
for _ in range(count):
x = mapping(x)
orbit.append(x)
q, p, *_ = torch.stack(orbit).T
plt.scatter(q, p, s =1, color='red')
plt.show()
[8]:
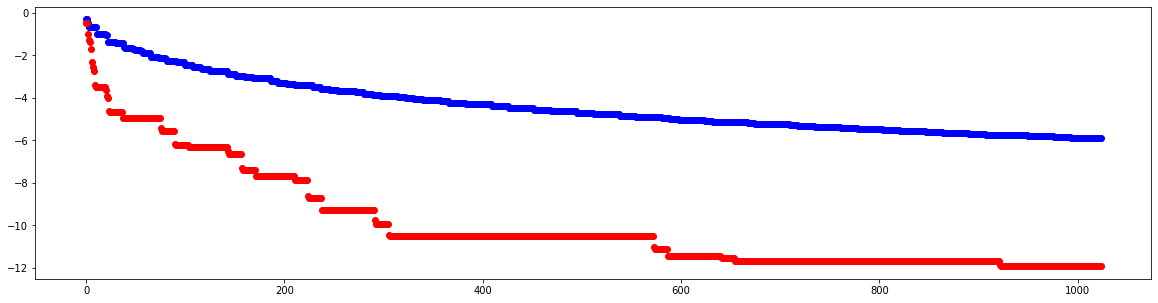
# Compute and plot the last gali index at each iteration
# Note, running minimum is appended at each iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
x = torch.tensor([0.50000, 0.0, 0.05, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
vs = torch.eye(4, dtype=dtype, device=device)
out = []
for _ in range(count):
x, vs = tangent(x, vs)
res = gali(vs)
out.append(res if not out else min(res, out[-1]))
out = torch.stack(out)
plt.scatter(range(count), out, color='blue', marker='o')
x = torch.tensor([0.68925, 0.0, 0.10, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
vs = torch.eye(4, dtype=dtype, device=device)
out = []
for _ in range(count):
x, vs = tangent(x, vs)
res = gali(vs)
out.append(res if not out else min(res, out[-1]))
out = torch.stack(out)
plt.scatter(range(count), out, color='red', marker='o')
plt.show()
[9]:
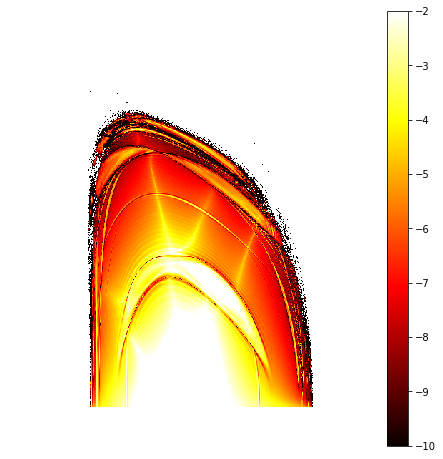
# Compute indicator using all avaliable vectors for a grid of initial conditions
def gali(vs):
return torch.linalg.svdvals(vs.nan_to_num()).prod()
# Set grid
n1 = 501
n2 = 501
q1 = torch.linspace(-1.0, +1.0, n1, dtype=dtype, device=device)
q2 = torch.linspace(+0.0, +1.0, n2, dtype=dtype, device=device)
qs = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid(q1, q2, indexing='ij')).swapaxes(-1, 0).reshape(n1*n2, -1)
ps = torch.full_like(qs, 1.0E-10)
q1, q2, p1, p2 = torch.hstack([qs, ps]).T
vs = torch.tensor(n1*n2*[torch.eye(4).tolist()], dtype=dtype, device=device)
qs = torch.stack([q1, p1, q2, p2]).T
# Set tast
# Perform 512 iterations, compute min of indicator value over the next 64 iterations
def task(qs, vs, count=512, total=64, level=1.0E-10):
for _ in range(count):
qs, vs = tangent(qs, vs)
out = []
for _ in range(total):
qs, vs = tangent(qs, vs)
out.append(gali(vs))
return (torch.stack(out).min() + level*torch.sign(qs.norm())).log10()
# Compute and clean data
out = torch.vmap(task)(qs, vs)
out = out.nan_to_num(neginf=0.0)
out[(out >= -2.0)*(out != 0.0)] = -2.0
out[out == 0.0] = torch.nan
out = out.reshape(n1, n2)
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(
out.cpu().numpy(),
vmin=-10.0,
vmax=-2.0,
aspect='equal',
origin='lower',
cmap='hot',
interpolation='nearest')
plt.colorbar()
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
Example-11: Closed orbit (dispersion)
[1]:
# In this example derivatives of closed orbit with respect to momentum deviation are computed
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=8, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
# Note, here observation poins are locations between elements, lattice start and lattice end
# An observable (closed orbit) is computed at observation points
# All maps are expected to have identical signature of differentible parameters
# State and momentum deviation in this example
# But each map can have any number of additional args and kwargs after required parameters
def map_01_02(x, w): return quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
def map_02_03(x, w): return drif(x, w, 0.45)
def map_03_04(x, w): return sext(x, w, 0.00, 0.10)
def map_04_05(x, w): return drif(x, w, 0.45)
def map_05_06(x, w): return bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 3.0)
def map_06_07(x, w): return drif(x, w, 0.45)
def map_07_08(x, w): return sext(x, w, 0.00, 0.10)
def map_08_09(x, w): return drif(x, w, 0.45)
def map_09_10(x, w): return quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
def map_10_11(x, w): return quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
def map_11_12(x, w): return drif(x, w, 0.45)
def map_12_13(x, w): return sext(x, w, 0.00, 0.10)
def map_13_14(x, w): return drif(x, w, 0.45)
def map_14_15(x, w): return bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 3.0)
def map_15_16(x, w): return drif(x, w, 0.45)
def map_16_17(x, w): return sext(x, w, 0.00, 0.10)
def map_17_18(x, w): return drif(x, w, 0.45)
def map_18_19(x, w): return quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
transport = [
map_01_02,
map_02_03,
map_03_04,
map_04_05,
map_05_06,
map_06_07,
map_07_08,
map_08_09,
map_09_10,
map_10_11,
map_11_12,
map_12_13,
map_13_14,
map_14_15,
map_15_16,
map_16_17,
map_17_18,
map_18_19
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, w):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, w)
return x
[6]:
# The first step is to compute dynamical fixed point
# Set initial guess
# Note, in this example zero is a fixed point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Set knobs
w = torch.tensor([0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Find fixed point
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, w, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Compute parametric closed orbit
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((2, ), fp, [w], fodo)
chop(pfp)
# Print series representation
for key, value in series((4, 1), (0, 2), pfp).items():
print(f'{key}: {value.cpu().numpy()}')
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0): [0. 0. 0. 0.]
(0, 0, 0, 0, 1): [1.81613351 0. 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 0, 0, 2): [0.56855511 0. 0. 0. ]
[8]:
# Check convergence
print(evaluate(series((4, 1), (0, 0), pfp), [x, w + 1.0E-3]))
print(evaluate(series((4, 1), (0, 1), pfp), [x, w + 1.0E-3]))
print(evaluate(series((4, 1), (0, 2), pfp), [x, w + 1.0E-3]))
print()
out = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, w + 1.0E-3, power=1)
chop([out])
print(out)
print()
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.81613351e-03, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.81670206e-03, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([ 1.81670185e-03, 1.13882757e-19, -5.50391130e-235, 0.00000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[9]:
# Propagate closed orbit
out = []
jet = identity((0, 1), fp, parametric=pfp)
out.append(jet)
for mapping in transport:
jet = propagate((4, 1), (0, 2), jet, [w], mapping)
out.append(jet)
[10]:
# Check periodicity
print(compare(pfp, jet))
True
[11]:
# Plot 1st order dispersion
pos = [0.00, 0.50, 0.95, 1.05, 1.50, 4.50, 4.95, 5.05, 5.50, 6.00, 6.50, 6.95, 7.05, 7.50, 10.50, 10.95, 11.05, 11.50, 12.00]
res = torch.stack([series((4, 1), (0, 2), jet)[(0, 0, 0, 0, 1)][0] for jet in out])
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.plot(pos, res.cpu().numpy(), marker='x', color='blue')
plt.show()
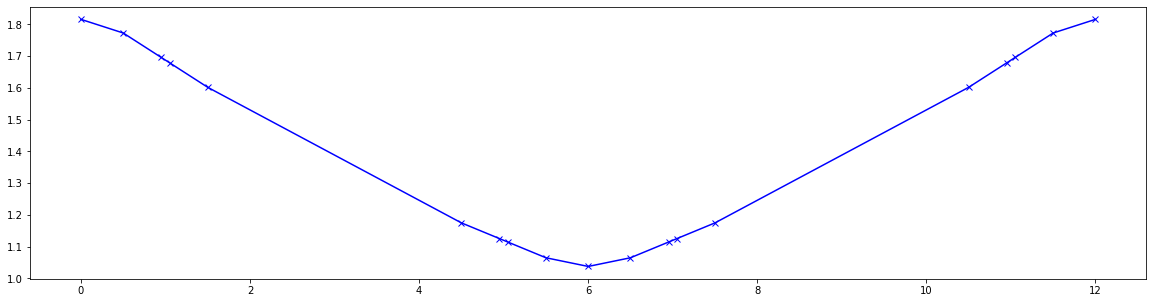
[12]:
# Plot 2nd order dispersion
pos = [0.00, 0.50, 0.95, 1.05, 1.50, 4.50, 4.95, 5.05, 5.50, 6.00, 6.50, 6.95, 7.05, 7.50, 10.50, 10.95, 11.05, 11.50, 12.00]
res = torch.stack([series((4, 1), (0, 2), jet)[(0, 0, 0, 0, 2)][0] for jet in out])
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.plot(pos, res.cpu().numpy(), marker='x', color='blue')
plt.show()
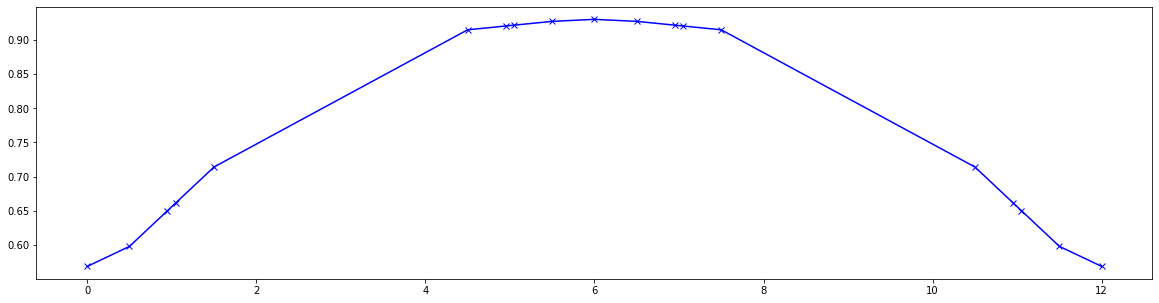
Example-12: Closed orbit (quadrupole shift)
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, d):
dxf, dyf, dxd, dyd = d
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
x = slip(x, -dxf, -dyf)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = slip(x, +dxd, +dyd)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = slip(x, -dxd, -dyd)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = slip(x, +dxf, +dyf)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, d):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, d)
return x
[5]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, d, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [d], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[6]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[-4.621551e-01, 0.000000e+00, 1.165780e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 3.344042e+00, 0.000000e+00, -4.891066e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[7]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 4), (0, 1), pfp, [d], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[-4.621551e-01, 0.000000e+00, 1.165780e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 3.344042e+00, 0.000000e+00, -4.891066e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Test single random shift
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = 1.0E-3*torch.randn_like(x)
fp = fixed_point(64, fodo, x, d, power=1, epsilon=1.0E-9)
chop([fp])
print(fp)
print(evaluate(pfp, [x, d]))
tensor([8.482363e-04, 8.125977e-21, 3.353913e-03, 6.171311e-20], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([8.482363e-04, 0.000000e+00, 3.353913e-03, 0.000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[9]:
# Estimate center & spread (tracking)
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = 1.0E-3*torch.randn(8192, 4, dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = torch.func.vmap(lambda d: fixed_point(64, fodo, x, d, power=1))(d)
chop([fp])
print(fp.T.mean(-1))
print(fp.T.std(-1))
tensor([-9.932218e-06, 4.372133e-22, -1.483549e-06, 1.693071e-21], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.253079e-03, 9.554150e-20, 5.881071e-03, 3.289974e-19], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Estimate center & spread (surrogate)
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = 1.0E-3*torch.randn(8192, 4, dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = torch.func.vmap(lambda d: evaluate(pfp, [x, d]))(d)
chop([fp])
print(fp.T.mean(-1))
print(fp.T.std(-1))
tensor([ 3.969686e-06, 0.000000e+00, -2.718688e-05, 0.000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.240640e-03, 0.000000e+00, 5.905480e-03, 0.000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Estimate spread (error propagation)
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
s = derivative(1, lambda d: evaluate(pfp, [x, d]), d, intermediate=False)
print((s @ (1.0E-3*torch.eye(4, dtype=dtype, device=device))**2 @ s.T).diag().sqrt())
tensor([1.254045e-03, 0.000000e+00, 5.924960e-03, 0.000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-13: Closed orbit (sextupole shift)
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, d):
dxsf1, dysf1, dxsd1, dysd1, dxsf2, dysf2, dxsd2, dysd2 = d
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = slip(x, +dxsf1, +dysf1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.50, 0.10)
x = slip(x, -dxsf1, -dysf1)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = slip(x, +dxsd1, +dysd1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], -0.50, 0.10)
x = slip(x, -dxsd1, -dysd1)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = slip(x, +dxsd2, +dysd2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], -0.50, 0.10)
x = slip(x, -dxsd2, -dysd2)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = slip(x, +dxsf2, +dysf2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.50, 0.10)
x = slip(x, -dxsf2, -dysf2)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, d):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, d)
return x
[5]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, d, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute & check parametric fixed point
# Note, there is no first order contribution from sextupole shifts
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((2, ), fp, [d], fodo)
out = propagate((4, 8), (0, 2), pfp, [d], fodo)
print(compare(pfp, out))
True
[7]:
# Test for a random shift
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = 1.0E-3*torch.randn(8, dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(64, fodo, x, d, power=1, epsilon=1.0E-9)
print(fp)
print(evaluate(pfp, [x, d]))
tensor([ 2.446138e-07, -1.144473e-08, -8.221335e-07, 6.156318e-09], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([ 2.442916e-07, -1.142839e-08, -8.240374e-07, 6.170032e-09], dtype=torch.float64)
[8]:
# Estimate center & spread (tracking)
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = 1.0E-3*torch.randn(8192, 8, dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = torch.func.vmap(lambda d: fixed_point(64, fodo, x, d, power=1))(d)
chop([fp])
print(fp.T.mean(-1))
print(fp.T.std(-1))
tensor([-1.018030e-09, -2.975896e-10, -1.314171e-08, -2.126598e-11], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([6.895581e-07, 3.187716e-08, 1.813973e-06, 2.939394e-08], dtype=torch.float64)
[9]:
# Estimate center & spread (surrogate)
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = 1.0E-3*torch.randn(8192, 8, dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = torch.func.vmap(lambda d: evaluate(pfp, [x, d]))(d)
chop([fp])
print(fp.T.mean(-1))
print(fp.T.std(-1))
tensor([-4.887936e-09, -1.410492e-10, -3.069499e-09, -4.740614e-10], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([6.769223e-07, 3.104300e-08, 1.819394e-06, 2.833964e-08], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-14: Closed orbit (responce matrix & correction)
[1]:
# In this example orbit responce matrix is computed
# Quadrupole shifts are introduced and responce matrix is used to correct the orbit at observation locations
# Correctors are at sextupole centers
# Observation points are at bend centers
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=25):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, c, d):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = c
dxf, dyf, dxd, dyd = d
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
x = slip(x, -dxf, -dyf)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsf1, cysf1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def map_02_03(x, c, d):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = c
dxf, dyf, dxd, dyd = d
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsd1, cysd1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = slip(x, +dxd, +dyd)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = slip(x, -dxd, -dyd)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsd2, cysd2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def map_03_04(x, c, d):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = c
dxf, dyf, dxd, dyd = d
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsf2, cysf2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = slip(x, +dxf, +dyf)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02,
map_02_03,
map_03_04
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, c, d):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, c, d)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
c = torch.tensor(8*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, c, d))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
c = torch.tensor(8*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, c, d, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [c], fodo, d)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[7.583253e+00, 5.939607e+00, 7.583253e+00, 5.939607e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[-4.334732e-01, -9.086786e-02, 4.334732e-01, 9.086786e-02, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 1.349234e+01, 2.165892e+01, 1.349234e+01, 2.165892e+01],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, -4.019148e-01, -7.725758e-02, 4.019148e-01, 7.725758e-02]],
dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 8), (0, 1), pfp, [c], fodo, d)
chop(out)
out
[8]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[7.583253e+00, 5.939607e+00, 7.583253e+00, 5.939607e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[-4.334732e-01, -9.086786e-02, 4.334732e-01, 9.086786e-02, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 1.349234e+01, 2.165892e+01, 1.349234e+01, 2.165892e+01],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, -4.019148e-01, -7.725758e-02, 4.019148e-01, 7.725758e-02]],
dtype=torch.float64)]]
[9]:
# Orbit derivatives at observation locations
bag = []
pfp = propagate((4, 8), (0, 1), pfp, [c], map_01_02, d)
chop(pfp)
bag.append(pfp)
pfp = propagate((4, 8), (0, 1), pfp, [c], map_02_03, d)
chop(pfp)
bag.append(pfp)
[10]:
# Compute responce matrix
def orbit(c, pfp):
qx, _, qy, _ = evaluate(pfp, [x, c])
return torch.stack([qx, qy])
pfp1, pfp2 = bag
rx1, ry1 = derivative(1, orbit, c, pfp1, intermediate=False)
rx2, ry2 = derivative(1, orbit, c, pfp2, intermediate=False)
rm = torch.stack([rx1, rx2, ry1, ry2])
print(rm)
tensor([[6.221115e+00, 4.042085e+00, 6.753998e+00, 4.569069e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[6.753998e+00, 4.569069e+00, 6.221115e+00, 4.042085e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 1.808222e+01, 2.754871e+01, 1.855563e+01, 2.802741e+01],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 1.855563e+01, 2.802741e+01, 1.808222e+01, 2.754871e+01]],
dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Generate perturbed orbit
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
c = torch.tensor(8*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
d = torch.tensor([0.001, 0.001, -0.001, 0.001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, c, d, power=1)
qx1, _, qy1, _ = map_01_02(fp, c, d)
qx2, _, qy2, _ = map_02_03(map_01_02(fp, c, d), c, d)
o = torch.stack([qx1, qx2, qy1, qy2])
chop([o])
print(o)
tensor([-2.161122e-03, -2.161122e-03, -3.001730e-03, -3.001730e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Correct orbit
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
c = - (torch.linalg.pinv(rm) @ o)
d = torch.tensor([0.001, 0.001, -0.001, 0.001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, c, d, power=1)
qx1, _, qy1, _ = map_01_02(fp, c, d)
qx2, _, qy2, _ = map_02_03(map_01_02(fp, c, d), c, d)
o = torch.stack([qx1, qx2, qy1, qy2])
chop([o])
print(o)
tensor([-1.070014e-18, 3.763685e-18, -1.733072e-17, -1.661201e-17], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-15: Tune (chromaticity)
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, w, k):
ksf, ksd, ksb = k
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, ksf, 0.10)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, ksb, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, ksd, 0.10)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, ksd, 0.10)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, ksb, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, ksf, 0.10)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, d, k):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, d, k)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor(1*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, w, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[5]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor(1*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, w, k, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, 1), fp, [w, k], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[6]:
[[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)],
[tensor([[1.816134e+00],
[0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]]], dtype=torch.float64)]]]
[7]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 1, 3), (0, 1, 1), pfp, [w, k], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[7]:
[[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)],
[tensor([[1.816134e+00],
[0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]]], dtype=torch.float64)]]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric identity (surrogate model for linear dynamics)
jet = identity((1, 1, 1), fp, parametric=pfp)
jet = propagate((4, 1, 3), (1, 1, 1), jet, [w, k], fodo)
[9]:
# Compute tune
def tune(w, k):
m = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, w, k]), fp, intermediate=False)
t, *_ = twiss(m)
return t
print(tune(w, k))
tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Compute parametric tune
t = derivative((1, 1), tune, w, k)
print(t)
[[tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)], [tensor([[-2.343079e-01],
[-2.416176e-01]], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[[3.618782e-01],
[8.705079e-02],
[5.873074e+00]],
[[-2.986097e-01],
[-4.727344e-01],
[-1.106560e+01]]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[11]:
# Check convergence
print(evaluate(t, [w, k]))
print(evaluate(t, [w + 1.0E-3, k]))
print()
print(tune(w + 1.0E-3, k))
tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.525452e-01, 1.196688e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.525452e-01, 1.196687e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Check convergence
print(evaluate(t, [w, k]))
print(evaluate(t, [w + 1.0E-3, k]))
print(evaluate(t, [w + 1.0E-3, k + 1.0E-2]))
print()
print(tune(w + 1.0E-3, k + 1.0E-2))
tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.525452e-01, 1.196688e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.526084e-01, 1.195504e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.526084e-01, 1.195502e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
[13]:
# Series representation
for key, value in clean(series((1, 3), (1, 1), t)).items():
print(f'{key}: {value}')
(0, 0, 0, 0): tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 0, 0): tensor([-2.343079e-01, -2.416176e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 1, 0, 0): tensor([3.618782e-01, -2.986097e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 1, 0): tensor([8.705079e-02, -4.727344e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 0, 1): tensor([5.873074e+00, -1.106560e+01], dtype=torch.float64)
[14]:
# Set chromaticity to zero
A = derivative((1, 1), lambda w, k: evaluate(t, [w, k]), w, k, intermediate=False)
b = derivative(1, lambda w, k: evaluate(t, [w, k]), w, k, intermediate=False).flatten()
print(derivative(1, lambda w: evaluate(t, [w, k]), w, intermediate=False).flatten())
print(derivative(1, lambda w: evaluate(t, [w, - (torch.linalg.pinv(A.squeeze()) @ b)]), w, intermediate=False).flatten())
tensor([-2.343079e-01, -2.416176e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-2.914335e-15, 1.165734e-15], dtype=torch.float64)
[15]:
# Set chromaticity to one
A = derivative((1, 1), lambda w, k: evaluate(t, [w, k]), w, k, intermediate=False)
b = -1.0 + derivative(1, lambda w, k: evaluate(t, [w, k]), w, k, intermediate=False).flatten()
print(derivative(1, lambda w: evaluate(t, [w, k]), w, intermediate=False).flatten())
print(derivative(1, lambda w: evaluate(t, [w, - (torch.linalg.pinv(A.squeeze()) @ b)]), w, intermediate=False).flatten())
tensor([-2.343079e-01, -2.416176e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.000000e+00, 1.000000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-16: Tune (responce matrix & correction)
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, k):
kqf, kqd, kqb = k
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kqf, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.0, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kqd, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kqd, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.0, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kqf, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, k):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[5]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, k, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [k], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[6]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[7]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 3), (0, 1), pfp, [k], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric identity (surrogate model for linear dynamics)
jet = identity((1, 1), fp, parametric=pfp)
jet = propagate((4, 3), (1, 1), jet, [k], fodo)
[9]:
# Compute tune
def tune(k):
m = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k]), fp, intermediate=False)
t, *_ = twiss(m)
return t
print(tune(k))
tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Compute parametric tune
t = derivative((1, ), tune, k)
[11]:
# Check convergence
print(evaluate(t, [k]))
print(evaluate(t, [k + torch.tensor([5.0E-3, 5.0E-3, 1.0E-3], dtype=dtype, device=device)]))
print()
print(tune(k + torch.tensor([5.0E-3, 5.0E-3, 1.0E-3], dtype=dtype, device=device)))
tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.646746e-01, 9.564416e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.646564e-01, 9.339156e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Responce matrix
print(derivative(1, lambda k: evaluate(t, [k]), k, intermediate=False))
tensor([[1.217003e+00, 3.230152e-01, 4.195000e+00],
[-7.757018e-01, -2.437956e+00, -8.197983e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)
[13]:
# Correct tunes (increase horizontal by 0.01)
A = derivative(1, lambda k: evaluate(t, [k]), k, intermediate=False)
b = -torch.tensor([0.01, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(tune(k))
print(tune(-(torch.linalg.pinv(A) @ b)))
print()
tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.627666e-01, 1.199040e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-17: Tune (spread)
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, k):
kqf, kqd, kqb = k
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kqf, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.0, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kqd, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kqd, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.0, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kqf, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, k):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[5]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, k, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((2, ), fp, [k], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[6]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[7]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 3), (0, 2), pfp, [k], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric identity (surrogate model for linear dynamics)
jet = identity((1, 2), fp, parametric=pfp)
jet = propagate((4, 3), (1, 2), jet, [k], fodo)
[9]:
# Compute tune
def tune(k):
m = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k]), fp, intermediate=False)
t, *_ = twiss(m)
return t
print(tune(k))
tensor([2.527795e-01, 1.199104e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Compute tune spread (direct)
sf = 1.0E-3
sd = 1.0E-3
sb = 1.0E-4
def wrapper(k):
t, *_ = twiss(derivative(1, fodo, x, k, intermediate=False))
return t
err = torch.tensor([sf, sd, sb])*torch.randn(8192).unsqueeze(1).to(dtype).to(device)
out = torch.func.vmap(wrapper)(err).T
print(out.mean(-1))
print(out.std(-1))
print()
tensor([2.527650e-01, 1.198656e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.958515e-03, 4.040516e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Compute parametric tune
t = derivative((1, ), tune, k)
[12]:
# Compute tune spread (surrogate)
sf = 1.0E-3
sd = 1.0E-3
sb = 1.0E-4
err = torch.tensor([sf, sd, sb])*torch.randn(8192).unsqueeze(1).to(dtype).to(device)
out = torch.func.vmap(lambda k: evaluate(t, [k]))(err).T
print(out.mean(-1))
print(out.std(-1))
print()
tensor([2.528075e-01, 1.198527e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.973939e-03, 4.063140e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-18: Parametric twiss
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
from twiss.wolski import propagate as propagate_twiss
from twiss.convert import wolski_to_cs
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, k):
kqf, kqd, kqb = k
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kqf, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def map_02_03(x, k):
kqf, kqd, kqb = k
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kqd, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kqd, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.1)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def map_03_04(x, k):
kqf, kqd, kqb = k
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.1)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kqf, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02,
map_02_03,
map_03_04
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, k):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[5]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, k, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [k], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[6]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[7]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 3), (0, 1), pfp, [k], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric identity (surrogate model for linear dynamics)
jet = identity((1, 1), fp, parametric=pfp)
jet = propagate((4, 3), (1, 1), jet, [k], fodo)
[9]:
# Compute twiss
# Note, exact or jet one-turn transport can be used
# Other maps can be replaced with jets too
def fn(k, fodo):
bxs = []
bys = []
m = derivative(1, fodo, fp, intermediate=False)
t, _, w = twiss(m)
_, bx, _, by = wolski_to_cs(w)
for mapping in transport:
w = propagate_twiss(w, derivative(1, mapping, x, k, intermediate=False))
_, bx, _, by = wolski_to_cs(w)
bxs.append(bx)
bys.append(by)
return torch.stack([*t, *bxs, *bys])
print(fn(k, fodo=lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k])))
tensor([2.528e-01, 1.199e-01, 8.703e+00, 8.703e+00, 1.553e+01, 1.678e+01, 1.678e+01, 9.586e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Compute parametric derivative using exact map (tune & beta)
d = derivative((1, ), lambda k: fn(k, fodo=lambda x: fodo(x, k)), k)
print(d)
[tensor([2.528e-01, 1.199e-01, 8.703e+00, 8.703e+00, 1.553e+01, 1.678e+01, 1.678e+01, 9.586e+00], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[ 1.217e+00, 3.230e-01, 4.195e+00],
[-7.757e-01, -2.438e+00, -8.198e+00],
[-3.111e+01, -1.531e+01, -1.101e+02],
[-3.111e+01, -1.531e+01, -1.101e+02],
[-1.749e+00, -3.120e+01, -1.799e+02],
[ 1.153e+02, 3.308e+02, 1.106e+03],
[ 1.153e+02, 3.308e+02, 1.106e+03],
[ 5.215e+01, 2.146e+02, 6.957e+02]], dtype=torch.float64)]
[11]:
# Compute parametric derivative using jet map (tune & beta)
d = derivative((1, ), lambda k: fn(k, fodo=lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k])), k)
print(d)
[tensor([2.528e-01, 1.199e-01, 8.703e+00, 8.703e+00, 1.553e+01, 1.678e+01, 1.678e+01, 9.586e+00], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[ 1.217e+00, 3.230e-01, 4.195e+00],
[-7.757e-01, -2.438e+00, -8.198e+00],
[-3.111e+01, -1.531e+01, -1.101e+02],
[-3.111e+01, -1.531e+01, -1.101e+02],
[-1.749e+00, -3.120e+01, -1.799e+02],
[ 1.153e+02, 3.308e+02, 1.106e+03],
[ 1.153e+02, 3.308e+02, 1.106e+03],
[ 5.215e+01, 2.146e+02, 6.957e+02]], dtype=torch.float64)]
[12]:
# Check covergence
dk = torch.tensor([1.0E-3, 1.0E-3, 1.0E-4], dtype=dtype, device=device)
values = fn(k, fodo=lambda x: fodo(x, k))
print(' '.join([f'{value:.3f}' for value in values.cpu().tolist()]))
values = evaluate(d, [dk])
print(' '.join([f'{value:.3f}' for value in values.cpu().tolist()]))
values = fn(k + dk, fodo=lambda x: fodo(x, k + dk))
print(' '.join([f'{value:.3f}' for value in values.cpu().tolist()]))
0.253 0.120 8.703 8.703 15.532 16.780 16.780 9.586
0.255 0.116 8.645 8.645 15.481 17.337 17.337 9.922
0.255 0.116 8.646 8.646 15.482 17.366 17.366 9.940
[13]:
# Responce matrix
m = derivative((1, ), lambda k: fn(k, fodo=lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k])), k, intermediate=False)
print(m)
tensor([[ 1.217e+00, 3.230e-01, 4.195e+00],
[-7.757e-01, -2.438e+00, -8.198e+00],
[-3.111e+01, -1.531e+01, -1.101e+02],
[-3.111e+01, -1.531e+01, -1.101e+02],
[-1.749e+00, -3.120e+01, -1.799e+02],
[ 1.153e+02, 3.308e+02, 1.106e+03],
[ 1.153e+02, 3.308e+02, 1.106e+03],
[ 5.215e+01, 2.146e+02, 6.957e+02]], dtype=torch.float64)
[14]:
# Correction
# The target values (tunes and beta functions) are associated with model response matrix
# Given measured values, the goal is to alter knobs to get target values
# Set target values
vf = fn(k, fodo=lambda x: fodo(x, k))
# Set initial solution
sol = torch.zeros_like(dk)
# Iterate
for _ in range(4):
# Compute current values and set difference
vi = fn(k + dk + sol, fodo=lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k + dk + sol]))
# Set difference
dv = vf - vi
# Update solution
sol += torch.linalg.pinv(m) @ dv
# Verbose
print(-dk)
print(sol)
print(dv.norm())
print()
# Continue
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.064e-03, -1.258e-03, -4.094e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(9.036e-01, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -9.990e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(4.251e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(8.589e-05, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.559e-10, dtype=torch.float64)
[15]:
# Note, similar to tune spread example, it is possible to compute twiss spread
# First order computation can be performed using error propagation
# Or higher order jets can be sampled
Example-19: Parametric phase advance
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
from twiss.wolski import propagate as propagate_twiss
from twiss.wolski import advance
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, k):
kqf, kqd, kqb = k
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kqf, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def map_02_03(x, k):
kqf, kqd, kqb = k
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kqd, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kqd, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.1)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def map_03_04(x, k):
kqf, kqd, kqb = k
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015 + kqb, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.1)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kqf, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02,
map_02_03,
map_03_04
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, k):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[5]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, k, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [k], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[6]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[7]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 3), (0, 1), pfp, [k], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric identity (surrogate model for linear dynamics)
jet = identity((1, 1), fp, parametric=pfp)
jet = propagate((4, 3), (1, 1), jet, [k], fodo)
[9]:
# Compute phase advance
# Note, exact or jet one-turn transport can be used
# Other maps can be replaced with jets too
def fn(k, fodo):
mus = []
m = derivative(1, fodo, fp, intermediate=False)
t, n, _ = twiss(m)
for mapping in transport:
mu, n = advance(n, derivative(1, mapping, x, k, intermediate=False))
mus.append(mu)
mus = torch.stack(mus).T
return torch.stack([*t, *mus.flatten()])
print(fn(k, fodo=lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k])))
tensor([2.528e-01, 1.199e-01, 2.521e-01, 1.084e+00, 2.521e-01, 2.468e-01, 2.599e-01, 2.468e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Compute parametric derivative using exact map (tune & advance)
d = derivative((1, ), lambda k: fn(k, fodo=lambda x: fodo(x, k)), k)
print(d)
[tensor([2.528e-01, 1.199e-01, 2.521e-01, 1.084e+00, 2.521e-01, 2.468e-01, 2.599e-01, 2.468e-01], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[1.217e+00, 3.230e-01, 4.195e+00],
[-7.757e-01, -2.438e+00, -8.198e+00],
[4.458e-01, 4.852e-01, 2.926e+00],
[6.755e+00, 1.059e+00, 2.051e+01],
[4.458e-01, 4.852e-01, 2.926e+00],
[-1.523e+00, -5.303e+00, -1.726e+01],
[-1.827e+00, -4.712e+00, -1.699e+01],
[-1.523e+00, -5.303e+00, -1.726e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)]
[11]:
# Compute parametric derivative using jet map (tune & advance)
d = derivative((1, ), lambda k: fn(k, fodo=lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k])), k)
print(d)
[tensor([2.528e-01, 1.199e-01, 2.521e-01, 1.084e+00, 2.521e-01, 2.468e-01, 2.599e-01, 2.468e-01], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[1.217e+00, 3.230e-01, 4.195e+00],
[-7.757e-01, -2.438e+00, -8.198e+00],
[4.458e-01, 4.852e-01, 2.926e+00],
[6.755e+00, 1.059e+00, 2.051e+01],
[4.458e-01, 4.852e-01, 2.926e+00],
[-1.523e+00, -5.303e+00, -1.726e+01],
[-1.827e+00, -4.712e+00, -1.699e+01],
[-1.523e+00, -5.303e+00, -1.726e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)]
[12]:
# Check covergence
dk = torch.tensor([1.0E-3, 1.0E-3, 1.0E-4], dtype=dtype, device=device)
values = fn(k, fodo=lambda x: fodo(x, k))
print(' '.join([f'{value:.3f}' for value in values.cpu().tolist()]))
values = evaluate(d, [dk])
print(' '.join([f'{value:.3f}' for value in values.cpu().tolist()]))
values = fn(k + dk, fodo=lambda x: fodo(x, k + dk))
print(' '.join([f'{value:.3f}' for value in values.cpu().tolist()]))
0.253 0.120 0.252 1.084 0.252 0.247 0.260 0.247
0.255 0.116 0.253 1.094 0.253 0.238 0.252 0.238
0.255 0.116 0.253 1.094 0.253 0.238 0.251 0.238
[13]:
# Responce matrix
m = derivative((1, ), lambda k: fn(k, fodo=lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k])), k, intermediate=False)
print(m)
tensor([[1.217e+00, 3.230e-01, 4.195e+00],
[-7.757e-01, -2.438e+00, -8.198e+00],
[4.458e-01, 4.852e-01, 2.926e+00],
[6.755e+00, 1.059e+00, 2.051e+01],
[4.458e-01, 4.852e-01, 2.926e+00],
[-1.523e+00, -5.303e+00, -1.726e+01],
[-1.827e+00, -4.712e+00, -1.699e+01],
[-1.523e+00, -5.303e+00, -1.726e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[14]:
# Correction
# The target values (tunes and advance functions) are associated with model response matrix
# Given measured values, the goal is to alter knobs to get target values
# Set target values
vf = fn(k, fodo=lambda x: fodo(x, k))
# Set initial solution
sol = torch.zeros_like(dk)
# Iterate
for _ in range(4):
# Compute current values and set difference
vi = fn(k + dk + sol, fodo=lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k + dk + sol]))
# Set difference
dv = vf - vi
# Update solution
sol += torch.linalg.pinv(m) @ dv
# Verbose
print(-dk)
print(sol)
print(dv.norm())
print()
# Continue
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.043e-03, -1.068e-03, -8.224e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.846e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(2.001e-04, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(2.786e-08, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.000e-03, -1.000e-03, -1.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(2.344e-15, dtype=torch.float64)
[15]:
# Note, similar to tune spread example, it is possible to compute advance spread
# First order computation can be performed using error propagation
# Or higher order jets can be sampled
Example-20: Poisson bracket
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.bracket import bracket
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Poisson bracket between observable/mapping or mapping/observable or mapping/mapping
# [f, g] -> [f, g]
# [[f1, f2], g] -> [[f1, g], [f2, g]]
# [f, [g1, g2]] -> [[f, g1], [f, g2]]
# [[f1, f2], [g1, g2]] -> [[f1, g1], [f2, g2]]
def f(x): q, p = x ; return q
def g(x): q, p = x ; return p
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(bracket(f, g)(x))
def f(x): q, p = x ; return torch.stack([q, p])
def g(x): q, p = x ; return p
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(bracket(f, g)(x))
def f(x): q, p = x ; return q
def g(x): q, p = x ; return torch.stack([q, p])
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(bracket(f, g)(x))
def f(x): q, p = x ; return torch.stack([q, p])
def g(x): q, p = x ; return torch.stack([q, p])
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(bracket(f, g)(x))
tensor(1.000e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.000e+00, 0.000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([0.000e+00, 1.000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[4]:
# Returns a function that can be differentiated
def f(x): q, p = x ; return q**2
def g(x): q, p = x ; return p
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(derivative(1, bracket(f, g), x, intermediate=False))
tensor([2.000e+00, 0.000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[5]:
# Accepts Table input
# Note, evaluation is at deviation point
tf = propagate((2, ), (2, ), identity((2, ), [x]), [], f)
tg = propagate((2, ), (2, ), identity((2, ), [x]), [], g)
print(derivative(1, bracket(tf, tg), x, intermediate=False))
tensor([2.000e+00, 0.000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Accepts Series input
# Note, evaluation is at deviation point
sf = propagate((2, ), (2, ), identity((2, ), [x], flag=True), [], f)
sg = propagate((2, ), (2, ), identity((2, ), [x], flag=True), [], g)
print(derivative(1, bracket(tf, tg), x, intermediate=False))
tensor([2.000e+00, 0.000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Propagate identity
t = propagate((2, ), (1, ), identity((1, ), [x]), [], bracket(f, g))
print(t)
[tensor(0., dtype=torch.float64), tensor([2.000e+00, 0.000e+00], dtype=torch.float64)]
Example-21: Taylor integrator
[1]:
# Given an autonomous hamiltonian function H
# The exact solution is x(t) = exp([-t H]) x with Poisson bracket operator [f] g := [f, g]
# Truncated solution is x(t) = exp([-t H]) x = x + t [-H] x + 1/2! t**2 [-H]**2 x + ...
# Such series solution doesn't preserve symplectic structure in general
# Taylor integration is differentiable with respect to time step, initial value and parameters
# Note, generation or derivatives can be extremely slow
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.taylor import taylor
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float32
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Integrate for a given time step and ititial condition
# Note, hamiltonian is not preserved for all cases, but the hamiltonian drift time scale is different
# Set nonlinear oscillator hamiltonian function
def h(x):
q, p = x
return p**2/2 + q**2/2 + q**3/3
# Set time step
dt = torch.tensor(0.15, dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Set initial condition
xi = torch.tensor([0.4, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Integrate and plot orbits for several values of truncation order
count = 1024
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.xlim(-1.0, 1.0)
plt.ylim(-1.0, 1.0)
for order, color in zip([1, 2, 4], ['black', 'red', 'blue']):
orbit = []
x = torch.clone(xi)
for _ in range(count):
x = taylor(order, dt, h, x)
orbit.append(x)
orbit = torch.stack(orbit)
plt.scatter(*orbit.T.cpu().numpy(), color=color, s=1)
plt.show()
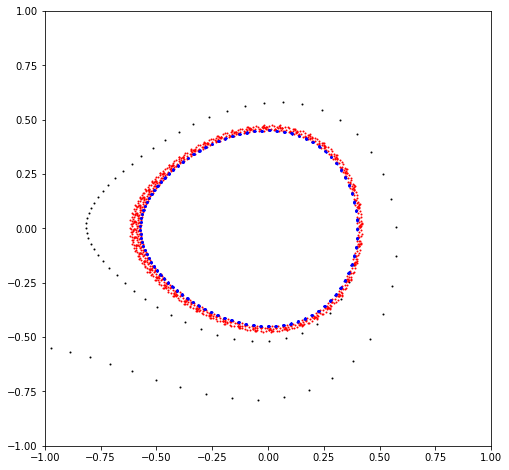
[5]:
# Generate derivative table representation at zero
# Note, here a smaller time step is used
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
t = derivative(4, lambda x: taylor(6, 0.05, h, x), x)
# Compute series representation
s = series((2, ), (4, ), t)
# Print series
for key, value in s.items():
print(f'{key}: {value.cpu()}')
(0, 0): tensor([0., 0.])
(1, 0): tensor([9.987502e-01, -4.997917e-02])
(0, 1): tensor([4.997917e-02, 9.987502e-01])
(2, 0): tensor([-1.249219e-03, -4.993753e-02])
(1, 1): tensor([-4.164063e-05, -2.497397e-03])
(0, 2): tensor([-5.206163e-07, -4.164063e-05])
(3, 0): tensor([5.203993e-07, 4.161458e-05])
(2, 1): tensor([2.604167e-08, 2.601563e-06])
(1, 2): tensor([4.340278e-10, 5.208334e-08])
(0, 3): tensor([0.000000e+00, 4.340278e-10])
(4, 0): tensor([-2.170139e-10, -2.604167e-08])
(3, 1): tensor([ 0.000000e+00, -1.736111e-09])
(2, 2): tensor([0., 0.])
(1, 3): tensor([0., 0.])
(0, 4): tensor([0., 0.])
[6]:
# Integrate using derivative table and a batch of initials
q = torch.linspace(0.1, 0.6, 21)
p = torch.zeros_like(q)
x = torch.stack([q, p]).T
orbits = []
for _ in range(count):
x = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: evaluate(t, [x]))(x)
orbits.append(x)
orbits = torch.stack(orbits).swapaxes(0, 1)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.xlim(-1.5, 1)
plt.ylim(-1, 1)
for orbit in orbits:
plt.scatter(*orbit.T.cpu().numpy(), color='black', s=1)
plt.show()
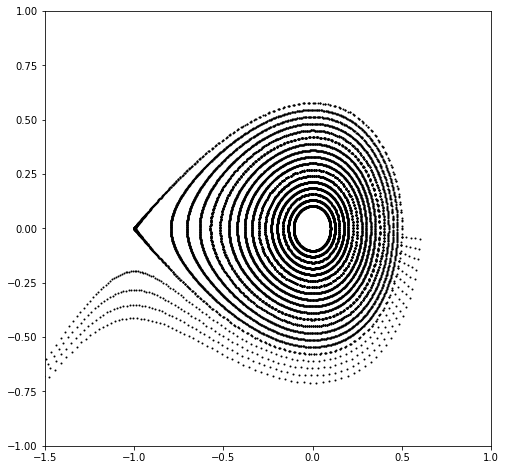
[7]:
# Derivatives with respect to time step and other parameters
def h(x, kq, ks):
q, p = x
return p**2/2 + kq**2/2 + ks*q**3/3
dt = torch.tensor(0.01, dtype=dtype, device=device)
xi = torch.tensor([0.4, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
kq = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=dtype, device=device)
ks = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=dtype, device=device)
t = derivative((2, 1, 1, 1), lambda xi, dt, kq, ks: taylor(4, dt, h, xi, kq, ks), xi, dt, kq, ks)
[8]:
# Check table
dxi = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
ddt = torch.tensor(0.005, dtype=dtype, device=device)
dkq = torch.tensor(0.01, dtype=dtype, device=device)
dks = torch.tensor(0.01, dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(taylor(4, dt + ddt, h, xi + dxi, kq + dkq, ks + dks))
print(evaluate(t, [dxi, ddt, dkq, dks]))
tensor([4.999716e-01, -3.787356e-03])
tensor([4.999748e-01, -3.787395e-03])
Example-22: Yoshida integrator
[1]:
# Given a time-reversible integration step of difference order 2n
# Yoshida coefficients can be used to construct integration step of difference order 2(n+1)
# s(2(n+1))(dt) = s(2n)(x1 dt) o s(2n)(x2 dt) o s(2n)(x1 dt)
# If a hamiltonian vector field can be splitted into several sovable parts
# Second order time-reversible symmetric integrator can be easily constructed
# s1(dt/2) o s2(dt/2) o ... o sn(dt/2) o sn(dt/2) o ... o s2(dt/2) o s1(dt/2)
# Yoshida procedure can be then applied repeatedly to obtain higher order integration steps
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.util import nest
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.yoshida import coefficients
from ndmap.yoshida import yoshida
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Given integration step on Yoshida order n
# Yoshida coefficent for the next order can be computed
# Note, sum of coefficients is equal to one
print(coefficients(1)) # 2 -> 4
print(coefficients(2)) # 4 -> 6
print(coefficients(3)) # 6 -> 8
print(coefficients(4)) # 8 -> 10
[1.3512071919596578, -1.7024143839193153, 1.3512071919596578]
[1.1746717580893635, -1.349343516178727, 1.1746717580893635]
[1.1161829393253857, -1.2323658786507714, 1.1161829393253857]
[1.0870271062991708, -1.1740542125983413, 1.0870271062991708]
[4]:
# Given integration step on Yoshida order n
# Yoshida coefficent for m order can be computed
# Note, sum of coefficients is equal to one
print([f'{coefficient:.3f}' for coefficient in coefficients(1, 1)]) # 2 -> 4
print([f'{coefficient:.3f}' for coefficient in coefficients(1, 2)]) # 2 -> 6
print([f'{coefficient:.3f}' for coefficient in coefficients(2, 2)]) # 4 -> 6
['1.351', '-1.702', '1.351']
['1.587', '-2.000', '1.587', '-1.823', '2.297', '-1.823', '1.587', '-2.000', '1.587']
['1.175', '-1.349', '1.175']
[5]:
# Given a set of mappings and (start, final) Yoshida orders
# Corresponding Yoshida coefficients can be computed
# Note, mapping can be an integation step
# Mapping is a step (last argument should be False)
ns, cs = coefficients(1, 1, 1, False) ; print([ns, [f'{c:.3f}' for c in cs]]) # 2 -> 4
ns, cs = coefficients(1, 1, 2, False) ; print([ns, [f'{c:.3f}' for c in cs]]) # 2 -> 6
ns, cs = coefficients(1, 2, 2, False) ; print([ns, [f'{c:.3f}' for c in cs]]) # 4 -> 6
print()
# Two mappings (merge edge mappings)
# Note, number of mappings can be arbitrary
ns, cs = coefficients(2, 0, 0, True) ; print([ns, [f'{c:.3f}' for c in cs]]) # 2 -> 2
ns, cs = coefficients(2, 0, 1, True) ; print([ns, [f'{c:.3f}' for c in cs]]) # 2 -> 4
print()
[[0, 0, 0], ['1.351', '-1.702', '1.351']]
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], ['1.587', '-2.000', '1.587', '-1.823', '2.297', '-1.823', '1.587', '-2.000', '1.587']]
[[0, 0, 0], ['1.175', '-1.349', '1.175']]
[[0, 1, 0], ['0.500', '1.000', '0.500']]
[[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0], ['0.676', '1.351', '-0.176', '-1.702', '-0.176', '1.351', '0.676']]
[6]:
# Integrate rotation
# h = h1 + h2
# h1 = 1/2 q**2 -> [q, p] -> [q, p - t*q]
# h2 = 1/2 p**2 -> [q, p] -> [q + t*q, p]
# Set mappings
def fn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - t*q])
def gn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
# Set time step
t = torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=torch.float64)
# Set initial condition
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
# Without merging
for i in range(10):
print(yoshida(0, i, False, [fn, gn])(x, t), len(first(yoshida(0, i, False, [fn, gn]).table)))
print()
# With merging
for i in range(10):
print(yoshida(0, i, True, [fn, gn])(x, t), len(first(yoshida(0, i, True, [fn, gn]).table)))
print()
tensor([1.375000e-01, 4.062500e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 3
tensor([1.354787e-01, 3.997254e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 9
tensor([1.357446e-01, 3.982467e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 27
tensor([1.357004e-01, 3.981894e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 81
tensor([1.356984e-01, 3.981700e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 243
tensor([1.357016e-01, 3.981564e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 729
tensor([1.357009e-01, 3.981567e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 2187
tensor([1.357007e-01, 3.981572e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 6561
tensor([1.357009e-01, 3.981567e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 19683
tensor([1.357007e-01, 3.981573e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 59049
tensor([1.375000e-01, 4.062500e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 3
tensor([1.354787e-01, 3.997254e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 7
tensor([1.357446e-01, 3.982467e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 19
tensor([1.357004e-01, 3.981894e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 55
tensor([1.356984e-01, 3.981700e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 163
tensor([1.357016e-01, 3.981564e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 487
tensor([1.357009e-01, 3.981567e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 1459
tensor([1.357007e-01, 3.981572e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 4375
tensor([1.357009e-01, 3.981567e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 13123
tensor([1.357007e-01, 3.981573e-02], dtype=torch.float64) 39367
[7]:
# Several steps
count = 100
t = torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
for _ in range(count):
x = yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn])(x, t/count)
print(x)
count = 100
t = torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
x = nest(count, yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn]))(x, t/count)
print(x)
tensor([1.357008e-01, 3.981570e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.357008e-01, 3.981570e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
[8]:
# Multistep
# h = h1 + h2
# h1 = 1/2 q**2 + 1/3 q**3 -> [q, p] -> [q, p - t*q - t*q**2]
# h2 = 1/2 p**2 -> [q, p] -> [q + t*q, p]
def fn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - t*q - t*q**2])
def gn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
t = torch.tensor(0.1, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
print(yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn])(x, t))
print()
# h = h1 + h2 + h3
# h1 = 1/2 q**2 -> [q, p] -> [q, p - t*q]
# h2 = 1/3 q**3 -> [q, p] -> [q, p - t*q**2]
# h3 = 1/2 p**2 -> [q, p] -> [q + t*q, p]
def fn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - t*q])
def gn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - t*q**2])
def hn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
t = torch.tensor(0.1, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
print(yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn, hn])(x, t))
print()
# Note, the last mapping has the smallest number of evaluations
sequence, _ = yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn, hn]).table
print([*map(sequence.count, sorted(set(sequence)))])
print()
tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
[4, 6, 3]
[9]:
# Increase order
def fn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - t*q - t*q**2])
def gn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
t = torch.tensor(0.1, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
s2 = yoshida(0, 0, True, [fn, gn])
print(torch.allclose(s2(x, t), yoshida(0, 0, True, [fn, gn])(x, t)))
s4 = yoshida(1, 1, False, [s2])
print(torch.allclose(s4(x, t), yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn])(x, t)))
s6 = yoshida(1, 2, False, [s2])
print(torch.allclose(s6(x, t), yoshida(0, 2, True, [fn, gn])(x, t)))
s6 = yoshida(2, 2, False, [s4])
print(torch.allclose(s6(x, t), yoshida(0, 2, True, [fn, gn])(x, t)))
True
True
True
True
[10]:
# Step with parameters (matched signatures)
def fn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - a*t*q - b*t*q**2])
def gn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
t = torch.tensor(0.1, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
a = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float64)
b = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float64)
print(yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn])(x, t, a, b))
tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Step with parameters (pass fixed parameters)
def fn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - a*t*q - b*t*q**2])
def gn(x, t):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
t = torch.tensor(0.1, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
a = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float64)
b = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float64)
print(yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn], parameters=[[a, b], []])(x, t))
tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Step can be differentiated with respect to initials, time step and/or parametes
def fn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - a*t*q - b*t*q**2])
def gn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
t = torch.tensor(0.1, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
a = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float64)
b = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float64)
# Derivative with respect to initial
print(derivative(1, yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn]), x, t, a, b))
print()
# Derivative with respect to time step
print(derivative(1, lambda t, x, a, b: yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn])(x, t, a, b), t, x, a, b))
print(derivative((0, 1), yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn]), x, t, a, b))
print()
[tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[9.939735e-01, 9.979712e-02],
[-1.207179e-01, 9.939427e-01]], dtype=torch.float64)]
[tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([8.841321e-02, -1.214017e-01], dtype=torch.float64)]
[[tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([8.841321e-02, -1.214017e-01], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[13]:
# For derivative table propagation all knobs should be vectors
def fn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - a*t*q - b*t*q**2])
def gn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
t = torch.tensor([0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
a = torch.tensor([1.0], dtype=torch.float64)
b = torch.tensor([1.0], dtype=torch.float64)
step = yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn])
def wrapper(x, t, a, b):
(t, ), (a, ), (b, ) = t, a, b
return step(x, t, a, b)
print(step(x, *t, *a, *b))
print(wrapper(x, t, a, b))
print()
out = propagate((2, 1, 1, 1),
4*(1, ),
identity(4*(1, ), [x, t, a, b]),
[t, a, b],
wrapper)
dt = torch.tensor([+0.001], dtype=torch.float64)
dx = torch.tensor([+0.005, -0.005], dtype=torch.float64)
da = torch.tensor([-0.001], dtype=torch.float64)
db = torch.tensor([+0.001], dtype=torch.float64)
print(wrapper(x + dx, t + dt, a + da, b + db))
print(evaluate(out, [dx, dt, da, db]))
tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.094304e-01, 8.841961e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.139844e-01, 8.272697e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.139846e-01, 8.272929e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
[14]:
# Given a step, its derivatives can be used as a taylor model
# Note, taylor model is not symplectic in general
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
def fn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q, p - a*t*q - b*t*q**2])
def gn(x, t, a, b):
q, p = x
return torch.stack([q + t*p, p])
t = torch.tensor(0.1, dtype=torch.float64)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
a = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float64)
b = torch.tensor(1.0, dtype=torch.float64)
dx = torch.tensor([+0.1, -0.1], dtype=torch.float64)
print(yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn])(x, t, a, b))
print(yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn])(x + dx, t, a, b))
print()
print(evaluate(derivative(1, yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn]), x, t, a, b), [dx]))
print(evaluate(derivative(2, yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn]), x, t, a, b), [dx]))
print(evaluate(derivative(3, yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn]), x, t, a, b), [dx]))
print(evaluate(derivative(4, yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn]), x, t, a, b), [dx]))
print(evaluate(derivative(5, yoshida(0, 1, True, [fn, gn]), x, t, a, b), [dx]))
print()
tensor([1.094303556041e-01, 8.841960703680e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.988014274981e-01, -2.394392236666e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.988479888736e-01, -2.304645602610e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.988014166220e-01, -2.394421962623e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.988014274804e-01, -2.394392240255e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.988014274981e-01, -2.394392236643e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.988014274981e-01, -2.394392236666e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-23: Direct invariant
[1]:
# In this example Taylor invariants are constructed by solving I(f(x)) = I(x) order-by-order
# Mapping f(x) can be replaced with its derivative table representation of a given order n
# Or mapping can be used directly
# Invariant of order n+1 can be computed
# Note, to avoid trivial solution, initial invariant guess should be provided, e.g. linear part invariant
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.invariant import invariant
from twiss.wolski import twiss
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
[3]:
# Data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=20):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x):
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
[6]:
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x)
return x
[7]:
# Set evaluation point
# Note, zero is a fixed point and derivatives with respect to parameters are not used, i.e. no need to compute paraetric fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fodo(x)
[7]:
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[8]:
# Generate derivative table representation for given order
t = identity(4, x, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd)
t = propagate((4, ), (4, ), t, [], fodo, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd)
[9]:
# Compute linear normalization matrix
_, n, _ = twiss(derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(t, [x]), x, intermediate=False))
[10]:
# Set initial invariants
def ix(x):
qx, px, qy, py = torch.linalg.inv(n) @ x
return 1/2*(qx**2 + px**2)
def iy(x):
qx, px, qy, py = torch.linalg.inv(n) @ x
return 1/2*(qy**2 + py**2)
[11]:
# Check conservation of linear invariants
print(derivative(2, ix, x, intermediate=False))
print(propagate((4, ), (2, ), t, [], ix, intermediate=False))
print()
print(derivative(2, iy, x, intermediate=False))
print(propagate((4, ), (2, ), t, [], iy, intermediate=False))
print()
tensor([[ 6.775970e-02, -1.148888e-15, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[-1.148888e-15, 1.475804e+01, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[ 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[ 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([[ 6.775970e-02, -1.151856e-15, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[-1.151856e-15, 1.475804e+01, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[ 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[ 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 8.242765e-02, 1.472561e-15],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 1.472561e-15, 1.213185e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 8.242765e-02, 1.554312e-15],
[0.000000e+00, 0.000000e+00, 1.554312e-15, 1.213185e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Compute nonlinear invariants
# Note, computation is not optimized and requires a lot of memory
tx, _ = invariant((4, ), x, [], ix, t, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd, threshold=1.0E-3)
ty, _ = invariant((4, ), x, [], iy, t, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd, threshold=1.0E-3)
[13]:
# Generate and plot trajectory
x = torch.tensor([0.005, 0.0, 0.005, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
bag = []
for _ in range(2048):
x = fodo(x)
bag.append(x)
bag = torch.stack(bag)
qx, px, qy, py = bag.T
plt.figure(figsize=(2*8, 8))
ax = plt.subplot(121)
ax.scatter(qx.cpu().numpy(), px.cpu().numpy(), marker='x', s=1, color='red')
ax = plt.subplot(122)
ax.scatter(qy.cpu().numpy(), py.cpu().numpy(), marker='x', s=1, color='red')
plt.show()
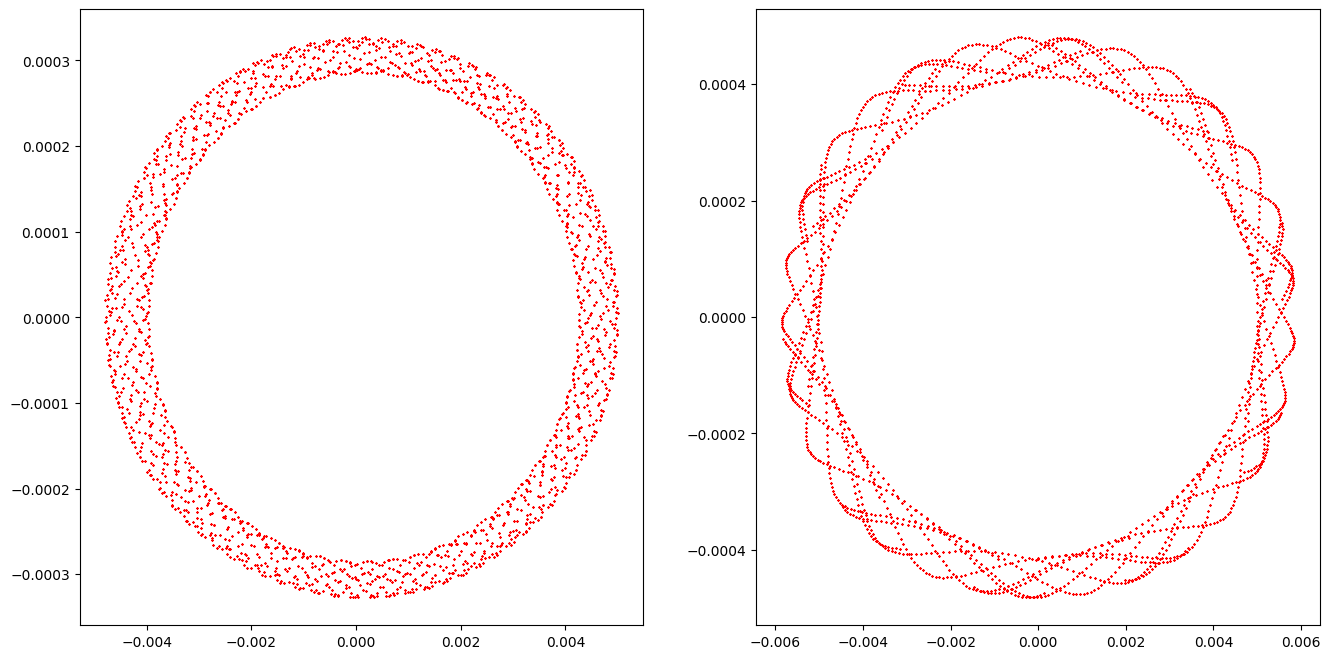
[14]:
# 1st invariant conservation
# Note, for different initial conditions higher order invariants can give worse results
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
for order, color in zip([2, 3, 4], ['black', 'red', 'blue']):
sx = series((4, ), (order, ), tx)
vx = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: evaluate(sx, [x]))(bag)
print(vx.mean())
print(vx.std())
print()
plt.scatter(range(len(vx)), vx.cpu().numpy(), color=color, marker='x')
plt.show()
tensor(6.939136e-07, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(8.133688e-08, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(7.033768e-07, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(2.919483e-09, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(7.008737e-07, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.419347e-09, dtype=torch.float64)
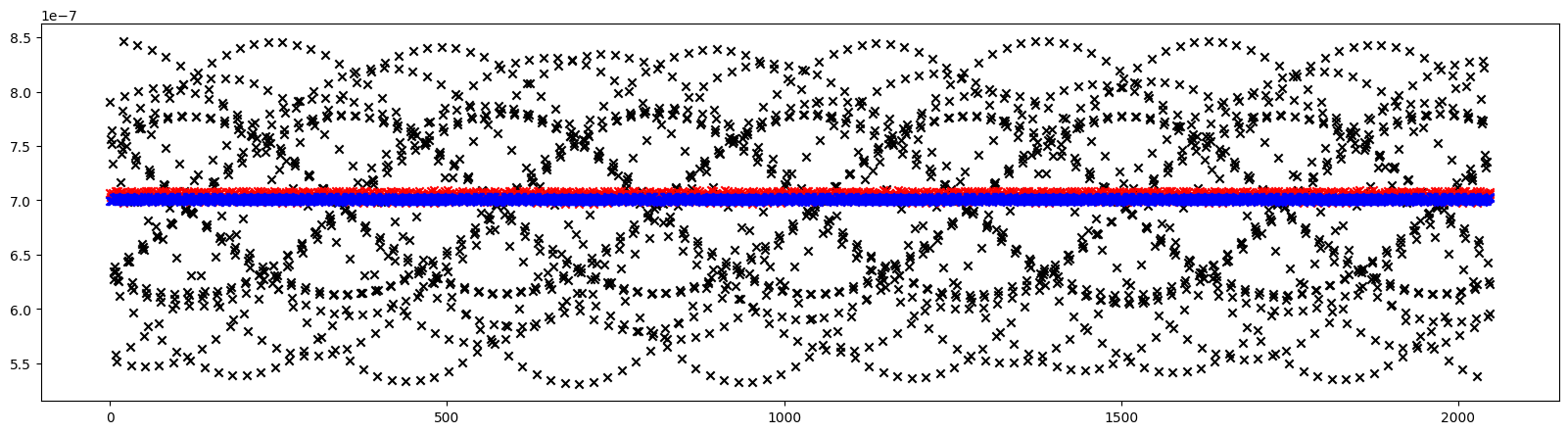
[15]:
# 2nd invariant conservation
# Note, for different initial conditions higher order invariants can give worse results
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
for order, color in zip([2, 3, 4], ['black', 'red', 'blue']):
sy = series((4, ), (order, ), ty)
vy = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: evaluate(sy, [x]))(bag)
print(vy.mean())
print(vy.std())
print()
plt.scatter(range(len(vy)), vy.cpu().numpy(), color=color, marker='x')
plt.show()
tensor(1.222613e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.538842e-07, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.200414e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(7.017794e-09, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.206937e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.553736e-09, dtype=torch.float64)
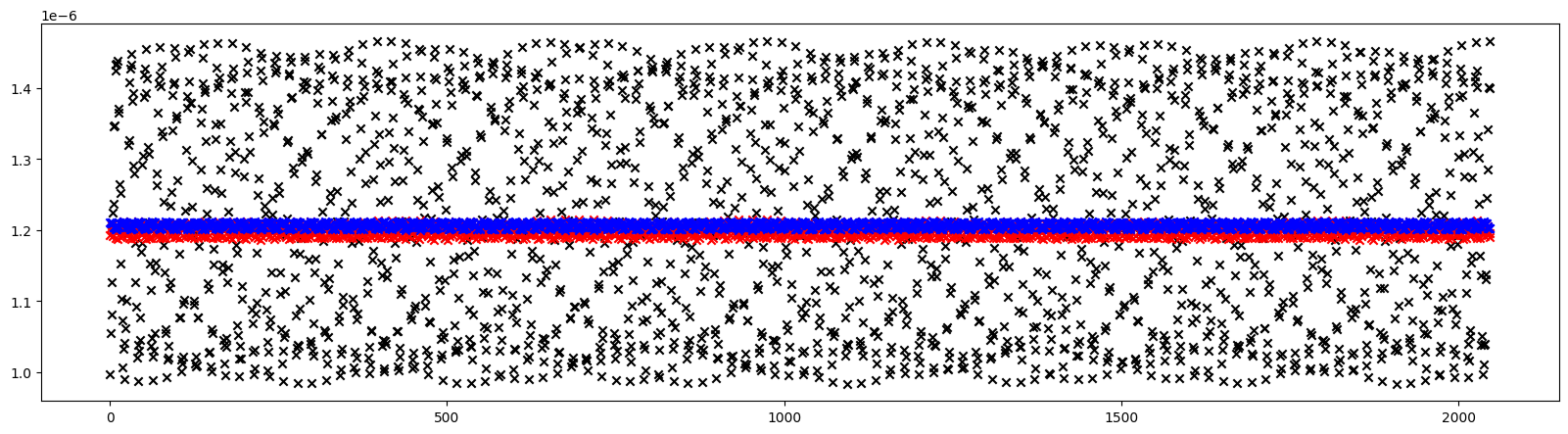
Example-24: Direct invariant (parametric)
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.series import split
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from ndmap.invariant import invariant
from twiss.wolski import twiss
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
[2]:
# Data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=20):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, w, k):
ksf, ksd, ksb = k
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, +0.5 + ksf)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.25 + ksb, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, -0.5 + ksd)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, -0.5 + ksd)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.25 + ksb, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, +0.5 + ksf)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
[5]:
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, k, w):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k, w)
return x
[6]:
# Find fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor(1*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(3*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(32, fodo, x, w, k, power=1)
print(fp)
print(fodo(fp, w, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Set computation orders
(nx, nw, nk) = (3, 1, 1)
[8]:
# Find parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((nw, nk), fp, [w, k], fodo)
[9]:
# Test parametric fixed point
# Note, if fp is not zero, redefine one-turn transport to map zero to zero
print(compare(pfp, propagate((4, 1, 3), (0, nw, nk), pfp, [w, k], fodo)))
True
[10]:
# Define a fodo variant around parametric fixed point
def mapping(x, w, k):
x = x + evaluate(first(pfp), [w, k])
x = fodo(x, w, k)
x = x - evaluate(first(pfp), [w, k])
return x
print(mapping(x, w, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Compute derivative table representation
# Note, no parametric part should be passed, parametric zero is transformed to parametric zero
t = identity((nx, nw, nk), x)
t = propagate((4, 1, 3), (nx - 1, nw, nk), t, [w, k], mapping)
chop(t)
print(first(t))
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)], [tensor([[0.],
[0.],
[0.],
[0.]], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.]]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[12]:
# Compute parametric normalization matrix
def fn(w, k):
m = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(t, [x, w, k]), fp, intermediate=False)
_, n, _ = twiss(m)
return n
tn = derivative((nw, nk), fn, w, k)
[13]:
# Set initial invariants
def ix(x, w, k):
qx, px, qy, py = torch.inverse(evaluate(tn, [w, k])) @ x
return 1/2*(qx**2 + px**2)
def iy(x, w, k):
qx, px, qy, py = torch.inverse(evaluate(tn, [w, k])) @ x
return 1/2*(qy**2 + py**2)
[14]:
# 1st invariant
tx, _ = invariant((nx, nw, nk), x, [w, k], ix, t, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev, threshold=0.01)
_
[14]:
[]
[15]:
# 2nd invariant
ty, _ = invariant((nx, nw, nk), x, [w, k], iy, t, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev, threshold=0.01)
_
[15]:
[]
[16]:
# Test conservation
# Note, here propagate is used as composition
print(compare(propagate((4, 1, 3), (nx-1, nw, nk), t, [w, k], tx), tx))
print(compare(propagate((4, 1, 3), (nx-1, nw, nk), t, [w, k], ty), ty))
True
True
[17]:
# Series representation
# Note, generalized monomial is qx px qy py w ksf ksd ksb
s, *_ = split(clean(series((4, 1, 3), (nx, nw, nk), tx)))
s
[17]:
{(2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0): tensor(3.387985e-02, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0): tensor(7.379018e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-6.047879e-03, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0): tensor(-6.517039e-03, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0): tensor(1.317226e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0): tensor(1.419409e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0): tensor(1.994743e-01, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0): tensor(-4.344542e+01, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-6.188913e-02, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0): tensor(-8.813844e-02, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1): tensor(6.534032e-01, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-2.031422e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0): tensor(2.482422e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1): tensor(-1.423110e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0): tensor(5.742237e-02, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0): tensor(7.908874e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0): tensor(-1.249413e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0): tensor(8.887557e+01, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0): tensor(-2.613173e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-2.180292e-02, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0): tensor(-3.543561e-02, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1): tensor(2.292041e-01, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0): tensor(7.152281e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0): tensor(1.584743e+01, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1): tensor(1.861577e+01, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-7.509155e-01, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0): tensor(-1.639441e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1): tensor(-5.148461e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0): tensor(6.392325e+01, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0): tensor(1.341707e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1): tensor(3.638539e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-2.452915e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0): tensor(-4.911196e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1): tensor(-1.064586e+03, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0): tensor(-5.835809e-01, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0): tensor(6.243185e+01, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0): tensor(1.617990e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0): tensor(-1.601207e+04, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0): tensor(4.860999e+04, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-8.770463e-02, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0): tensor(-4.631656e-01, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1): tensor(-4.557887e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0): tensor(9.372351e+01, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0): tensor(1.993612e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1): tensor(5.704250e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 2, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0): tensor(2.404182e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0): tensor(5.584620e+02, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1): tensor(1.295549e+03, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-2.229816e+04, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 0): tensor(-5.022342e+04, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1): tensor( -1.279140e+05, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0): tensor(7.791695e+04, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0): tensor( 1.680246e+05, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1): tensor( 3.876573e+05, dtype=torch.float64)}
Example-25: Composition
[1]:
# In this example the following homomorphism is illustrated
# t(f o g) = t(f) o t(g)
# Meaning, table of composition is equal to composition of tables
# Mappings f and g that map zero to zero, i.e. are without constant part
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=20):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x):
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
return x
def map_02_03(x):
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
return x
[6]:
# Set computation order & evaluation point
n = 4
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[7]:
# Note, both mapping map zero to zero
# Also, parameters that effect closed orbit are not used
print(map_01_02(x))
print(map_02_03(x))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[8]:
# Direct table generation
T = derivative(n, lambda x: map_02_03(map_01_02(x)), x)
[9]:
# Propagation of identity (equvalent to direct table generation)
t = identity((n, ), [x])
t = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t, [], lambda x: map_02_03(map_01_02(x)))
print(compare(T, t))
True
[10]:
# Propagation (split)
# Table is propagated through mappings
# Note, this evaluation is inherently sequential
t = identity((n, ), [x])
t = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t, [], map_01_02)
t = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t, [], map_02_03)
print(compare(T, t))
True
[11]:
# Composition
# Note, given an evaluation point (e.g. closed orbit at each element)
# Identity can be propagated (or just perform direct computation) for each element
# This can significantly reduce computation cost
# Note, evaluations of t_01_02 and t_02_03 are independent and can be performed in parallel
# Also, propagation of table through table might be computationally less expensive
t_01_02 = identity((n, ), [x])
t_01_02 = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t_01_02, [], map_01_02)
t_02_03 = identity((n, ), [x])
t_02_03 = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t_02_03, [], map_02_03)
t = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t_01_02, [], t_02_03)
print(compare(T, t))
True
Example-26: Composition (closed orbit)
[1]:
# Composition illustration with non-zero closed orbit
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=20):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
# Note, kick is used to generate non-zero (dynamical) closed orbit
# Momentum deviation is used as a parameter (coupled to closed orbit via dispersion)
def map_01_02(x, w):
x = kick(x, +1.0E-4, -1.0E-4)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
return x
def map_02_03(x, w):
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
return x
[6]:
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor(1*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[7]:
# Find (dynamical) fixed point
fp = fixed_point(32, lambda x, w: map_02_03(map_01_02(x, w), w), x, w, power=1)
# Check fixed point
print(fp)
print(map_02_03(map_01_02(fp, w), w))
tensor([ 8.418072943377e-04, -5.000000000000e-05, -2.043309959087e-03,
5.000000000000e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([ 8.418072943377e-04, -5.000000000000e-05, -2.043309959087e-03,
5.000000000000e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
[8]:
# Set computation orders for state and each knob group
(nx, nw) = (4, 2)
[9]:
# Find parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((nw, ), fp, [w], lambda x, w: map_02_03(map_01_02(x, w), w))
# Check
print(compare(pfp, propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), pfp, [w], lambda x, w: map_02_03(map_01_02(x, w), w))))
True
[10]:
# Set parametric fixed points at each map entrance
pfp_01 = identity((0, nw), [x, w], parametric=pfp)
pfp_02 = propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), pfp_01, [w], map_01_02)
# Check
print(compare(pfp_01, propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), pfp_01, [w], lambda x, w: map_02_03(map_01_02(x, w), w))))
print(compare(pfp_02, propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), pfp_02, [w], lambda x, w: map_01_02(map_02_03(x, w), w))))
True
True
[11]:
# Define transformations around parametric fixed points
# Note, this transformation map zero (parametric) state to zero (upto given order)
# This is true by construction
def fn_01_02(x, w):
return map_01_02(x + evaluate(first(pfp_01), [w]), w) - evaluate(first(pfp_02), [w])
def fn_02_03(x, w):
return map_02_03(x + evaluate(first(pfp_02), [w]), w) - evaluate(first(pfp_01), [w])
print(propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), identity((0, nw), [x, w]), [w], fn_01_02))
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[0.],
[0.],
[0.],
[0.]], dtype=torch.float64), tensor([[[0.]],
[[0.]],
[[0.]],
[[0.]]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[12]:
# Propagate identity sequentially
T = identity((nx, nw), [x, w], parametric=pfp)
T = propagate((4, 1), (nx, nw), T, [w], lambda x, w: map_01_02(x, w))
T = propagate((4, 1), (nx, nw), T, [w], lambda x, w: map_02_03(x, w))
[13]:
# Composition
# Note, parametric part is zero, other elements of t should be equal to corresponding elements of T
t_01_02 = identity((nx, nw), [x, w])
t_01_02 = propagate((4, 1), (nx, nw), t_01_02, [w], fn_01_02)
t_02_03 = identity((nx, nw), [x, w])
t_02_03 = propagate((4, 1), (nx, nw), t_02_03, [w], fn_02_03)
t = propagate((4, 1), (nx, nw), t_01_02, [w], t_02_03)
[14]:
# Compare phase space trajectories
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
qx = torch.linspace(0.0, 0.01, 10, dtype=dtype, device=device)
px = torch.zeros_like(qx) + 1.0E-12
qy = torch.zeros_like(qx) + 1.0E-03
py = torch.zeros_like(qx) + 1.0E-12
x = torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py]).T
w = torch.tensor([1.0E-3], dtype=dtype, device=device)
count = 256
table = []
y = torch.clone(x)
for _ in range(count):
table.append(y)
y = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: map_02_03(map_01_02(x, w), w))(y)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qx, px, *_ = table
for q, p in zip(qx.cpu().numpy(), px.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='gray', marker='o')
count = 256
table = []
y = torch.clone(x)
for _ in range(count):
table.append(y)
y = y - evaluate(first(pfp), [w])
y = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: evaluate(T, [x, w]))(y)
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qx, px, *_ = table
for q, p in zip(qx.cpu().numpy(), px.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='red', marker='o')
count = 256
table = []
y = torch.clone(x)
for _ in range(count):
table.append(y)
y = y - evaluate(first(pfp), [w])
y = torch.func.vmap(lambda x: evaluate(t, [x, w]))(y)
y = y + evaluate(first(pfp), [w])
table = torch.stack(table).swapaxes(0, -1)
qx, px, *_ = table
for q, p in zip(qx.cpu().numpy(), px.cpu().numpy()):
plt.scatter(q, p, color='blue', marker='x')
plt.show()
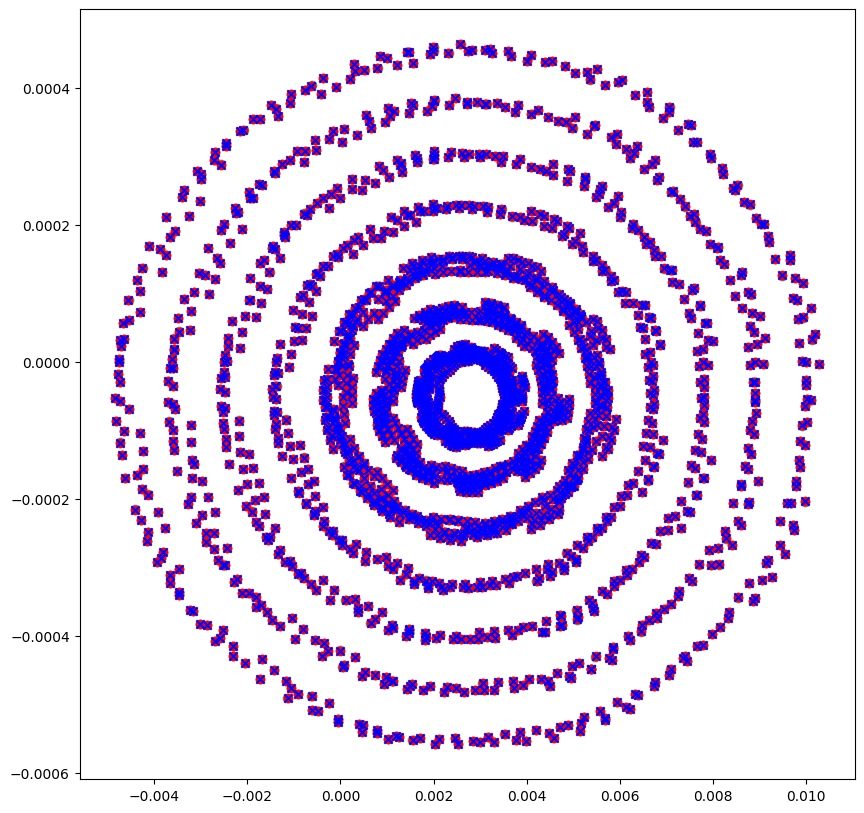
Example-27: Inverse
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.inverse import inverse
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=20):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x):
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
return x
[5]:
# Set computation order & evaluation point
n = 3
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(map_01_02(x))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute derivative table
t = identity((n, ), [x])
t = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t, [], lambda x: map_01_02(x))
[7]:
# Compute inverse
t_inv = inverse((n, ), x, [], t)
[8]:
# Check
out = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t_inv, [], t)
chop(out, replace=True)
out
[8]:
[[],
tensor([[1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00]],
dtype=torch.float64),
[],
[]]
Example-28: Inverse (closed orbit)
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from ndmap.inverse import inverse
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=20):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, w):
x = kick(x, +1.0E-4, -1.0E-4)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
return x
[5]:
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor(1*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[6]:
# Find (dynamical) fixed point
fp = fixed_point(32, lambda x, w: map_01_02(x, w), x, w, power=1)
# Check fixed point
print(fp)
print(map_01_02(fp, w))
tensor([ 8.418072943377e-04, -5.000000000000e-05, -2.043309959087e-03,
5.000000000000e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([ 8.418072943377e-04, -5.000000000000e-05, -2.043309959087e-03,
5.000000000000e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Set computation orders for state and each knob group
(nx, nw) = (3, 2)
[8]:
# Find parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((nw, ), fp, [w], lambda x, w: map_01_02(x, w))
# Check
print(compare(pfp, propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), pfp, [w], lambda x, w: map_01_02(x, w))))
True
[9]:
# Define transformations around parametric fixed points
# Note, this transformation map zero (parametric) state to zero (upto given order)
# This is true by construction
def fn_01_02(x, w):
return map_01_02(x + evaluate(first(pfp), [w]), w) - evaluate(first(pfp), [w])
out = propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), identity((0, nw), [x, w]), [w], fn_01_02)
chop(out, replace=True)
out
[9]:
[[[], [], []]]
[10]:
# Compute derivative table
t = identity((nx, nw), [x, w])
t = propagate((4, 1), (nx, nw), t, [w], lambda x, w: fn_01_02(x, w))
[11]:
# Compute inverse
t_inv = inverse((nx, nw), x, [w], t)
[12]:
# Check
out = propagate((4, 1), (nx, nw), t_inv, [w], t)
chop(out, replace=True)
out
[12]:
[[[], [], []],
[tensor([[1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00]],
dtype=torch.float64),
[],
[]],
[[], [], []],
[[], [], []]]
Example-29: Momenta generator
[1]:
# In this example initial and final monemta are computed from given initial and final coordinates
# Given an origing preserving mapping, its table representation can be computed upto some order
# This representation can be considered as exact
# Next, given initial and final coordinates, corresponding momenta can be computed using momenta generator
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from ndmap.momenta import momenta
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=20):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, w):
x = kick(x, +1.0E-4, -1.0E-4)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19, 0.50)
return x
[6]:
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor(1*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[7]:
# Find (dynamical) fixed point
fp = fixed_point(32, lambda x, w: map_01_02(x, w), x, w, power=1)
# Check fixed point
print(fp)
print(map_01_02(fp, w))
tensor([ 8.418072943377e-04, -5.000000000000e-05, -2.043309959087e-03,
5.000000000000e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([ 8.418072943377e-04, -5.000000000000e-05, -2.043309959087e-03,
5.000000000000e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
[8]:
# Set computation orders for state and each knob group
(nx, nw) = (4, 2)
[9]:
# Find parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((nw, ), fp, [w], lambda x, w: map_01_02(x, w))
# Check
print(compare(pfp, propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), pfp, [w], lambda x, w: map_01_02(x, w))))
True
[10]:
# Define transformations around parametric fixed points
# Note, this transformation map zero (parametric) state to zero (upto given order)
# This is true by construction
def fn_01_02(x, w):
return map_01_02(x + evaluate(first(pfp), [w]), w) - evaluate(first(pfp), [w])
out = propagate((4, 1), (0, nw), identity((0, nw), [x, w]), [w], fn_01_02)
chop(out)
out
[10]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0.],
[0.],
[0.],
[0.]], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[[0.]],
[[0.]],
[[0.]],
[[0.]]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[11]:
# Compute derivative table
t = identity((nx, nw), [x, w])
t = propagate((4, 1), (nx, nw), t, [w], lambda x, w: fn_01_02(x, w))
[12]:
# Compute momenta generator
# Note, computation order can be different from that of the input table
# Accuracy is strongly related to computation order and magnitude of initial coordinates
m = momenta((nx, nw), x, [w], t)
[13]:
# Recover momenta from coordinates
# Set deviations
xi = torch.tensor([0.0005, 0.0001, -0.0005, -0.0001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dw = torch.tensor(1*[0.0001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Evaluate final state using table representation
xf = evaluate(t, [xi, dw])
print(xf)
print()
# Set initial and final coordinates
qi, _ = xi.reshape(-1, 2).T
qf, _ = xf.reshape(-1, 2).T
qs = torch.cat([qf, qi])
print(qs)
print()
# Set initial and final momenta
_, pi, = xi.reshape(-1, 2).T
_, pf, = xf.reshape(-1, 2).T
ps = torch.cat([pf, pi])
print(ps)
print()
# Evaluate generator using coordinates
print(evaluate(m, [qs, 0*dw]))
print(evaluate(m, [qs, 1*dw]))
tensor([ 1.536782226285e-03, -2.360460895977e-05, -1.128298475344e-03,
-6.800430927953e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.536782226285e-03, -1.128298475344e-03, 5.000000000000e-04, -5.000000000000e-04],
dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-2.360460895977e-05, -6.800430927953e-05, 1.000000000000e-04,
-1.000000000000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-2.353065307569e-05, -6.780339520304e-05, 9.993585406462e-05,
-1.001716171999e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-2.360460892419e-05, -6.800430928312e-05, 9.999999996933e-05,
-1.000000000050e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
Example-30: Factorization (kick)
[1]:
# Given a derivative table representation (taylor series) of an origin preserving mapping
# It is possible to factorize it into composition of linear and nonlinear table representations
# If original mapping represents a single turn, linear part can be brought to its normal form
# This can be done using linear theory
# The nonlinear part is a near identity transformation, it can be represented with Lie transformation
# t = tl o tn and tn = exp(-[h])
# In this example (generator) h is computed for a single kick
# It can be used to construct nonlinear normal forms or as a redundancy free representation
[2]:
# Import
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.taylor import taylor
from ndmap.inverse import inverse
from ndmap.factorization import hamiltonian
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set transformation
# Note, this transformation can be exactly represented with a taylor series (i.e. polynomial)
def mapping(x, k, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (k, ), l = x, k, l/2
qx, qy = qx + l*px, qy + l*py
px, py = px - 1.0*l*k*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*k*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px, qy + l*py
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
# Test origin propagation
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(1*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(mapping(x, k, 0.1))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[5]:
# Compute table representation
t = identity((2, 1), [x, k])
t = propagate((4, 1), (2, 1), t, [k], mapping, 0.1)
[6]:
# Compare for some deviation
dx = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.01, 0.05, 0.01], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dk = torch.tensor([1.0],dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(mapping(x + dx, k + dk, 0.1))
print(evaluate(t, [dx, dk]))
tensor([1.009811250000e-01, 9.622500000000e-03, 5.102537625000e-02, 1.050752500000e-02],
dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.009811250000e-01, 9.622500000000e-03, 5.102537625000e-02, 1.050752500000e-02],
dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Linear part is not near identity
print(derivative(1, lambda x, k: evaluate(t, [x, k]), x, k, intermediate=False))
tensor([[1.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e-01, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e-01],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00]],
dtype=torch.float64)
[8]:
# Set linear part and compose with its inverse
l = derivative(1, lambda x, k: evaluate(t, [x, k]), x, k)
t = propagate((4, 1), (2, 1), inverse(1, x, [k], l), [k], t)
chop(t)
[9]:
# Now table represents a near identity transformation
print(derivative(1, lambda x, k: evaluate(t, [x, k]), x, k, intermediate=False))
tensor([[1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00]],
dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Compute single exponent generator
h = hamiltonian((2, 1), x, [k], t)
chop(h)
# Compute series representation
# Note, each coefficient is proportional to strength
s = clean(series((4, 1), (3, 1), h))
for index, value in s.items():
print(index, value.squeeze())
(3, 0, 0, 0, 1) tensor(1.666666666667e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 1, 0, 0, 1) tensor(-2.500000000000e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 2, 0, 0, 1) tensor(1.250000000000e-04, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 2, 0, 1) tensor(-5.000000000000e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 1, 1, 1) tensor(5.000000000000e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 0, 2, 1) tensor(-1.250000000000e-04, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 3, 0, 0, 1) tensor(-2.083333333333e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 2, 0, 1) tensor(2.500000000000e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 1, 1, 1) tensor(-2.500000000000e-04, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 0, 2, 1) tensor(6.250000000000e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# In this example, this hamiltonian generates exact solution with taylor intergator
print(mapping(x + dx, k + dk, 0.1))
print(taylor(1, 1.0, lambda x, k: evaluate(h, [x, k]), evaluate(l, [dx, dk]), dk))
tensor([1.009811250000e-01, 9.622500000000e-03, 5.102537625000e-02, 1.050752500000e-02],
dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.009811250000e-01, 9.622500000000e-03, 5.102537625000e-02, 1.050752500000e-02],
dtype=torch.float64)
Example-31: Factorization (fodo)
[1]:
# Import
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.taylor import taylor
from ndmap.inverse import inverse
from ndmap.factorization import hamiltonian
from ndmap.factorization import solution
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=1):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[4]:
# Set fodo
def fodo(x):
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, -0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.25, 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.1, +0.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19, 0.50)
return x
[5]:
# Set computation order & evaluation point
n = 4
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Note, origin is preserved
fodo(x)
[5]:
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute derivative table
t = identity((n, ), [x])
t = propagate((4, ), (n, ), t, [], lambda x: fodo(x))
[7]:
# Set linear part
l = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(t, [x]), x)
l
[7]:
[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[8.259928915375e-02, 1.470387298165e+01, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[-6.754528950779e-02, 8.259928915375e-02, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 8.239443265215e-01, 6.857644998910e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, -4.682595072274e-02, 8.239443265215e-01]],
dtype=torch.float64)]
[8]:
# Set nonlinear part
u = propagate((4, ), (n, ), inverse(1, x, [], l), [], t)
chop(u)
derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(u, [x]), x)
[8]:
[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00],
[0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 0.000000000000e+00, 1.000000000000e+00]],
dtype=torch.float64)]
[9]:
# Compute hamiltonian
h = hamiltonian((n, ), x, [], u)
chop(h)
[10]:
# Compute series representation
s = clean(series((4, ), (n + 1, ), h), epsilon=1.0E-9)
for index, value in s.items():
print(index, value.squeeze())
(3, 0, 0, 0) tensor(5.024988945080e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 1, 0, 0) tensor(-8.027849817894e-01, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 2, 0, 0) tensor(1.242554019904e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 2, 0) tensor(-5.976214487541e-01, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 1, 1) tensor(3.719621673904e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 0, 2) tensor(-6.659517059512e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 3, 0, 0) tensor(-1.465736828313e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 2, 0) tensor(7.616595688746e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 1, 1) tensor(-6.812652464723e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 0, 2) tensor(1.637189795764e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(4, 0, 0, 0) tensor(-2.670453079972e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
(3, 1, 0, 0) tensor(1.592046859279e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 2, 0, 0) tensor(-4.015290100155e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 0, 2, 0) tensor(1.098921583040e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 0, 1, 1) tensor(-1.150214563563e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 0, 0, 2) tensor(5.596016324538e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 3, 0, 0) tensor(2.720415502394e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 1, 2, 0) tensor(9.092563694884e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 1, 1, 1) tensor(-7.311435065924e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 1, 0, 2) tensor(1.043406910282e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 4, 0, 0) tensor(-8.872464473277e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 2, 2, 0) tensor(2.515413272498e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 2, 1, 1) tensor(6.993401944277e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 2, 0, 2) tensor(-3.593047920669e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 0, 4, 0) tensor(-1.258999636146e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 0, 3, 1) tensor(1.898846058062e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 0, 2, 2) tensor(-1.062500223737e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 0, 1, 3) tensor(2.608144282259e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 0, 0, 4) tensor(-2.419706859670e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(5, 0, 0, 0) tensor(3.720153703396e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
(4, 1, 0, 0) tensor(-2.470046738149e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(3, 2, 0, 0) tensor(5.465213020046e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(3, 0, 2, 0) tensor(6.994399435987e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
(3, 0, 1, 1) tensor(-9.734770779462e-01, dtype=torch.float64)
(3, 0, 0, 2) tensor(5.509140066922e-01, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 3, 0, 0) tensor(-7.728896235979e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 1, 2, 0) tensor(1.614402519455e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 1, 1, 1) tensor(-1.014114400601e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(2, 1, 0, 2) tensor(2.099498728183e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 4, 0, 0) tensor(6.599464974629e+03, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 2, 2, 0) tensor(-1.831472433171e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 2, 1, 1) tensor(1.658609587412e+03, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 2, 0, 2) tensor(-4.455648121228e+03, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 4, 0) tensor(-2.372154036991e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 3, 1) tensor(3.120364861986e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 2, 2) tensor(-1.392873544053e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 1, 3) tensor(2.280297561995e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(1, 0, 0, 4) tensor(-5.830536198793e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 5, 0, 0) tensor(-1.712807218852e+04, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 3, 2, 0) tensor(-5.278629070820e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 3, 1, 1) tensor(3.474912442117e+03, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 3, 0, 2) tensor(1.999757814650e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 4, 0) tensor(2.874466602579e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 3, 1) tensor(-5.199961828427e+02, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 2, 2) tensor(3.267795295152e+03, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 1, 3) tensor(-8.677457594504e+03, dtype=torch.float64)
(0, 1, 0, 4) tensor(8.128231575922e+03, dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Restore mapping table nonlinear part from hamiltonian
print(compare(u, solution((n, ), x, [], h)))
print(compare(t, propagate((4, ), (n, ), l, [], solution((n, ), x, [], h))))
True
True
Example-32: Factorization (factorize)
[1]:
# Import
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.series import split
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.bracket import bracket
from ndmap.factorization import hamiltonian
from ndmap.factorization import solution
from ndmap.factorization import factorize
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set test hamiltonian function and compute corresponding table representation
# Note, test hamiltonian is near identity
def h(x, u, v):
q, p = x
u, = u
v, = v
h1 = (1 + u + u**2)*q**3 + q**2*p + q*p**2 + p**3
h2 = (1 + v)*q**4 + q**3*p + q**2*p**2 + q*p**3 + p**4
h3 = q**5 + q**4*p + q**3*p**2 + q**2*p**3 + q*p**4 + p**5
return h1 + h2 + h3
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
u = torch.tensor([0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
v = torch.tensor([0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
h = derivative((5, 2, 1), h, x, u, v)
chop(h, replace=True)
s, *_ = split(clean(series((2, 1, 1), (5, 2, 1), h)))
s
[3]:
{(3, 0, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 1, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 3, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 1, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 2, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(4, 0, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 1, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 2, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 3, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 4, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(4, 0, 0, 1): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(5, 0, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(4, 1, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 2, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 3, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 4, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 5, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64)}
[4]:
# Compute solution
t = solution((4, 2, 1), x, [u, v], h)
[5]:
# Compute hamiltonian from solution and compare
compare(h, hamiltonian((4, 2, 1), x, [u, v], t))
[5]:
True
[6]:
# Perform factorization
h1, h2, h3, *_ = factorize((4, 2, 1), x, [u, v], t)
[7]:
# Examine series representation
s, *_ = split(clean(series((2, 1, 1), (5, 1), h1)))
s
[7]:
{(3, 0, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 1, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 2, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 3, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 0, 1, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64)}
[8]:
# Examine series representation
s, *_ = split(clean(series((2, 1, 1), (5, 1), h2)))
s
[8]:
{(4, 0, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 1, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 2, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 3, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 4, 0, 0): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(4, 0, 0, 1): tensor(1.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64)}
[9]:
# Examine series representation
s, *_ = split(clean(series((2, 1, 1), (5, 1), h3)))
s
[9]:
{(5, 0, 0, 0): tensor(5.000000000000e-01, dtype=torch.float64),
(4, 1, 0, 0): tensor(-5.000000000000e-01, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 2, 0, 0): tensor(-2.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 3, 0, 0): tensor(4.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(1, 4, 0, 0): tensor(2.500000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(0, 5, 0, 0): tensor(1.500000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(5, 0, 0, 1): tensor(-2.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(4, 1, 0, 1): tensor(-4.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 2, 0, 1): tensor(-6.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(5, 0, 1, 0): tensor(1.500000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(4, 1, 1, 0): tensor(3.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(3, 2, 1, 0): tensor(4.500000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64),
(2, 3, 1, 0): tensor(6.000000000000e+00, dtype=torch.float64)}
[10]:
# Compute solutions
t1 = solution((4, 2, 1), x, [u, v], h1)
t2 = solution((4, 2, 1), x, [u, v], h2)
t3 = solution((4, 2, 1) ,x, [u, v], h3)
[11]:
# Compose individual solutions and compare with initial solution
T = identity((4, 2, 1), [x, u, v])
T = propagate((2, 1, 1), (4, 2, 1), T, [u, v], t1)
T = propagate((2, 1, 1), (4, 2, 1), T, [u, v], t2)
T = propagate((2, 1, 1), (4, 2, 1), T, [u, v], t3)
compare(t, T)
[11]:
True
Example-33: Nonlinear mapping approximation (gradient)
[1]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.gradient import series
from ndmap.series import clean
torch.set_printoptions(precision=12, sci_mode=True)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
True
[2]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[3]:
# Set test mapping
# Rotation with two sextupoles separated by negative identity linear transformation
# Note, result is expected to have zero degree two coefficients due to negative identity linear transformation between sextupoles
def spin(x, mux, muy):
(qx, px, qy, py), mux, muy = x, mux, muy
return torch.stack([qx*mux.cos() + px*mux.sin(), px*mux.cos() - qx*mux.sin(), qy*muy.cos() + py*muy.sin(), py*muy.cos() - qy*muy.sin()])
def drif(x, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), l = x, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px, px, qy + l*py, py])
def sext(x, ks, l, n=1):
(qx, px, qy, py), ks, l = x, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px, qy + l*py
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px, qy + l*py
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def ring(x):
mux, muy = 2.0*numpy.pi*torch.tensor([1/3 + 0.01, 1/4 + 0.01], dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = spin(x, mux, muy)
x = drif(x, -0.05)
x = sext(x, 10.0, 0.1, 100)
x = drif(x, -0.05)
mux, muy = 2.0*numpy.pi*torch.tensor([0.50, 0.50], dtype=dtype, device=device)
x = spin(x, mux, muy)
x = drif(x, -0.05)
x = sext(x, 10.0, 0.1, 100)
x = drif(x, -0.05)
return x
[4]:
# Set evaluation point
x = torch.tensor([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Compute and print series
n = 4
s = clean(series((n, ), ring, x, retain=False), epsilon=1.0E-12)
print(*[f'{key}: {value.cpu().numpy()}' for key, value in clean(s, epsilon=1.0E-14).items()], sep='\n')
(1, 0, 0, 0): [0.55339155 0.83292124 0. 0. ]
(0, 1, 0, 0): [-0.83292124 0.55339155 0. 0. ]
(0, 0, 1, 0): [0. 0. 0.06279052 0.99802673]
(0, 0, 0, 1): [ 0. 0. -0.99802673 0.06279052]
(3, 0, 0, 0): [-7.53257307e-09 2.82424677e-03 -0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00]
(2, 1, 0, 0): [-1.96250238e-08 -1.27525063e-02 -0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00]
(2, 0, 1, 0): [-0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 9.21186111e-06 3.34331441e-04]
(2, 0, 0, 1): [-0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 1.59704766e-05 -5.06941449e-03]
(1, 2, 0, 0): [-1.11004920e-08 1.91940679e-02 -0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00]
(1, 1, 1, 0): [-0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -2.98671134e-05 -9.79459005e-04]
(1, 1, 0, 1): [-0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -1.48185697e-05 1.53623878e-02]
(1, 0, 2, 0): [-1.05857397e-06 1.97282603e-05 -0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00]
(1, 0, 1, 1): [ 1.48154798e-05 -1.18570682e-03 -0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00]
(1, 0, 0, 2): [ 2.88067554e-05 9.18409783e-03 -0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00]
(0, 3, 0, 0): [-9.21338045e-10 -9.62979589e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 2, 1, 0): [0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 2.40366928e-05 7.09979811e-04]
(0, 2, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -1.38786549e-05 -1.15294375e-02]
(0, 1, 2, 0): [ 1.80396305e-06 -2.59196622e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 1, 1, 1): [-2.98509155e-05 1.72488752e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 1, 0, 2): [ 1.66318846e-05 -1.38269522e-02 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 3, 0): [-0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -1.47704279e-08 4.12534350e-06]
(0, 0, 2, 1): [-0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 -3.31103168e-09 -1.96719688e-04]
(0, 0, 1, 2): [-0.00000000e+00 -0.00000000e+00 3.93325786e-09 3.12683573e-03]
(0, 0, 0, 3): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 2.56887204e-10 -1.65665408e-02]
(4, 0, 0, 0): [ 6.48869023e-07 -3.91844462e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(3, 1, 0, 0): [-3.91685700e-06 1.51001133e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(3, 0, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -4.36165465e-07 5.76316391e-06]
(3, 0, 0, 1): [0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 6.56410859e-06 1.31668166e-05]
(2, 2, 0, 0): [ 8.85501662e-06 -1.48880894e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(2, 1, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 1.92232731e-06 -2.78183189e-05]
(2, 1, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -2.96894787e-05 -3.16635607e-05]
(2, 0, 2, 0): [1.81838643e-08 2.18816315e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(2, 0, 1, 1): [-9.93314202e-07 -3.25277215e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(2, 0, 0, 2): [ 7.67316422e-06 -2.51871510e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 3, 0, 0): [-8.88618620e-06 -4.33921249e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 2, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -2.81910856e-06 4.44963121e-05]
(1, 2, 0, 1): [0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 4.47107608e-05 6.22767407e-06]
(1, 1, 2, 0): [-5.02653030e-08 -6.69892371e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 1, 1, 1): [2.90625131e-06 1.04277202e-04 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 1, 0, 2): [-2.28808176e-05 2.60346923e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(1, 0, 3, 0): [0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 2.09236592e-09 3.51323891e-08]
(1, 0, 2, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -6.41657941e-09 -1.78350571e-06]
(1, 0, 1, 2): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -6.10954936e-07 1.86435774e-05]
(1, 0, 0, 3): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 3.05503037e-06 -5.00150901e-05]
(0, 4, 0, 0): [3.33982092e-06 8.88114110e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 3, 1, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 1.37553970e-06 -2.36217768e-05]
(0, 3, 0, 1): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -2.24184174e-05 1.77513110e-05]
(0, 2, 2, 0): [3.54703897e-08 5.11986525e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 2, 1, 1): [-2.15414781e-06 -8.31702815e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 2, 0, 2): [1.72952174e-05 1.78791226e-05 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 1, 3, 0): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -3.32576455e-09 -2.16775859e-08]
(0, 1, 2, 1): [0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 1.73891518e-08 1.32003603e-06]
(0, 1, 1, 2): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 8.58583303e-07 -7.35197022e-06]
(0, 1, 0, 3): [ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 -4.60205741e-06 -3.44817289e-05]
(0, 0, 4, 0): [-2.95410616e-10 -3.91436795e-10 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 3, 1): [ 1.72261161e-08 -3.76703368e-08 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 2, 2): [-3.76632244e-07 1.04173914e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 1, 3): [ 3.81179356e-06 -5.44741177e-06 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
(0, 0, 0, 4): [-1.51552013e-05 -3.46854944e-07 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
Example-34: ORM optics correction
[1]:
# In this example orbit responce matrix (ORM) is used to correct linear optics in a simple FODO cell
# Two gradient errors are introduced into cell quadrupoles
# This example illustrates one optimization step
# Given a measured ORM, the model knobs are fitted to reproduce it
# Next, the corrections should be applied and the matrix should be remeasured
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=1):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
# Note, transport maps are expected to have identical (differentiable) signature
def t_01_02(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kf, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsf1, cysf1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def t_02_03(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsd1, cysd1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kd, 0.50)
return x
def t_03_04(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kd, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsd2, cysd2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def t_04_05(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsf2, cysf2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kf, 0.50)
return x
ts = [t_01_02,t_02_03, t_03_04, t_04_05]
[6]:
# Set deviation variables
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
cs = torch.tensor(8*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dk = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[7]:
# Define one-turn transport at the lattice entrance
def fodo(x, cs, kq):
for t in ts:
x = t(x, cs, kq)
return x
[8]:
# Test one-turn transport
print(fodo(x, cs, dk))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[9]:
# Compute (dynamical) fixed point
# Note, dynamical part is assumed to be fixed during optimization
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, cs, dk, power=1, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Define parametric responce matrix
def rm(dk):
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [cs], lambda x, cs: fodo(x, cs, dk), jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
chop(pfp)
_, (dqx, _, dqy, _) = first(pfp)
out = [torch.stack([dqx, dqy])]
for t in ts:
pfp = propagate((4, 8), (0, 1), pfp, [cs], lambda x, cs: t(x, cs, dk), jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
chop(pfp)
_, (dqx, _, dqy, _) = first(pfp)
out.append(torch.stack([dqx, dqy]))
return torch.stack(out).swapaxes(0, 1).reshape(-1, len(cs))
print(2*(len(ts) + 1), len(cs))
print(rm(dk).shape)
print()
print(rm(dk))
10 8
torch.Size([10, 8])
tensor([[7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.216e+00, 4.039e+00, 6.749e+00, 4.566e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[5.110e+00, 2.611e+00, 5.110e+00, 2.611e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.749e+00, 4.566e+00, 6.216e+00, 4.039e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.801e+01, 2.744e+01, 1.849e+01, 2.792e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 2.509e+01, 3.667e+01, 2.509e+01, 3.667e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.849e+01, 2.792e+01, 1.801e+01, 2.744e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Test responce matrix
dc = 1.0E-3*torch.ones_like(cs)
o = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, cs + dc, dk, power=1, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
os = []
qx, _, qy, _ = o
os.append(torch.stack([qx, qy]))
for t in ts:
o = t(o, dc, dk)
qx, _, qy, _ = o
os.append(torch.stack([qx, qy]))
print(torch.allclose(torch.stack(os).T.flatten(), rm(dk) @ dc))
True
[12]:
# Set quadrupole gradient errors
ek = torch.tensor([-0.010, 0.005], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[13]:
# Measure ORM
erm = rm(ek)
print(erm)
tensor([[8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.658e+00, 4.415e+00, 7.190e+00, 4.942e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[5.488e+00, 2.923e+00, 5.488e+00, 2.923e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[7.190e+00, 4.942e+00, 6.658e+00, 4.415e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.943e+01, 2.915e+01, 1.990e+01, 2.963e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 2.678e+01, 3.865e+01, 2.678e+01, 3.865e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.990e+01, 2.963e+01, 1.943e+01, 2.915e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[14]:
# Define objective to minimize
def objective(dk):
return ((erm - rm(dk))**2).sum()
print(objective(dk))
tensor(5.298e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
[15]:
# Set model class
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, knobs):
super().__init__()
self.knobs = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.clone(knobs))
def forward(self):
return objective(self.knobs)
[16]:
# Set model instance
# Note, initial knobs are set to zero
model = Model(torch.zeros_like(dk))
print(model())
tensor(5.298e+01, dtype=torch.float64, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
[17]:
# Set optimizer
lr = 2.5E-3
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
[18]:
# Fit model
epochs = 256
print(ek)
print(model.knobs)
print(model.forward())
print()
knobs, errors = [], []
for epoch in range(epochs):
error = model.forward()
with torch.no_grad():
knobs.append(model.knobs.clone().detach())
errors.append(error.clone().detach())
error.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
if epoch % 10 == 0:
print(f'epoch: {epoch}, error: {error.item()}')
print(ek)
print(model.knobs)
print(model.forward())
print()
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Parameter containing:
tensor([0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
tensor(5.298e+01, dtype=torch.float64, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
epoch: 0, error: 52.97690929514796
epoch: 10, error: 9.061476544019179
epoch: 20, error: 4.116026193086178
epoch: 30, error: 4.4716138801849885
epoch: 40, error: 2.5934201513661606
epoch: 50, error: 1.320221084167608
epoch: 60, error: 0.7104114404644974
epoch: 70, error: 0.39073287332555584
epoch: 80, error: 0.17765207040232386
epoch: 90, error: 0.07092862791751303
epoch: 100, error: 0.024482773974344098
epoch: 110, error: 0.006731421279765544
epoch: 120, error: 0.001272143234908415
epoch: 130, error: 0.00019181854968944713
epoch: 140, error: 2.3799691903263396e-05
epoch: 150, error: 2.155612473667951e-05
epoch: 160, error: 2.4284316948196817e-05
epoch: 170, error: 1.359976274459628e-05
epoch: 180, error: 4.543935327150297e-06
epoch: 190, error: 1.1354899250982208e-06
epoch: 200, error: 1.718342123892043e-07
epoch: 210, error: 2.551350446132945e-08
epoch: 220, error: 2.8003866265404305e-08
epoch: 230, error: 2.1762818183897804e-08
epoch: 240, error: 9.432013407780834e-09
epoch: 250, error: 2.3809020247549156e-09
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Parameter containing:
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
tensor(5.351e-10, dtype=torch.float64, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
[19]:
# Plot error vs iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.plot(range(len(errors)), torch.stack(errors).cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
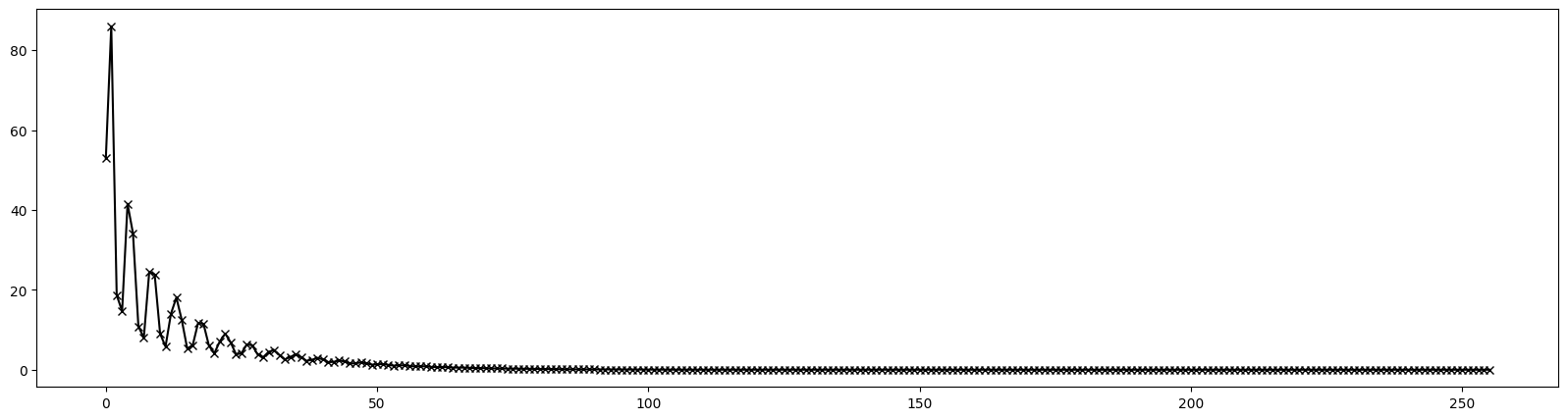
[20]:
# Plot knobs vs iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.hlines(ek.cpu().numpy(), 0, epochs, linestyles='dashed', color='gray', alpha=0.75)
for knob in torch.stack(knobs).T:
plt.plot(range(len(knob)), knob.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
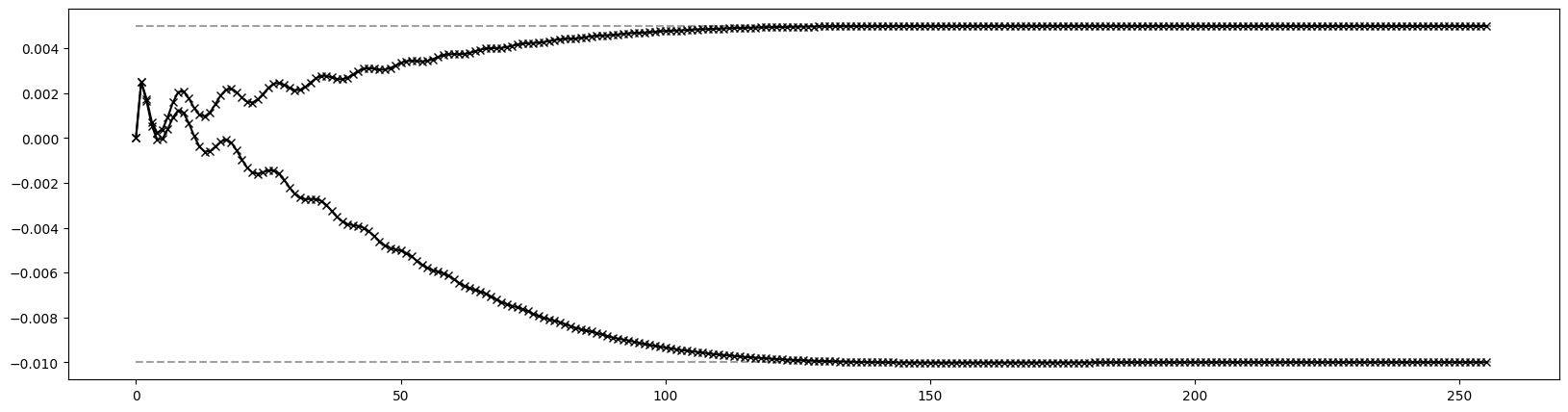
[21]:
# Higher order derivatives can be used to create surrogate Taylor model of the ORM
# Taylor model can be expensive to compute, but computation is performed only one time
# Note, model can be also updated duaring optimization
n = 5
t = derivative(n, rm, dk, jacobian=torch.func.jacfwd)
[22]:
# Redefine objective fuction to use Taylor model
def objective(dk):
return ((erm - evaluate(t, [dk]))**2).sum()
print(objective(dk))
tensor(5.298e+01, dtype=torch.float64)
[23]:
# Set model instance
# Note, initial knobs are set to zero
model = Model(torch.zeros_like(dk))
print(model())
tensor(5.298e+01, dtype=torch.float64, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
[24]:
# Set optimizer
lr = 2.5E-3
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
[25]:
# Fit model
epochs = 256
print(ek)
print(model.knobs)
print(model.forward())
print()
knobs, errors = [], []
for epoch in range(epochs):
error = model.forward()
with torch.no_grad():
knobs.append(model.knobs.clone().detach())
errors.append(error.clone().detach())
error.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
if epoch % 10 == 0:
print(f'epoch: {epoch}, error: {error.item()}')
print(ek)
print(model.knobs)
print(model.forward())
print()
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Parameter containing:
tensor([0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
tensor(5.298e+01, dtype=torch.float64, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
epoch: 0, error: 52.976909295147884
epoch: 10, error: 9.059850191301422
epoch: 20, error: 4.116647404613835
epoch: 30, error: 4.472951117480212
epoch: 40, error: 2.5922560001567434
epoch: 50, error: 1.3204603071831524
epoch: 60, error: 0.7100392325724316
epoch: 70, error: 0.39053200207952343
epoch: 80, error: 0.17757259750915444
epoch: 90, error: 0.07088795313036353
epoch: 100, error: 0.024459899278350294
epoch: 110, error: 0.006720239692606007
epoch: 120, error: 0.001269417957035261
epoch: 130, error: 0.00019187232318368966
epoch: 140, error: 2.3597651642216307e-05
epoch: 150, error: 2.1673080207299973e-05
epoch: 160, error: 2.426302907045522e-05
epoch: 170, error: 1.3607180530103824e-05
epoch: 180, error: 4.539802198450803e-06
epoch: 190, error: 1.1314656087725447e-06
epoch: 200, error: 1.710558210516473e-07
epoch: 210, error: 2.5644830807954306e-08
epoch: 220, error: 2.8132779788222537e-08
epoch: 230, error: 2.1802735069022923e-08
epoch: 240, error: 9.435223715979277e-09
epoch: 250, error: 2.377689322793694e-09
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Parameter containing:
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
tensor(5.331e-10, dtype=torch.float64, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)
[26]:
# Plot error vs iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.plot(range(len(errors)), torch.stack(errors).cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
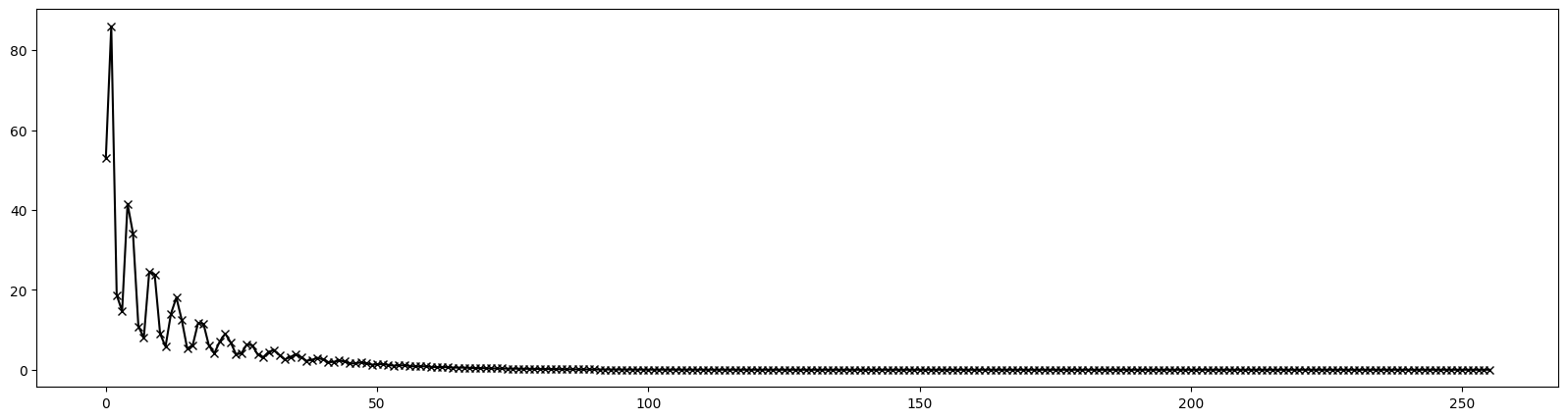
[27]:
# Plot knobs vs iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.hlines(ek.cpu().numpy(), 0, epochs, linestyles='dashed', color='gray', alpha=0.75)
for knob in torch.stack(knobs).T:
plt.plot(range(len(knob)), knob.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
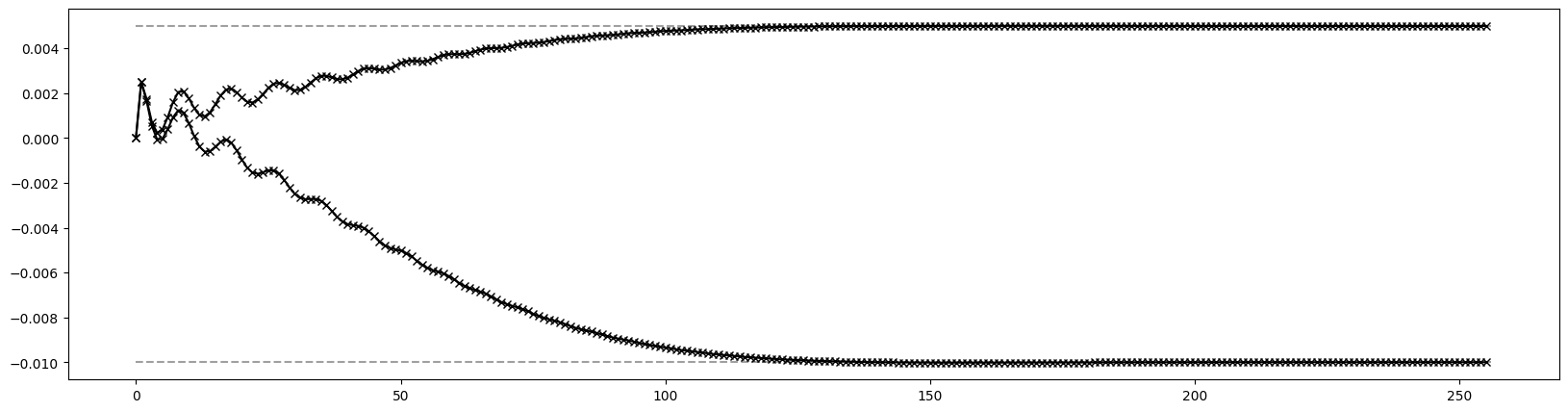
Example-35: ORM optics correction (training loop)
[1]:
# In this example orbit responce matrix (ORM) is used to correct linear optics in a simple FODO cell
# Two gradient errors are introduced into cell quadrupoles
# This example illustrates one optimization step
# Given a measured ORM, the model knobs are fitted to reproduce it
# Next, the corrections should be applied and the matrix should be remeasured
# Fitting step mirrors neural net training loop
# Elements of measured responce matrix are used as targets
# Note, full ORM is computed for each batch
# It is also possible to define elementwise computation (see the next example)
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.data import random_split
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=1):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
# Note, transport maps are expected to have identical (differentiable) signature
def t_01_02(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kf, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsf1, cysf1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def t_02_03(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsd1, cysd1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kd, 0.50)
return x
def t_03_04(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kd, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsd2, cysd2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def t_04_05(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsf2, cysf2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kf, 0.50)
return x
ts = [t_01_02,t_02_03, t_03_04, t_04_05]
[6]:
# Set deviation variables
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
cs = torch.tensor(8*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dk = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[7]:
# Define one-turn transport at the lattice entrance
def fodo(x, cs, kq):
for t in ts:
x = t(x, cs, kq)
return x
[8]:
# Test one-turn transport
print(fodo(x, cs, dk))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[9]:
# Compute (dynamical) fixed point
# Note, dynamical part is assumed to be fixed during optimization
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, cs, dk, power=1, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Define parametric responce matrix
def rm(dk):
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [cs], lambda x, cs: fodo(x, cs, dk), jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
chop(pfp)
_, (dqx, _, dqy, _) = first(pfp)
out = [torch.stack([dqx, dqy])]
for t in ts:
pfp = propagate((4, 8), (0, 1), pfp, [cs], lambda x, cs: t(x, cs, dk), jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
chop(pfp)
_, (dqx, _, dqy, _) = first(pfp)
out.append(torch.stack([dqx, dqy]))
return torch.stack(out).swapaxes(0, 1).reshape(-1, len(cs))
print(2*(len(ts) + 1), len(cs))
print(rm(dk).shape)
print()
print(rm(dk))
10 8
torch.Size([10, 8])
tensor([[7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.216e+00, 4.039e+00, 6.749e+00, 4.566e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[5.110e+00, 2.611e+00, 5.110e+00, 2.611e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.749e+00, 4.566e+00, 6.216e+00, 4.039e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.801e+01, 2.744e+01, 1.849e+01, 2.792e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 2.509e+01, 3.667e+01, 2.509e+01, 3.667e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.849e+01, 2.792e+01, 1.801e+01, 2.744e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Test responce matrix
dc = 1.0E-3*torch.ones_like(cs)
o = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, cs + dc, dk, power=1, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
os = []
qx, _, qy, _ = o
os.append(torch.stack([qx, qy]))
for t in ts:
o = t(o, dc, dk)
qx, _, qy, _ = o
os.append(torch.stack([qx, qy]))
print(torch.allclose(torch.stack(os).T.flatten(), rm(dk) @ dc))
True
[12]:
# Set quadrupole gradient errors
ek = torch.tensor([-0.010, 0.005], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[13]:
# Measure ORM
erm = rm(ek)
print(erm)
tensor([[8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.658e+00, 4.415e+00, 7.190e+00, 4.942e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[5.488e+00, 2.923e+00, 5.488e+00, 2.923e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[7.190e+00, 4.942e+00, 6.658e+00, 4.415e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.943e+01, 2.915e+01, 1.990e+01, 2.963e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 2.678e+01, 3.865e+01, 2.678e+01, 3.865e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.990e+01, 2.963e+01, 1.943e+01, 2.915e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[14]:
# Set data
i_max, j_max = erm.shape
i_val, j_val = torch.arange(i_max), torch.arange(j_max)
X = torch.vstack([*torch.stack(torch.meshgrid(i_val, j_val, indexing='xy')).swapaxes(0, -1)])
y = erm.clone().flatten()
batch_size = 16
dataset = TensorDataset(X.clone(), y.clone())
dataset, validation = random_split(dataset, [0.80, 0.20])
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
[15]:
# Set model
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, knobs):
super().__init__()
self.knobs = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.clone(knobs))
def forward(self, x):
i, j = x.unsqueeze(0).swapaxes(0, -1)
return (rm(self.knobs)[i, j]).squeeze()
[16]:
# Set model instance
# Note, initial knobs are set to zero
model = Model(torch.zeros_like(dk))
[17]:
# Test model
i, j = 0, 0
print(rm(dk)[i, j])
print(model(torch.tensor([[i, j]])))
print()
tensor(7.577e+00, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(7.577e+00, dtype=torch.float64, grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward0>)
[18]:
# Set optimizer
lr = 1.0E-3
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
[19]:
# Set loss function
lf = torch.nn.MSELoss()
[20]:
# Fit model
# Note, each epoch loss is computed for full validation set
epochs = 128
print()
print(ek)
print(model.knobs)
print()
knobs, errors = [], []
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
y_hat = model(X)
error = lf(y_hat, y)
with torch.no_grad():
knobs.append(model.knobs.clone().detach())
errors.append(error.clone().detach())
error.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
model.eval()
X, y = validation.dataset.tensors
test = lf(model(X[validation.indices]), y[validation.indices])
if epoch % 10 == 0:
print(f'epoch: {epoch}, error: {error.item()} / {test.item()}')
print()
print(ek)
print(model.knobs)
print()
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Parameter containing:
tensor([0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
epoch: 0, error: 0.37529107626509794 / 0.72679523282213
epoch: 10, error: 0.019561891190916357 / 0.08595406190271199
epoch: 20, error: 0.028442131733101884 / 0.059218224485797756
epoch: 30, error: 0.024756037639704742 / 0.03382898705876869
epoch: 40, error: 0.007808066790505313 / 0.014454231605437087
epoch: 50, error: 0.003117435961114121 / 0.006542069654623646
epoch: 60, error: 0.0012404708769704496 / 0.00196001107485135
epoch: 70, error: 0.0002826792552836003 / 0.000523081505929046
epoch: 80, error: 6.0312874463179874e-05 / 0.0001471941670079705
epoch: 90, error: 2.3739166186638856e-05 / 5.9827396259044656e-05
epoch: 100, error: 6.057427185883081e-06 / 7.80155998736023e-06
epoch: 110, error: 1.3473974612042764e-06 / 1.5022630951121078e-06
epoch: 120, error: 7.86204138851082e-08 / 1.297239564506323e-07
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Parameter containing:
tensor([-9.994e-03, 4.998e-03], dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
[21]:
# Plot error vs iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.plot(range(len(errors)), torch.stack(errors).cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
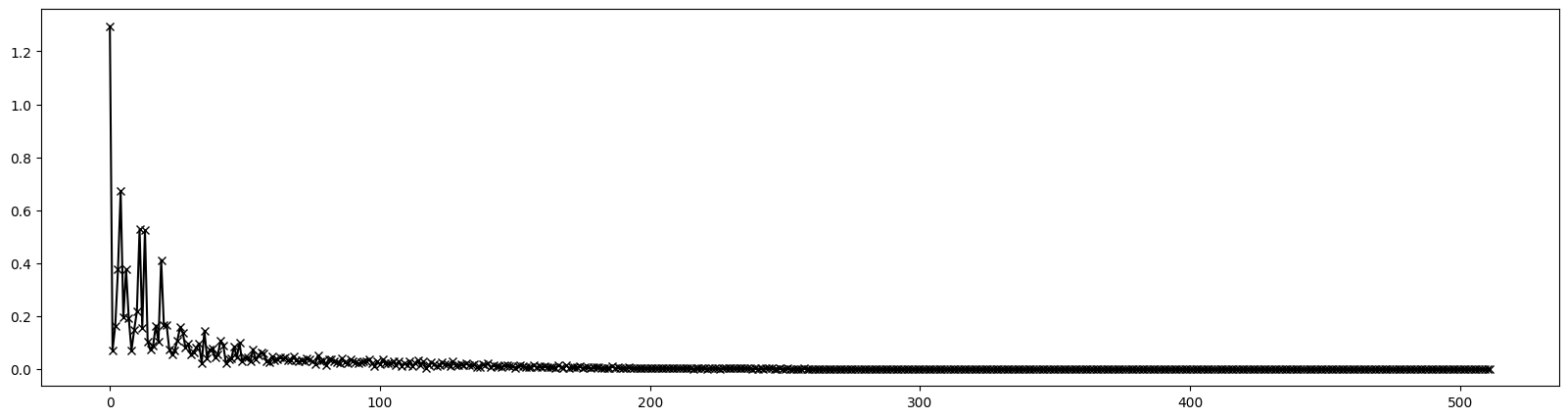
[22]:
# Plot knobs vs iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.hlines(ek.cpu().numpy(), 0, len(errors), linestyles='dashed', color='gray', alpha=0.75)
for knob in torch.stack(knobs).T:
plt.plot(range(len(knob)), knob.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
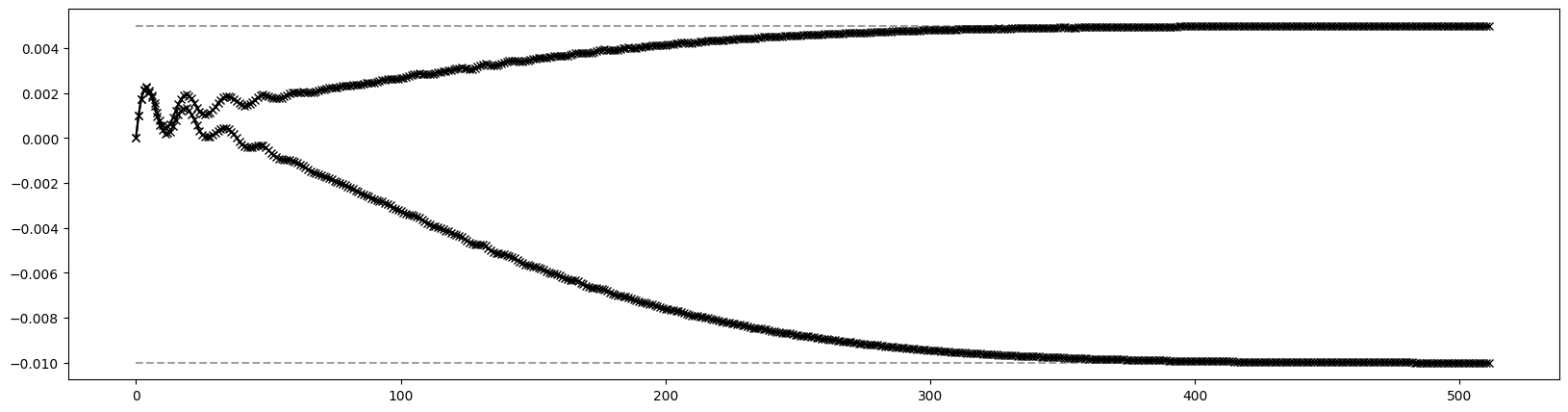
Example-36: ORM optics correction (training loop + elementwise computation)
[1]:
# In this example orbit responce matrix (ORM) is used to correct linear optics in a simple FODO cell
# Two gradient errors are introduced into cell quadrupoles
# This example illustrates one optimization step
# Given a measured ORM, the model knobs are fitted to reproduce it
# Next, the corrections should be applied and the matrix should be remeasured
# Fitting step mirrors neural net training loop
# Elements of measured responce matrix are used as targets
# Note, elements of ORM are computed in forward method, but computation is sequential
[2]:
# Import
from functools import partial
import numpy
import torch
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.data import random_split
from ndmap.util import flatten
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=1):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
# Note, transport maps are expected to have identical (differentiable) signature
def t_01_02(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kf, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsf1, cysf1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def t_02_03(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsd1, cysd1)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kd, 0.50)
return x
def t_03_04(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.21 + kd, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsd2, cysd2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def t_04_05(x, cs, dk):
cxsf1, cxsd1, cxsf2, cxsd2, cysf1, cysd1, cysf2, cysd2 = cs
kf, kd = dk
x = bend(x, [0.0], 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = kick(x, cxsf2, cysf2)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.00, 0.05)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.19 + kf, 0.50)
return x
[6]:
# Set deviation variables
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
cs = torch.tensor(8*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dk = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[7]:
# Define one-turn transport at the lattice entrance
def fodo(x, cs, kq):
for t in [t_01_02, t_02_03, t_03_04, t_04_05]:
x = t(x, cs, kq)
return x
[8]:
# Test one-turn transport
print(fodo(x, cs, dk))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[9]:
# Set rings at observation points
def ring(x, cs, dk, s=0):
ts = [t_01_02, t_02_03, t_03_04, t_04_05]
ts = ts[s:] + ts[:s]
for t in ts:
x = t(x, cs, dk)
return x
rs = [partial(ring, s=s) for s in range(5)]
[10]:
# Compute fixed point
# Note, dynamical part is assumed to be fixed during optimization
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, cs, dk, power=1, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Compute fixed points for all rings
# Note, dynamical part is assumed to be fixed during optimization
fps = torch.stack([fixed_point(16, r, x, cs, dk, power=1, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev) for r in rs])
print(fps)
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Define parametric responce matrix
def rm(dk):
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [cs], lambda x, cs: fodo(x, cs, dk), jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
chop(pfp)
_, (dqx, _, dqy, _) = first(pfp)
out = [torch.stack([dqx, dqy])]
for t in [t_01_02, t_02_03, t_03_04, t_04_05]:
pfp = propagate((4, 8), (0, 1), pfp, [cs], lambda x, cs: t(x, cs, dk), jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
chop(pfp)
_, (dqx, _, dqy, _) = first(pfp)
out.append(torch.stack([dqx, dqy]))
return torch.stack(out).swapaxes(0, 1).reshape(-1, len(cs))
print(2*(len([t_01_02, t_02_03, t_03_04, t_04_05]) + 1), len(cs))
print(rm(dk).shape)
print()
print(rm(dk))
10 8
torch.Size([10, 8])
tensor([[7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.216e+00, 4.039e+00, 6.749e+00, 4.566e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[5.110e+00, 2.611e+00, 5.110e+00, 2.611e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.749e+00, 4.566e+00, 6.216e+00, 4.039e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 7.577e+00, 5.936e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.801e+01, 2.744e+01, 1.849e+01, 2.792e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 2.509e+01, 3.667e+01, 2.509e+01, 3.667e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.849e+01, 2.792e+01, 1.801e+01, 2.744e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01, 1.344e+01, 2.158e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[13]:
# Test responce matrix
dc = 1.0E-3*torch.ones_like(cs)
o = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, cs + dc, dk, power=1, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
os = []
qx, _, qy, _ = o
os.append(torch.stack([qx, qy]))
for t in [t_01_02, t_02_03, t_03_04, t_04_05]:
o = t(o, dc, dk)
qx, _, qy, _ = o
os.append(torch.stack([qx, qy]))
print(torch.allclose(torch.stack(os).T.flatten(), rm(dk) @ dc))
True
[14]:
# Define parametric responce matrix element
def rm_ijk(dk, ijk):
i, j, k = ijk
t = lambda x, *cs: rs[i](x, torch.stack(cs).flatten(), dk)
v = tuple(torch.eye(len(cs), dtype=torch.int)[j].tolist())
fp = fps[i]
pfp = parametric_fixed_point(v, fp, list(cs.reshape(-1, 1)), t, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
_, (dqx, _, dqy, _) = [*flatten(pfp, target=list)]
return torch.stack([dqx, dqy])[k].squeeze()
[15]:
# Set quadrupole gradient errors
ek = torch.tensor([-0.010, 0.005], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[16]:
# Measure ORM
erm = rm(ek)
print(erm)
tensor([[8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[6.658e+00, 4.415e+00, 7.190e+00, 4.942e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[5.488e+00, 2.923e+00, 5.488e+00, 2.923e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[7.190e+00, 4.942e+00, 6.658e+00, 4.415e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 8.038e+00, 6.338e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.943e+01, 2.915e+01, 1.990e+01, 2.963e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 2.678e+01, 3.865e+01, 2.678e+01, 3.865e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.990e+01, 2.963e+01, 1.943e+01, 2.915e+01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01, 1.470e+01, 2.316e+01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[17]:
# Set data
i_max, j_max, k_max = 5, 8, 2
i_val, j_val, k_val = torch.arange(i_max), torch.arange(j_max), torch.arange(k_max)
X = torch.vstack([*torch.vstack([*torch.stack(torch.meshgrid(i_val, j_val, k_val, indexing='xy')).swapaxes(0, -1)])])
y = torch.stack([rm_ijk(ek, ijk) for ijk in X])
batch_size = 16
dataset = TensorDataset(X.clone(), y.clone())
dataset, validation = random_split(dataset, [0.80, 0.20])
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
[18]:
# Set model
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, knobs):
super().__init__()
self.knobs = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.clone(knobs))
def forward(self, x):
return torch.stack([rm_ijk(self.knobs, ijk) for ijk in x]).squeeze()
[19]:
# Set model instance
# Note, initial knobs are set to zero
model = Model(torch.zeros_like(dk))
[20]:
# Set optimizer
lr = 1.0E-3
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
[21]:
# Set loss function
lf = torch.nn.MSELoss()
[22]:
# Fit model
# Note, each epoch loss is computed for full validation set
epochs = 128
print()
print(ek)
print(model.knobs)
print()
knobs, errors = [], []
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
y_hat = model(X)
error = lf(y_hat, y)
with torch.no_grad():
knobs.append(model.knobs.clone().detach())
errors.append(error.clone().detach())
error.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
model.eval()
X, y = validation.dataset.tensors
test = lf(model(X[validation.indices]), y[validation.indices])
if epoch % 10 == 0:
print(f'epoch: {epoch}, error: {error.item()} / {test.item()}')
print()
print(ek)
print(model.knobs)
print()
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Parameter containing:
tensor([0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
epoch: 0, error: 0.3207854421804211 / 0.4834669895527817
epoch: 10, error: 0.06071210114479893 / 0.04106920029560601
epoch: 20, error: 0.017744182732083627 / 0.01457174468546367
epoch: 30, error: 0.003963890419609968 / 0.0034633084736078864
epoch: 40, error: 0.0009804767999389498 / 0.0005130453666292978
epoch: 50, error: 8.948304821381796e-05 / 0.00014339307948138367
epoch: 60, error: 4.0143085845154395e-06 / 2.272965287854233e-05
epoch: 70, error: 3.4453470618958206e-06 / 3.3214685216885225e-06
epoch: 80, error: 1.387860215946706e-07 / 9.034775495586135e-08
epoch: 90, error: 6.611469669425412e-08 / 4.719136099019071e-09
epoch: 100, error: 3.0221850571449367e-10 / 2.1032181485124297e-09
epoch: 110, error: 1.9253040326146467e-11 / 2.887542634043959e-13
epoch: 120, error: 1.9606914010193334e-13 / 5.526546647035777e-14
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
Parameter containing:
tensor([-1.000e-02, 5.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
[23]:
# Plot error vs iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.plot(range(len(errors)), torch.stack(errors).cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
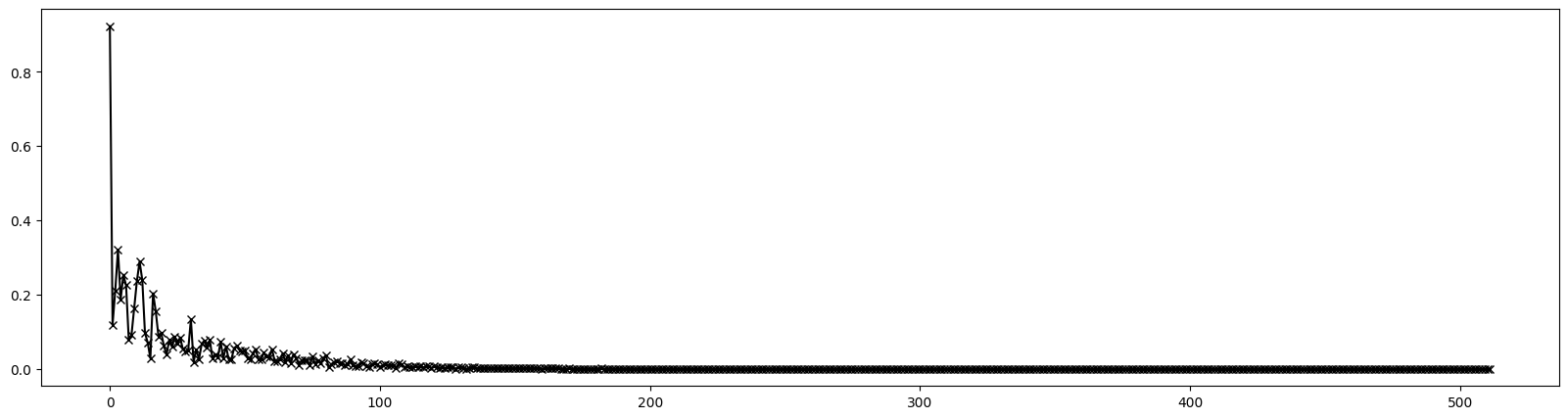
[24]:
# Plot knobs vs iteration
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
plt.hlines(ek.cpu().numpy(), 0, len(errors), linestyles='dashed', color='gray', alpha=0.75)
for knob in torch.stack(knobs).T:
plt.plot(range(len(knob)), knob.cpu().numpy(), color='black', marker='x')
plt.show()
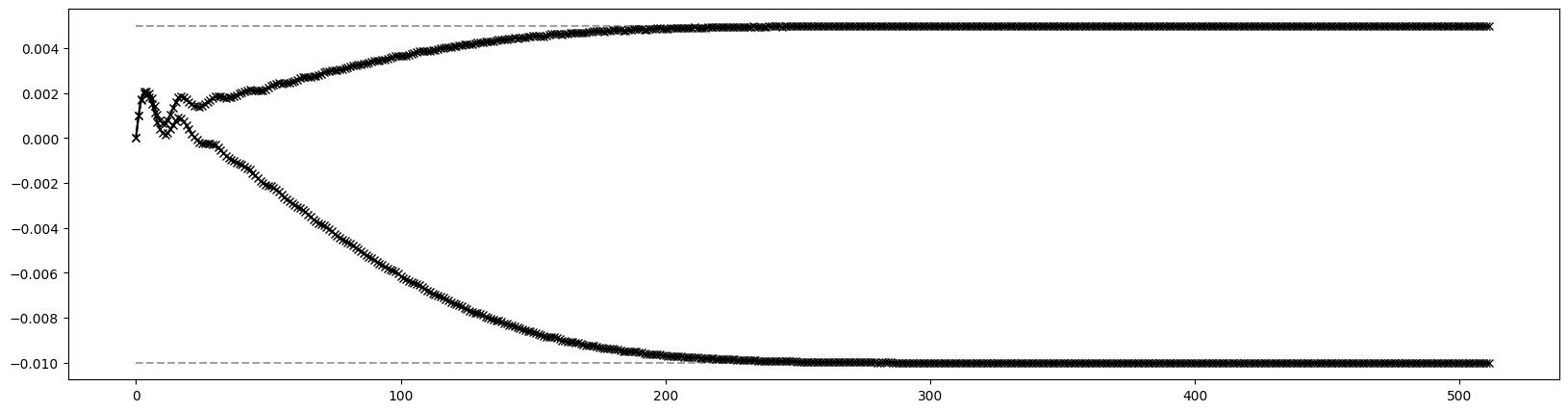
Example-37: Normalized dispersion
[1]:
# Normalized dispersion can be used for calibration independent correction (10.1109/PAC.2007.4440536)
# In this example derivatives of normalized dispersion with respect to quadrupole amplitudes are computed
[2]:
# Import
from functools import partial
import numpy
import torch
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.data import random_split
from ndmap.util import flatten
from ndmap.util import first
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.evaluate import compare
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
from twiss.wolski import propagate as propagate_twiss
from twiss.convert import wolski_to_cs
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
True
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=5):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=1):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def kick(x, cx, cy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx, px + cx, qy, py + cy])
def slip(x, dx, dy):
(qx, px, qy, py) = x
return torch.stack([qx + dx, px, qy + dy, py])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
# Note, transport maps are expected to have identical (differentiable) signature
def t_01_02(x, w, dk):
kf, kd = dk
x = quad(x, w, 0.19 + kf, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.00, 0.1)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def t_02_03(x, w, dk):
kf, kd = dk
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.00, 0.1)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, -0.21 + kd, 0.50)
return x
def t_03_04(x, w, dk):
kf, kd = dk
x = quad(x, w, -0.21 + kd, 0.50)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.00, 0.1)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
return x
def t_04_05(x, w, dk):
kf, kd = dk
x = bend(x, w, 22.92, 0.015, 0.00, 1.5)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = sext(x, w, 0.00, 0.1)
x = drif(x, w, 0.45)
x = quad(x, w, 0.19 + kf, 0.50)
return x
ts = [t_01_02,t_02_03, t_03_04, t_04_05]
[6]:
# Set deviation variables
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
w = torch.tensor(1*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dk = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[7]:
# Define one-turn transport at the lattice entrance
def fodo(x, w, dk):
for t in ts:
x = t(x, w, dk)
return x
[8]:
# Test one-turn transport
print(fodo(x, w, dk))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[9]:
# Compute (dynamical) fixed point
# Note, dynamical part is assumed to be fixed during optimization
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, w, dk, power=1, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[10]:
# Normalized (horizontal) dispersion
def dispersion(dk):
# Set container for parametric fixed points
pfps = []
# Set container for x and y dispersions
etas = []
# Compute parametric fixed point and set dispersion at the lattice entrance
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [w], lambda x, w: fodo(x, w, dk), jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
chop(pfp)
pfps.append(pfp)
_, (etax, _, etay, _) = first(pfp)
etas.append(torch.stack([etax, etay]))
# Propagate fixed point and set dispersion values
for t in ts:
pfp = propagate((4, 1), (0, 1), pfp, [w], lambda x, w: t(x, w, dk), jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
chop(pfp)
pfps.append(pfp)
_, (etax, _, etay, _) = first(pfp)
etas.append(torch.stack([etax, etay]))
# Set dispersion at all observation points
etaxs, etays = torch.hstack(etas)
# Define wrapper for transport maps
def wrapper(x, w, dk, transport, pfp_in, pfp_out):
x = x + evaluate(first(pfp_in), [w])
x = transport(x, w, dk)
x = x - evaluate(first(pfp_out), [w])
return x
# Set containers for beta functions
bxs = []
bys = []
# Compute beta functions at the lattice entrance
pfp_in = first(pfps)
pfp_out = first(pfps)
matrix = derivative(1, lambda x: wrapper(x, w, dk, fodo, pfp_in, pfp_out), fp, intermediate=False, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
*_, m = twiss(matrix)
_, bx, _, by = wolski_to_cs(m)
bxs.append(bx)
bys.append(by)
# Propagate twiss
for i, t in enumerate(ts):
pfp_in = pfps[i]
pfp_out = pfps[i + 1]
m = propagate_twiss(m, derivative(1, lambda x: wrapper(x, w, dk, t, pfp_in, pfp_out), x, intermediate=False, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev))
_, bx, _, by = wolski_to_cs(m)
bxs.append(bx)
bys.append(by)
bxs = torch.stack(bxs)
bys = torch.stack(bys)
# Set normalized dispersions (exclude lattice exit)
*etaxs, _ = etaxs/bxs
*etaxy, _ = etays/bys
return torch.stack([*etaxs, *etays])
[11]:
# Compute normalized dispersion derivatives (responce matrix)
rm = derivative(1, dispersion, dk, intermediate=False, jacobian=torch.func.jacrev)
print(rm)
tensor([[-8.795e-01, -1.390e-01],
[-8.732e-01, -2.077e-01],
[-4.797e-01, -4.941e-01],
[-8.732e-01, -2.077e-01],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00]], dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Check covergence
ek = torch.tensor([-0.001, 0.001], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(dispersion(dk))
print(dispersion(ek))
print(dispersion(dk) + rm @ ek)
tensor([1.169e-01, 1.568e-01, 2.615e-01, 1.568e-01, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.176e-01, 1.575e-01, 2.615e-01, 1.575e-01, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.176e-01, 1.575e-01, 2.615e-01, 1.575e-01, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
dtype=torch.float64)
[13]:
# Correction
# The target values (normalized dispersion) are associated with model response matrix
# Given measured values, the goal is to alter knobs to get target values
# Set target values
vf = dispersion(dk)
# Set initial solution
sol = torch.zeros_like(dk)
# Iterate
for _ in range(4):
# Compute current values and set difference
vi = dispersion(ek + sol)
# Set difference
dv = vf - vi
# Update solution
sol += torch.linalg.pinv(rm) @ dv
# Verbose
print(-dk)
print(sol)
print(dv.norm())
print()
# Continue
tensor([-0., -0.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([9.987e-04, -9.924e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.198e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-0., -0.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.000e-03, -1.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.185e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-0., -0.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.000e-03, -1.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.955e-11, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-0., -0.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.000e-03, -1.000e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(2.021e-16, dtype=torch.float64)
Example-38: Coupling (minimal tune distance)
[1]:
# In this example, minimal tune distance is computed using TEAPOT expression
# The value is compared with some approximate analytical expressions
# Computation dQmin of derivative (gradient) is illustrated
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
from twiss.convert import wolski_to_cs
from twiss.matrix import symplectic_conjugate
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
False
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def roll(x, a):
(qx, px, qy, py), cn, sn = x, a.cos(), a.sin()
return torch.stack([qx*cn + qy*sn, px*cn + py*sn, qy*cn - qx*sn, py*cn - py*sn])
def kick(x, kn, ks):
(qx, px, qy, py), kn, ks = x, kn, ks
return torch.stack([qx, px - kn*qx + ks*qy, qy, py + ks*qx + kn*qy])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, k):
kf, kd = k
x = kick(x, 0.0, kf/2.0)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.18, 0.50)
x = kick(x, 0.0, kd/2.0)
x = kick(x, 0.0, kd/2.0)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.18, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.21, 0.50)
x = kick(x, 0.0, kf/2.0)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, k):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, k, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [k], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 2), (0, 1), pfp, [k], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[8]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[9]:
# Propagate parametric identity (surrogate model for linear dynamics)
jet = identity((1, 1), fp, parametric=pfp)
jet = propagate((4, 2), (1, 1), jet, [k], fodo)
[10]:
# Compute uncoupled one-turn matrix (zero skew quadrupole amplitudes)
m = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k]), fp, intermediate=False)
m
[10]:
tensor([[2.192e-01, 1.772e+01, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[-5.372e-02, 2.192e-01, 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, 5.733e-01, 6.018e+00],
[0.000e+00, 0.000e+00, -1.116e-01, 5.733e-01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[11]:
# Compute (uncoupled) CS twiss parameters
(nux, nuy), _, w = twiss(m)
mux, muy = 2.0*torch.pi*nux, 2.0*torch.pi*nuy
ax, bx, ay, by = wolski_to_cs(w)
torch.stack([ax, bx, ay, by])
[11]:
tensor([7.539e-16, 1.816e+01, 1.423e-15, 7.345e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Compute coupled one-turn matrix
dm = derivative(1, kick, x, 0.0, 0.5E-3, intermediate=False)
dm @ m @ dm
[12]:
tensor([[ 2.192e-01, 1.772e+01, 8.859e-03, 0.000e+00],
[-5.372e-02, 2.192e-01, 3.963e-04, 3.009e-03],
[ 3.009e-03, 0.000e+00, 5.733e-01, 6.018e+00],
[ 3.963e-04, 8.859e-03, -1.115e-01, 5.733e-01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[13]:
# Coupled one-turn matrix from jet
# Note, jet is first order in skew quadrupole strenght
dkf = 1.0E-3
dkd = 0.0
dk = torch.tensor([dkf, dkd], dtype=dtype, device=device)
m = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k + dk]), fp, intermediate=False)
m
[13]:
tensor([[ 2.192e-01, 1.772e+01, 8.859e-03, 0.000e+00],
[-5.372e-02, 2.192e-01, 3.963e-04, 3.009e-03],
[ 3.009e-03, 0.000e+00, 5.733e-01, 6.018e+00],
[ 3.963e-04, 8.859e-03, -1.116e-01, 5.733e-01]], dtype=torch.float64)
[14]:
# |dQmin| (Edwards & Shyphers, first order in amplitude and unperturbed tune differenct)
f'{abs(dkf)/(2.0*torch.pi)*(bx*by).sqrt().item():.6e}'
[14]:
'1.838149e-03'
[15]:
# dQmin (first order in amplitude)
# Note, tunes in [0, 1/2] are assumed
f'{abs(dkf)/(torch.pi)*(bx*by).sqrt()*(mux.sin()*muy.sin()).abs().sqrt()/(mux.sin() + muy.sin()).item():.6e}'
[15]:
'1.831163e-03'
[16]:
# dQmin (TEAPOT manual, appendix G, 1996)
# Note,
(NUX, NUY), *_ = twiss(m)
mux, muy = 2.0*torch.pi*NUX, 2.0*torch.pi*NUY
B = m[:2, 2:]
C = m[2:, :2]
f'{torch.linalg.det(C + symplectic_conjugate(B)).abs().sqrt()/(torch.pi*(mux.sin() + muy.sin())).item():.6e}'
[16]:
'1.831193e-03'
[17]:
# Effect of skew quadrupole on tunes
torch.stack([nux - NUX, nuy - NUY]).abs()
[17]:
tensor([1.275e-05, 1.314e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
[18]:
# dQmin derivative (TEAPOT manual, appendix G, 1996)
def dQmin(k):
m = derivative(1, lambda x: fodo(x, k), fp, intermediate=False)
(nux, nuy), *_ = twiss(m)
mux, muy = 2.0*torch.pi*nux, 2.0*torch.pi*nuy
B = m[:2, 2:]
C = m[2:, :2]
return (C + symplectic_conjugate(B)).diag().prod().abs().sqrt()/(mux.sin() + muy.sin())/torch.pi
print(dQmin(k + dk))
print()
# Derivative a zero is not defined
print(derivative(1, dQmin, k, intermediate=False))
print()
# Derivatives at points near zero are valid (note the sign flip)
print(derivative(1, dQmin, k + 1.0E-16, intermediate=False))
print(derivative(1, dQmin, k - 1.0E-16, intermediate=False))
print()
# Derivative at a point
print(derivative(1, dQmin, k + dk, intermediate=False))
print()
tensor(1.831e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([nan, nan], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.835e+00, 1.715e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.835e+00, -1.715e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.831e+00, 1.725e+00], dtype=torch.float64)
[19]:
# Plot dQmin and its derivative norm on a grid
dkf = torch.linspace(-5.0E-3, +5.0E-3, 128, dtype=dtype, device=device)
dkd = torch.linspace(-5.0E-3, +5.0E-3, 128, dtype=dtype, device=device)
dk = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid(dkf, dkd, indexing='ij')).swapaxes(-1, 0).reshape(128*128, -1)
dQ = torch.vmap(dQmin)(dk).reshape(128, 128)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(dQ.cpu().numpy(), cmap='plasma', interpolation='bilinear', origin='upper', extent=(-5.0E-3, +5.0E-3, -5.0E-3, +5.0E-3))
plt.colorbar(fraction=0.045, pad=0.05)
plt.contour(dQ.cpu().numpy(), origin='lower', extend='both', linewidths=1, extent=(-5.0E-3, +5.0E-3, -5.0E-3, +5.0E-3), colors='black')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
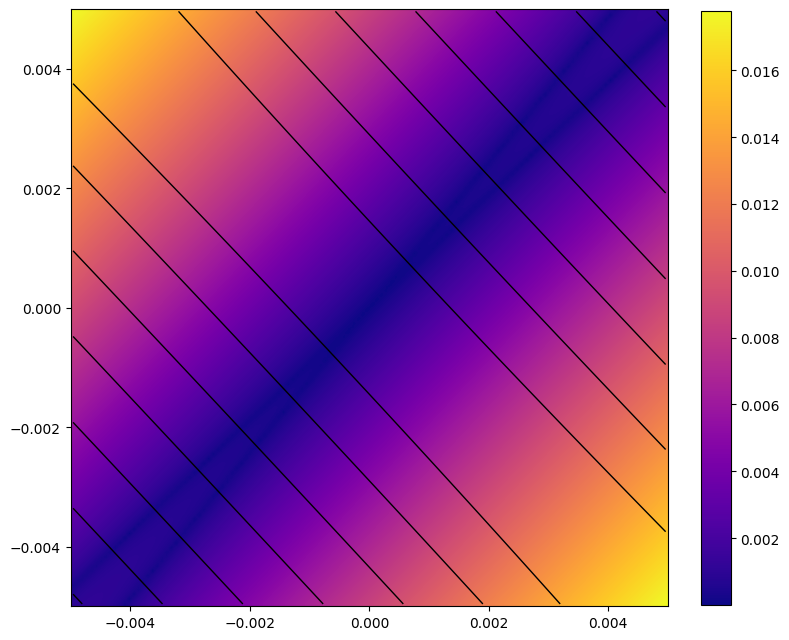
Example-39: Coupling (minimal tune distance correction)
[1]:
# In this example point derivative of dQmin (minimal tune distance) is used for coupling correction illustration
# A pair of skew quadrupole errors are added and correction is performed with GD
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
from twiss.convert import wolski_to_cs
from twiss.matrix import symplectic_conjugate
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
False
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def roll(x, a):
(qx, px, qy, py), cn, sn = x, a.cos(), a.sin()
return torch.stack([qx*cn + qy*sn, px*cn + py*sn, qy*cn - qx*sn, py*cn - py*sn])
def kick(x, kn, ks):
(qx, px, qy, py), kn, ks = x, kn, ks
return torch.stack([qx, px - kn*qx + ks*qy, qy, py + ks*qx + kn*qy])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points (close tunes, bends are replaced with drifts)
def map_01_02(x, k):
kf, kd = k
x = kick(x, 0.0, kf/2.0)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.18, 0.50)
x = kick(x, 0.0, kd/2.0)
x = kick(x, 0.0, kd/2.0)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.18, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.21, 0.50)
x = kick(x, 0.0, kf/2.0)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, k):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, k, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [k], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 2), (0, 1), pfp, [k], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[8]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[9]:
# Propagate parametric identity (surrogate model for linear dynamics)
jet = identity((1, 1), fp, parametric=pfp)
jet = propagate((4, 2), (1, 1), jet, [k], fodo)
[10]:
# Minimal tuen distance (using 1st order parametric matrix arounf closed orbit)
def dQmin(k):
m = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k]), fp, intermediate=False)
(nux, nuy), *_ = twiss(m)
mux, muy = 2.0*torch.pi*nux, 2.0*torch.pi*nuy
B = m[:2, 2:]
C = m[2:, :2]
(m11, m12), (m21, m22) = C + symplectic_conjugate(B)
return 1.0/torch.pi * (m11*m22 - m12*m21).abs().sqrt()/(mux.sin() + muy.sin()).abs()
[11]:
# Set skew errors
dkf = 1.0E-2
dkd = 1.0E-2
dk = torch.tensor([dkf, dkd], dtype=dtype, device=device)
[12]:
# Note, the sign flip doesn't change dQmin value
dQmin(+dk) - dQmin(-dk)
[12]:
tensor(0., dtype=torch.float64)
[13]:
# Compute dQmin and gradient
derivative(1, dQmin, k + dk, intermediate=True)
[13]:
[tensor(3.574e-02, dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([1.871e+00, 1.751e+00], dtype=torch.float64)]
[14]:
# Correction setup (minimize dQmin)
# Set objective
# Note, this objective represents a model with errors, the task is to find knob values that minimize it
error = dk
objective = lambda knobs: dQmin(knobs + error)
# Exact solution
print(objective(-error))
# Set initial guess (zero knobs values in this example)
solution = torch.zeros_like(error)
# Evaluate objective for initial guess
print(objective(solution))
tensor(0., dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.574e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
[15]:
# Correction loop (gradient descent)
# Note, small learning rate is required here for convergence
ni = 2048
lr = 2.5E-6
xs = []
for i in range(ni):
solution -= lr*derivative(1, objective, solution, intermediate=False)
xs.append(objective(solution))
xs = torch.stack(xs)
# Evaluate objective for final solution
print(dk)
print(-solution)
print(objective(solution))
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4))
plt.plot(xs.cpu().numpy(), color='blue')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
tensor([1.000e-02, 1.000e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([9.462e-03, 8.845e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(2.966e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
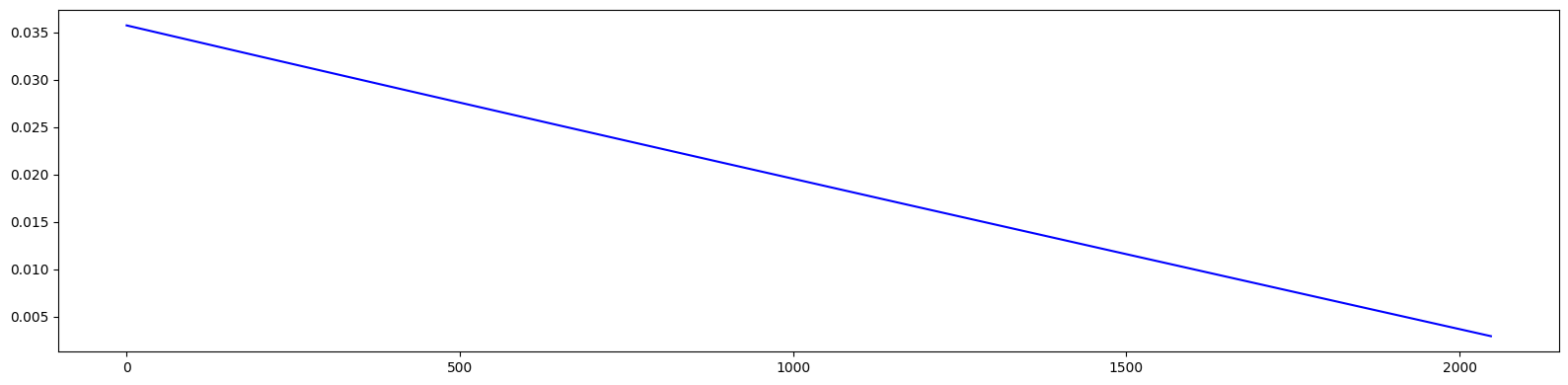
[16]:
# Another (prefered) approach would be to fit our model to observation
# In this case, observer value is computed first, the task is to find knob values that fit our model to the observed
# The next step is to interact with experemental model by applying fitted negativd knob values
[17]:
# Set objective
dQmin_observed = dQmin(error)
objective = lambda knobs: (dQmin(knobs) - dQmin_observed)**2
solution = torch.zeros_like(error)
print(dQmin(error))
print(dQmin(error - error))
print(objective(error))
tensor(3.574e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(0., dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(0., dtype=torch.float64)
[18]:
# The derivative at zero initial guess is not defined
derivative(1, objective, solution, intermediate=False)
[18]:
tensor([nan, nan], dtype=torch.float64)
[19]:
# Set random initial guess
solution = 1.0E-3*torch.randn_like(error)
derivative(1, objective, solution, intermediate=False)
[19]:
tensor([-1.113e-01, -1.049e-01], dtype=torch.float64)
[20]:
# Correction loop (gradient descent)
# Note, in this case learning rate is not as small as in the previouse case
# Thus, the number of iterations is also reduced
ni = 256
lr = 5.0E-3
xs = []
for i in range(ni):
solution -= lr*derivative(1, objective, solution, intermediate=False)
xs.append(objective(solution))
k1 = solution.clone()
xs = torch.stack(xs)
# Evaluate objective for final solution
print(dk)
print(-k1)
print(objective(k1))
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4))
plt.plot(xs.cpu().numpy(), color='blue')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
tensor([1.000e-02, 1.000e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.170e-02, -8.184e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(8.324e-19, dtype=torch.float64)
[21]:
# While objective is minimized, the knob values do not correspond to the set errors
# Note, objective values with '+' and '-' are the same here
print(objective(-error))
print(objective(+k1))
print(objective(-k1))
print()
tensor(0., dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(8.324e-19, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(8.324e-19, dtype=torch.float64)
[22]:
# Now, if we apply the obtained negative solution to the observed system, dQmin value will be reduced, but not as much as if the exact errors were recovered
# Note, a fraction of a fitted solution can be applied
# Also, new correction step can be performed using new observed value
print(dQmin(error - 0.00*k1))
print(dQmin(error - 0.25*k1))
print(dQmin(error - 0.50*k1))
print(dQmin(error - 1.00*k1))
print()
tensor(3.574e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(2.672e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.777e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.969e-04, dtype=torch.float64)
[23]:
# Perform next correction step
dQmin_observed = dQmin(error - 0.5*k1)
objective = lambda knobs: (dQmin(knobs) - dQmin_observed)**2
[24]:
# Set random initial guess
solution = 1.0E-3*torch.randn_like(error)
derivative(1, objective, solution, intermediate=False)
[24]:
tensor([-5.780e-02, -5.374e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
[25]:
# Correction loop
ni = 256
lr = 5.0E-3
xs = []
for i in range(ni):
solution -= lr*derivative(1, objective, solution, intermediate=False)
xs.append(objective(solution))
k2 = solution.clone()
xs = torch.stack(xs)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4))
plt.plot(xs.cpu().numpy(), color='blue')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
[26]:
print(dQmin(error))
print(dQmin(error - 0.5*k1))
print(dQmin(error - 0.5*k1 - 0.5*k2))
tensor(3.574e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.777e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(8.875e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
[27]:
# Note, there seems to be no guarantee for the above procedure to converge
Example-40: Coupling (amplitude ratio correction)
[1]:
# In this example an objective function constructed from ratio of coupled and uncoupled amplitudes is used to minimize coupling
# Amplitudes can be computed from simulated TbT data at one or several locations
[2]:
# Import
import numpy
import torch
from ndmap.derivative import derivative
from ndmap.signature import chop
from ndmap.series import series
from ndmap.series import clean
from ndmap.evaluate import evaluate
from ndmap.propagate import identity
from ndmap.propagate import propagate
from ndmap.pfp import fixed_point
from ndmap.pfp import parametric_fixed_point
from twiss.wolski import twiss
from twiss.convert import wolski_to_cs
from twiss.matrix import symplectic_conjugate
torch.set_printoptions(precision=3, sci_mode=True, linewidth=128)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
False
[3]:
# Set data type and device
dtype = torch.float64
device = torch.device('cpu')
[4]:
# Set elements
def drif(x, w, l):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), l = x, w, l
return torch.stack([qx + l*px/(1 + w), px, qy + l*py/(1 + w), py])
def quad(x, w, kq, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), kq, l = x, w, kq, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx, py + 2.0*l*kq*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def sext(x, w, ks, l, n=10):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), ks, l = x, w, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2), py + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def bend(x, w, r, kq, ks, l, n=50):
(qx, px, qy, py), (w, ), r, kq, ks, l = x, w, r, kq, ks, l/(2.0*n)
for _ in range(n):
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
px, py = px - 2.0*l*kq*qx - 1.0*l*ks*(qx**2 - qy**2) + 2.0*l/r**2*(w*r - qx), py + 2.0*l*kq*qy + 2.0*l*ks*qx*qy
qx, qy = qx + l*px/(1 + w), qy + l*py/(1 + w)
return torch.stack([qx, px, qy, py])
def roll(x, a):
(qx, px, qy, py), cn, sn = x, a.cos(), a.sin()
return torch.stack([qx*cn + qy*sn, px*cn + py*sn, qy*cn - qx*sn, py*cn - py*sn])
def kick(x, kn, ks):
(qx, px, qy, py), kn, ks = x, kn, ks
return torch.stack([qx, px - kn*qx + ks*qy, qy, py + ks*qx + kn*qy])
[5]:
# Set transport maps between observation points
def map_01_02(x, k):
kf, kd = k
x = kick(x, 0.0, kf/2.0)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.21, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.18, 0.50)
x = kick(x, 0.0, kd/2.0)
return x
def map_02_03(x, k):
kf, kd = k
x = kick(x, 0.0, kd/2.0)
x = quad(x, [0.0], -0.18, 0.50)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 3.0)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = sext(x, [0.0], 0.0, 0.10)
x = drif(x, [0.0], 0.45)
x = quad(x, [0.0], 0.21, 0.50)
x = kick(x, 0.0, kf/2.0)
return x
transport = [
map_01_02,
map_02_03
]
# Define one-turn transport
def fodo(x, k):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k)
return x
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
print(fodo(x, k))
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[6]:
# Compute fixed point
x = torch.tensor(4*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
k = torch.tensor(2*[0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
fp = fixed_point(16, fodo, x, k, power=1)
print(fp)
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64)
[7]:
# Compute parametric fixed point
pfp = parametric_fixed_point((1, ), fp, [k], fodo)
chop(pfp)
pfp
[7]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[8]:
# Propagate parametric fixed point
out = propagate((4, 2), (0, 1), pfp, [k], fodo)
chop(out)
out
[8]:
[[tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]], dtype=torch.float64)]]
[9]:
# Propagate parametric identity (surrogate model for linear dynamics)
jet = identity((1, 1), fp, parametric=pfp)
jet = propagate((4, 2), (1, 1), jet, [k], fodo)
[10]:
# dQmin (TEAPOT manual, appendix G, 1996)
def dQmin(k):
m = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k]), fp, intermediate=False)
(nux, nuy), *_ = twiss(m)
mux, muy = 2.0*torch.pi*nux, 2.0*torch.pi*nuy
B = m[:2, 2:]
C = m[2:, :2]
(m11, m12), (m21, m22) = C + symplectic_conjugate(B)
return 1.0/torch.pi*(m11*m22 - m12*m21).abs().sqrt()/(mux.sin() + muy.sin()).abs()
[11]:
# Set skew errors
dkf = +1.5E-3
dkd = -0.5E-3
dk = torch.tensor([dkf, dkd], dtype=dtype, device=device)
dQmin(dk)
[11]:
tensor(1.881e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
[12]:
# Given qx TbT data, in linear approximation qx(n) = (cxx cos(mux n) + sxx sin(mux n)) + (cxy cos(muy n) + sxy sin(muy n))
# Amplitudes axx^2 = cxx^2 + sxx^2 and axy^2 = cxy^2 + cyx^2 are used to compute ratio axy/axx
# Similary, ayx/ayy can be computed using qy
# These ration are computed at each observation point
[13]:
# Observation function
# Fit 'experiment' to 'model' ('experiment' is 'model' with errors)
# The goal is to fit knobs so that 'experiment' observation matches 'model' observation (ratios are zero)
# Fit 'model' to 'experiment'
# The goal is to fit knobs so that 'model' observation matches 'experiment' observation (final ratios are non-zero)
# Set initial condition for TbT
# Exact value is not important, since the underlying model is linear
# Also, this initial should be set relative to (parametric) closed orbit
initial = torch.tensor([1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], dtype=dtype, device=device)
# Normalized window for computation of amplitudes
def window(n, *, s=1.0, dtype=dtype, device=device):
t = torch.linspace(0.0, (n - 1.0)/n, n, dtype=dtype, device=device)
f = torch.exp(-1.0/((1.0 - t)**s*t**s))
return f/torch.sum(f)
def fn(k, n, x, error):
if error:
k = k + dk
w = window(n)
t = torch.linspace(0.0, n - 1, n, dtype=dtype, device=device)
matrix = derivative(1, lambda x: evaluate(jet, [x, k]), fp, intermediate=False)
(nux, nuy), *_ = twiss(matrix)
mux = 2.0*torch.pi*nux
muy = 2.0*torch.pi*nuy
xs = []
for _ in range(n):
for mapping in transport:
x = mapping(x, k)
xs.append(x)
xs = torch.stack(xs).reshape(n, len(transport), -1).swapaxes(1, 0).swapaxes(1, -1)
cxx, cxy, cyx, cyy = [], [], [], []
sxx, sxy, syx, syy = [], [], [], []
for x in xs:
qx, _, qy, _ = x
cxx.append(w*qx @ (mux*t).cos())
cxy.append(w*qx @ (muy*t).cos())
cyx.append(w*qy @ (mux*t).cos())
cyy.append(w*qy @ (muy*t).cos())
sxx.append(w*qx @ (mux*t).sin())
sxy.append(w*qx @ (muy*t).sin())
syx.append(w*qy @ (mux*t).sin())
syy.append(w*qy @ (muy*t).sin())
cxx = torch.stack(cxx)
cxy = torch.stack(cxy)
cyx = torch.stack(cyx)
cyy = torch.stack(cyy)
sxx = torch.stack(sxx)
sxy = torch.stack(sxy)
syx = torch.stack(syx)
syy = torch.stack(syy)
axx = (cxx**2 + sxx**2).sqrt()
axy = (cxy**2 + sxy**2).sqrt()
ayx = (cyx**2 + syx**2).sqrt()
ayy = (cyy**2 + syy**2).sqrt()
return torch.stack([axy/axx, ayx/ayy]).T.flatten()
[14]:
# The above function returns ratios (as a vector, so that the derivative is a matrix)
# rx_1, rx_2, ..., ry_1, ry_2, ...
[15]:
# Without errors, the ratios should be zero
# The accuracy is determined by the TbT data length
print(fn(k, 128, initial, False))
print(fn(k, 256, initial, False))
print(fn(k, 512, initial, False))
print()
print(fn(k, 128, initial, True))
print(fn(k, 256, initial, True))
print(fn(k, 512, initial, True))
print()
tensor([1.041e-04, 1.041e-04, 1.041e-04, 1.041e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([7.097e-09, 7.097e-09, 7.097e-09, 7.097e-09], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.210e-02, 6.907e-03, 2.517e-02, 8.844e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.007e-03, 2.508e-02, 8.942e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
[16]:
# Correction ('experiment' to 'model')
# Target system is 'model'
# Learning rate
lr = 0.75
# Target values
vf = fn(k, 256, initial, False)
# Initial solution
solution = torch.zeros_like(dk)
# Correction loop
for _ in range(16):
vi, jacobian = derivative(1, fn, solution, 256, initial, True, intermediate=True)
dv = vf - vi
solution += lr * torch.linalg.pinv(jacobian) @ dv
print(solution)
print(vf)
print(vi)
print(dv.norm())
print()
tensor([-1.094e-03, 3.652e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(4.220e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.396e-03, 4.657e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([8.467e-03, 1.954e-03, 6.640e-03, 2.491e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.121e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.474e-03, 4.915e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.153e-03, 5.078e-04, 1.689e-03, 6.460e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(2.850e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.493e-03, 4.980e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([5.430e-04, 1.326e-04, 4.266e-04, 1.674e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(7.156e-04, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.498e-03, 4.996e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.385e-04, 3.790e-05, 1.093e-04, 4.665e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.791e-04, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.499e-03, 5.000e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.719e-05, 1.418e-05, 2.991e-05, 1.639e-05], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(4.491e-05, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.001e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([1.188e-05, 8.259e-06, 1.005e-05, 8.816e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.167e-05, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([5.555e-06, 6.783e-06, 5.081e-06, 6.915e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(4.302e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.961e-06, 6.415e-06, 3.839e-06, 6.430e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.323e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.551e-06, 6.324e-06, 3.529e-06, 6.305e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.249e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.445e-06, 6.301e-06, 3.452e-06, 6.272e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.245e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.418e-06, 6.295e-06, 3.432e-06, 6.263e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.244e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.411e-06, 6.293e-06, 3.427e-06, 6.261e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.244e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.409e-06, 6.293e-06, 3.426e-06, 6.261e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.244e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.408e-06, 6.293e-06, 3.426e-06, 6.261e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.244e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.500e-03, 5.002e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.408e-06, 6.293e-06, 3.426e-06, 6.260e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.244e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
[17]:
# Test final solution
print((vf - fn(0.0*solution, 256, initial, True)).norm())
print((vf - fn(1.0*solution, 256, initial, True)).norm())
print()
print(dQmin(dk))
print(dQmin(dk + solution))
print()
tensor(4.220e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.244e-06, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.881e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(5.079e-07, dtype=torch.float64)
[18]:
# Correction ('model' to 'experiment')
# Target system is 'experiment'
# Learning rate
lr = 0.75
# Target values
vf = fn(k, 256, initial, True)
solution = torch.zeros_like(dk)
for _ in range(16):
vi, jacobian = derivative(1, fn, solution, 256, initial, False, intermediate=True)
dv = vf - vi
solution += lr * torch.linalg.pinv(jacobian) @ dv
print(solution)
print(vf)
print(vi)
print(dv.norm())
print()
tensor([-1.019e-03, 3.612e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06, 4.081e-06], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(4.220e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.443e-03, 4.881e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.008e-02, 4.856e-03, 1.556e-02, 6.267e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.563e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.553e-03, 5.221e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([2.867e-02, 7.133e-03, 2.241e-02, 9.127e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(4.267e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.582e-03, 5.310e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.087e-02, 7.729e-03, 2.416e-02, 9.878e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.869e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.589e-03, 5.332e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.142e-02, 7.878e-03, 2.459e-02, 1.007e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.603e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.590e-03, 5.338e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.156e-02, 7.916e-03, 2.470e-02, 1.011e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.585e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.159e-02, 7.925e-03, 2.473e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.927e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.928e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.928e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.928e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.928e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.928e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.928e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.928e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([-1.591e-03, 5.340e-04], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.200e-02, 7.011e-03, 2.507e-02, 8.946e-03], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor([3.160e-02, 7.928e-03, 2.474e-02, 1.013e-02], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
[19]:
# Test final solution
print((vf - fn(0.0*solution, 256, initial, False)).norm())
print((vf - fn(1.0*solution, 256, initial, False)).norm())
print()
print(dQmin(dk))
print(dQmin(solution))
print(dQmin(dk + solution))
print(dQmin(dk - solution))
print()
tensor(4.220e-02, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.584e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.881e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.989e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(1.078e-04, dtype=torch.float64)
tensor(3.870e-03, dtype=torch.float64)
[20]:
# Plot
factors = torch.linspace(-1.5, 1.5, 128, dtype=dtype, device=device)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4))
plt.scatter(factors, torch.stack([dQmin(dk + factor*solution) for factor in factors]), color='blue')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
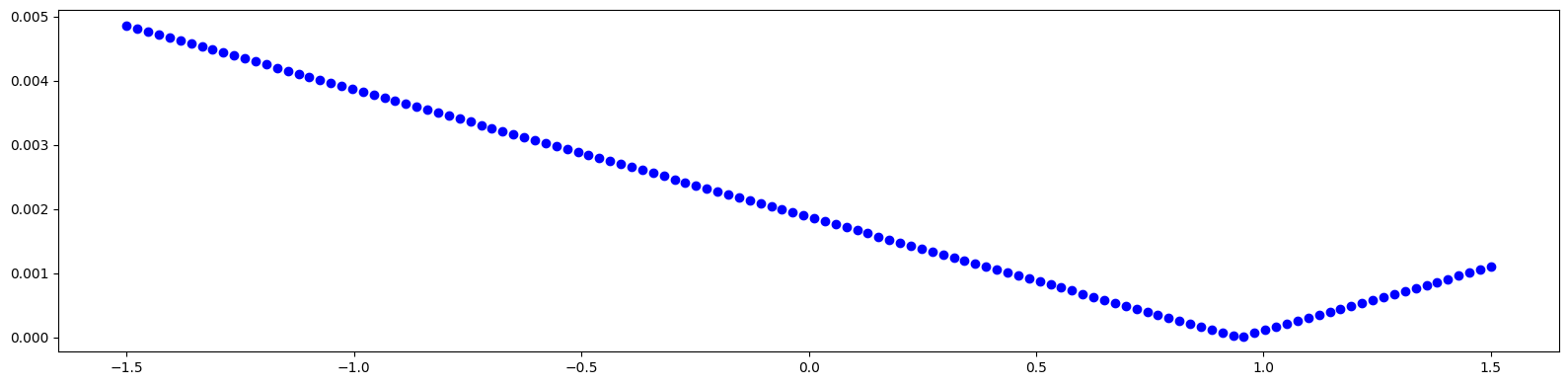
[ ]:
[ ]:
[ ]: